Abstract
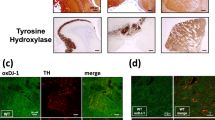
Beclin 1, a regulator of the autophagy pathway, plays an important role in Parkinson’s disease (PD). However, the crucial mechanism of Beclin 1 in PD remains unclear. Therefore, we investigated dynamic expressions of Beclin 1 and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) in different brain areas of 6-OHDA-induced rats. Beclin 1 and TH expressions were analyzed by flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry, respectively. The results showed that Beclin 1 expressions were low in the sham group, but rose significantly after 6-OHDA injection. In the striatum and cortex, Beclin 1 increased at 3 h, peaking at 12 h, while in the hippocampus, it increased at 3 h and peaked at 24 h, then it declined slowly and remained steady at 72 h. Beclin 1 expression in the striatum and cortex areas was higher than that of the hippocampus area at 12 h. In addition, the time-course of TH expression in the striatum was similar to that in the mesencephalon. TH expression declined dramatically between 0 and 12 h. Pearson analysis showed significant negative correlations between TH and Beclin 1 expression in the areas we analyzed. While TH expression declined gradually between 12 and 72 h, significant positive correlations between TH and Beclin 1 were detected during that interval. This indicated that activation of Beclin 1-dependent autophagy may inhibit the loss of TH-positive neurons.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed I, Liang Y, Schools S, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Savitt JM (2012) Development and characterization of a new Parkinson’s disease model resulting from impaired autophagy. J Neurosci 32(46):16503–16509
Anglade P, Vyas S, Javoy-Agid F, Herrero MT, Michel PP, Marquez J, Mouatt-Prigent A, Ruberg M, Hirsch EC, Agid Y (1997) Apoptosis and autophagy in nigral neurons of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Histol Histopathol 12:25–31
Chung KK, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2003) New insights into Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 250(Suppl 3):15–24
Cuervo AM, Stefanis L, Fredenburg R, Lansbury PT, Sulzer D (2004) Impaired degradation of mutant alpha-synuclein by chaperone-mediated autophagy. Science 305:1292–1295
Dagda RK, Zhu J, Kulich SM, Chu CT (2008) Mitochondrially localized ERK2 regulates mitophagy and autophagic cell stress: implications for Parkinson’s disease. Autophagy 4:770–782
Erlich S, Shohami E, Pinkas-Kramarski R (2006) Neurodegeneration induces upregulation of Beclin 1. Autophagy 2:49–51
Fimia GM, Stoykova A, Romagnoli A, Giunta L, Di Bartolomeo S, Nardacci R, Corazzari M, Fuoco C, Ucar A, Schwartz P, Gruss P, Piacentini M, Chowdhury K, Cecconi F (2007) Ambra1 regulates autophagy and development of the nervous system. Nature 447:1121–1125
Fouillet A, Levet C, Virgone A, Robin M, Dourlen P, Rieusset J, Belaidi E, Ovize M, Touret M, Nataf S, Mollereau B (2012) ER stress inhibits neuronal death by promoting autophagy. Autophagy 8(6):915–926
Funderburk SF, Wang QJ, Yue Z (2010) The Beclin 1-VPS34 complex at the crossroads of autophagy and beyond. Trends Cell Biol 20:355–362
Gee P, Davison AJ (1989) Intermediates in the aerobic autoxidation of 6-hydroxydopamine: relative importance under different reaction conditions. Free Radic Biol Med 6:271–284
Hamacher-Brady A, Brady NR, Gottlieb RA (2006) Enhancing macroautophagy protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem 281:29776–29787
He Y, Mo Z, Xue Z, Fang Y (2013) Establish a flow cytometric method for quantitative detection of Beclin-1 expression. Cytotechnology. doi:10.1007/s10616-012-9503-9
Hong Z, Wang G, Gu J, Pan J, Bai L, Zhang S, Chen SD (2007) Tripchlorolide protects against MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in C57BL/6 mice. Eur J Neurosci 26(6):1500–1508
Kuma A, Hatano M, Matsui M, Yamamoto A, Nakaya H, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y, Tokuhisa T, Mizushima N (2004) The role of autophagy during the early neonatal starvation period. Nature 432:1032–1036
