Abstract
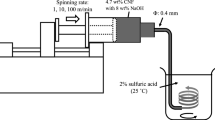
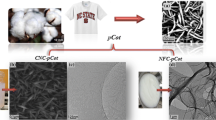
The effects of cellulases and their combination with mechanical fibrillation for nanofibrillation of cotton boll and dried cotton fibers and their subsequent application were investigated. The prepared nanofibrillated fibers were analyzed and compared in terms of morphology and solid-state properties. It was found that Trichoderma reesei cellulase, mainly consisting of cellobiohydrolases, was relatively suitable for nanofibrillation of cotton boll fibers. Nanofibrillation of cotton fibers, especially when previously dried, proved difficult without cellulases. Our results suggest that dried cotton fibers have strong hydrogen bonds, as in “hornification” during drying of wood pulp. However, we could nanofibrillate not only never-dried fibers of cotton boll but also dried cotton to 10–50 nm in width by treatment with cellulase mainly consisting of cellobiohydrolase, although a few bundles of around 100 nm remained. These results indicate that cellulase treatment cut and swelled the dried cotton fibers by breaking the strong hydrogen bonds, enabling their nanofibrillation. Nanofibrillated cotton fibers prepared using cellulases also contained relatively pure cellulose with greater crystallinity and higher thermal degradation temperatures compared with other cellulose nanofibers. Considering these characteristics, such cotton fibers nanofibrillated using cellulase would be applicable in medical and composite industries.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Yano H (2009) Comparison of the characteristics of cellulose microfibril aggregates of wood, rice straw and potato tuber. Cellulose 16:1017–1023. doi:10.1007/s10570-009-9334-9
Abe K, Yano H (2011) Formation of hydrogels from cellulose nanofibers. Carbohydr Polym 85:733–737. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.03.028
Abe K, Iwamoto S, Yano H (2007) Obtaining cellulose nanofibers with a uniform width of 15 nm from wood. Biomacromolecules 8:3276–3278. doi:10.1021/bm700624p
Bondeson D, Mathew A, Oksman K (2006) Optimization of the isolation of nanocrystals from microcrystalline cellulose by acid hydrolysis. Cellulose 13:171–180. doi:10.1007/s10570-006-9061-4
Chen W, Abe K, Uetani K, Yu H, Liu Y, Yano H (2014) Individual cotton cellulose nanofibers: pretreatment and fibrillation technique. Cellulose 21:1517–1528. doi:10.1007/s10570-014-0172-z
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896. doi:10.1007/s10570-013-0030-4
French AD, Santiago Cintrón S (2013) Cellulose polymorphy, crystallite size, and the Segal crystallinity index. Cellulose 20:583–588. doi:10.1007/s10570-012-9833-y
Garcia O, Torres AL, Colom JF, Pastor FIJ, Vidal T (2002) Effect of cellulase-assisted refining on the properties of dried and never-dried eucalyptus pulp. Cellulose 9(2):115–125. doi:10.1023/A:1020191622764
Hayashi N, Kondo T, Ishihara M (2005) Enzymatically produced nano-ordered short elements containing cellulose Ib crystalline domains. Carbohydr Polym 61:191–197. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.04.018
Henriksson M, Henriksson G, Berglund LA, Lindstrom T (2007) An environmentally friendly method for enzyme-assisted preparation of microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) nanofibers. Eur Polym J 43:3434–3441. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2007.05.038
Hideno A (2016) Comparison of the thermal degradation properties of crystalline and amorphous cellulose, as well as treated lignocellulosic biomass. BioResouces 11(3):6309–6319. doi:10.15376/biores.11.3.6309-6319
Hideno A, Abe K, Yano H (2014) Preparation using pectinase and characterization of nanofibers from orange peel waste in juice factories. J Food Sci 79:N1218–N1224. doi:10.1111/1750-3841.12471
Hon DNS (1994) Cellulose: a random walk along its historical path. Cellulose 1:1–25. doi:10.1007/BF00818796
Ibarra D, Kopcke V, Ek M (2010) Behavior of different monocomponent endoglucanases on the accessibility and reactivity of dissolving-grade pulps for viscose process. Enzyme Microbial Technol 47:355–362. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2010.07.016
Ifuku S, Adachi M, Morimoto M, Saimoto H (2011) Fabrication of cellulose nanofibers from parenchyma cells of pears and apples. Sen’i Gakkaishi 67:34–38. doi:10.2115/fiber.67.86