Lehmensiek V, Tan EM, Liebau S, Lenk T, Zettlmeisl H, Schwarz J, Storch A (2006) Dopamine transporter-mediated cytotoxicity of 6-hydroxydopamine in vitro depends on expression of mutant alpha-synucleins related to Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int 483:329–340
Levitt M, Spector S, Sjoerdsma A, Udenfriend S (1965) Elucidation of the rate limiting step in norepinephrine biosynthesis in the perfused guinea pig heart. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 148:1–8
Li L, Wang X, Fei X, Xia L, Qin Z, Liang Z (2011) Parkinson’s disease involves autophagy and abnormal distribution of cathepsin L. Neurosci Lett 489:62–67
Liang C, Feng P, Ku B, Dotan I, Canaani D, Oh BH, Jung JU (2006) Autophagic and tumour suppressor activity of a novel Beclin 1-binding protein UVRAG. Nat Cell Biol 8:688–699
Liu K, Shi N, Sun Y, Zhang T, Sun X (2013) Therapeutic effects of rapamycin on MPTP-induced Parkinsonism in mice. Neurochem Res 38:201–207
Lopez Verrilli MA, Pirola CJ, Pascual MM, Dominici FP, Turyn D, Gironacci MM (2009) Angiotensin-(1–7) through AT receptors mediates tyrosine hydroxylase degradation via the ubiquitin proteasome pathway. J Neurochem 109:326–335
Marin C, Aguilar E (2011) In vivo 6-OHDA-induced neurodegeneration and nigral autophagic markers expression. Neurochem Int 58(4):521–526
Nakashima A, Mori K, Kaneko YS, Hayashi N, Nagatsu T, Ota A (2011) Phosphorylation of the N-terminal portion of tyrosine hydroxylase triggers proteasomal digestion of the enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 407:343–347
Nishida Y, Arakawa S, Fujitani K, Yamaguchi H, Mizuta T, Kanaseki T, Komatsu M, Otsu K, Tsujimoto Y, Shimizu S (2009) Discovery of Atg5/Atg7-independent alternative macroautophagy. Nature 461:654–658
Pan T, Kondo S, Le W, Jankovic J (2008a) The role of autophagy-lysosome pathway in neurodegeneration associated with Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131:1969–1978
Pan T, Kondo S, Zhu W, Xie W, Jankovic J, Le W (2008b) Neuroprotection of rapamycin in lactacystin-induced neurodegeneration via autophagy enhancement. Neurobiol Dis 32:16–25
Paxinos G, Watson C (1982) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, San Diego
Rodríguez S, Uchida K, Nakayama H (2013) Striatal TH-immunopositive fibers recover after an intrastriatal injection of 6-hydroxydopamine in golden hamsters treated with prednisolone: roles of tumor necrosis factor-α and inducible nitric oxide synthase in neurodegeneration. Neurosci Res. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2013.02.004
Scatton B, Simon H, Le Moal M, Bischoff S (1980) Origin of dopaminergic innervation of the rat hippocampal formation. Neurosci Lett 18:125–131
Shen YF, Tang Y, Zhang XJ, Huang KX, Le WD (2013) Adaptive changes in autophagy after UPS impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34:667–673
Solesio ME, Saez-Atienzar S, Jordán J, Galindo MF (2012) Characterization of mitophagy in the 6-hydroxydopamine Parkinson’s disease model. Toxicol Sci 129(2):411–420
Spencer B, Potkar R, Trejo M, Rockenstein E, Patrick C, Gindi R, Adame A, Wyss-Coray T, Masliah E (2009) Beclin 1 Gene transfer activates autophagy and ameliorates the neurodegenerative pathology in α-synuclein models of Parkinson’s and lewy body diseases. J Neurosci 29(43):13578–13588
Yu L, Alva A, Su H, Dutt P, Freundt E, Welsh S, Baehrecke EH, Lenardo MJ (2004) Regulation of an ATG7-beclin 1 program of autophagic cell death by caspase-8. Science 304:1500–1502
Yue Z, Jin S, Yang C, Levine AJ, Heintz N (2003) Beclin 1, an autophagy gene essential for early embryonic development, is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:15077–15082
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Guangdong Natural Science Foundation of China (No. S2012010010625). We would like to express our sincere thanks to the reviewers and editors for the constructive and positive comments.
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Xue, ZF., Huang, LP. et al. Dynamic Expressions of Beclin 1 and Tyrosine Hydroxylase in Different Areas of 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Parkinsonian Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33, 973–981 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9964-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9964-1