Igarashi K, Uchinashi T, Koivula A, Wada M, Kimura S, Okamoto T, Penttila M, Ando T, Samejima M (2011) Traffic jams reduce hydrolytic efficiency of cellulase on cellulose surface. Science 333:1279–1282. doi:10.1126/science.1208386
Isogai A, Saito T, Fukuzumi H (2011) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. Nanoscale 3:71–85. doi:10.1039/C0NR00583E
Kato KL, Cameron RE (1999) A review of the relationship between thermally-accelerated ageing of paper and hornification. Cellulose 6:23–40. doi:10.1023/A:1009292120151
Kekalainen K, Liimatainen H, Illikainen M, Maloney TC, Niinimaki J (2014) The role of hornification in the disintegration behaviour of TEMPO-oxidized bleached hardwood fibers in a high-shear homogenizer. Cellulose 21:1163–1174. doi:10.1007/s10570-014-0210-x
Kohnke T, Lund K, Brelid H, Westman G (2010) Kraft pulp hornification: a closer look at the preventive effect gained by glucuronoxylan adsorption. Carbohydr Polym 81:226–233. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.02.023
Lagerwall JPF, Schutz C, Salajkova M, Noh JH, Park JH, Scalia G, Bergstom L (2014) Cellulose nanocrystal-based materials: from liquid crystal self-assembly and glass formation to multifunctional thin films. NPG Asia Mater 6(e80):1–12. doi:10.1038/am.2013.69
Niimura H, Yokoyama T, Kimura S, Matsumoto Y, Kuga S (2010) AFM observation of ultrathin microfibrils in fruit tissues. Cellulose 17:13–18. doi:10.1007/s10570-009-9361-6
Nyon MP, Prentice T, Day J, Kirkpatrick J, Sivalingam GN, Levy G, Haq I, Irving JA, Lomas DA, Christodoulou J, Gooptu B, Thalassinos K (2015) An integrative approach combining ion mobility mass spectrometry, X-ray crystallography, and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to study the conformational dynamics of a1-antitrypsin upon ligand binding. Protein Sci 24:1301–1312. doi:10.1002/pro.2706
Pääkko M, Ankerfors M, Kosonen H, Ahola ANS, Osterberg M, Ruokolainen J, Laine J, Larsson PT, Ikkala O, Lindstrom T (2007) Enzymatic hydrolysis combined with mechanical shearing and high-pressure homogenization for nanoscale cellulose fibrils and strong gels. Biomacromolecules 8:1934–1941. doi:10.1021/bm061215p
Rabinovich ML, Melnick MS, Bolobova AV (2002) The structure and mechanism of action of cellulolytic enzymes. Biochemistry 67(8):850–871. doi:10.1023/A:1019958419032
Saito T, Nishiyama Y, Putaux JL, Vignon M, Isogai A (2006) Homogeneous suspensions of individualized microfibrils from TEMPO-catalyzed oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromolecules 7(6):1687–1691. doi:10.1021/bm060154s
Sandgren M, Shaw A, Ropp TH, Wu S, Bott R, Cameron AD, Stahlberg J, Mitchinson C, Jones A (2001) The X-ray crystal structure of the Trichoderma reesei family 12 endoglucanase 3, Cel12A, at 1.9A resolution. J Mol Biol 308:295–310. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4583
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE, Conrad CM (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29:786–794. doi:10.1177/004051755902901003
Siro I, Plackett D (2010) Microfibrillated cellulose and new nanocomposite materials: a review. Cellulose 17:459–494. doi:10.1007/s10570-010-9405-y
Tsuboi K, Yokota S, Kondo T (2014) Difference between bamboo- and wood-derived cellulose nanofibers prepared by the aqueous counter collision method. Nord Pulp Paper Res J 29:69–76. doi:10.3183/NPPRJ-2014-29-01-p069-076
Uetani K, Watanabe Y, Abe K, Yano H (2014) Influence of drying method and precipitated salts on pyrolysis for nanocelluloses. Cellulose 21:1631–1639. doi:10.1007/s10570-014-0242-2
Yano H (2010) Production of cellulose nanofibers and their application. J Jpn Inst Energy 89:1134–1140 (in Japanese)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Foundation of Industrial Development of Ehime Prefecture, Japan, and by JSPS KAKENHI grants no. JP26850222 and JP16K07809 in Japan. The authors thank Mr. Fumihide Nishisaka [Saisaikiteya of the National Federation of Agricultural Cooperative Associations (JA)] and Dr. Sunao Morimoto (Marusan Industry Co., Ltd., Japan) for kindly supplying the cotton boll and dried cotton fibers, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hideno, A., Abe, K., Uchimura, H. et al. Preparation by combined enzymatic and mechanical treatment and characterization of nanofibrillated cotton fibers. Cellulose 23, 3639–3651 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1075-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1075-y