Abstract
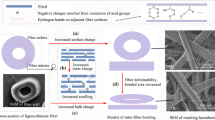
Cellulosic fiber has been increasingly used in many fields. The fiber charge, including the surface charge and inner charge, affects the properties of cellulosic fiber and fiber-based materials significantly. In this study, the cellulosic fiber was subjected to different treatments, including 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-piperidine-1-oxyl radical-mediated oxidation, carboxymethyl cellulose attachment and mechanical refining, to alter the fiber charge selectively. The effects of the fiber surface charge and inner charge on fiber performances and inter-fiber bonding strength for improving the high-value application of cellulosic fibers, respectively, were discussed. The results showed that the performances of cellulosic fiber can be improved with the increase of either surface or inner fiber charges, including the increased water retention value, flexibility and inter-fiber bonding strength, but with slightly decreased drainability. An increasing bulk fiber charge showed more significant enhancement of the inter-fiber bonding strength than only an increase of the fiber surface charge on cellulosic fiber. This was because the fiber inner charge contributed to the increase of fiber flexibility and deformability, which could benefit the inter-fiber bonding indirectly. As a consequence, the bulk fiber charge enhancement was better for tensile strength improvement of handsheets (fiber-based material) than only fiber surface charge enhancement. Increasing both the surface charge and inner charge improved the tensile strength effectively with less change of the bulky fiber network than the refining treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aracri E, Valls C, Vidal T (2012) Paper strength improvement by oxidative modification of sisal cellulose fibers with laccase-TEMPO system: influence of the process variables. Carbohydr Polym 88(3):830–837
Banavath HN, Bhardwaj NK, Ray AK (2011) A comparative study of the effect of refining on charge of various pulps. Bioresour Technol 102(6):4544–4551
Barzyk D, Page DH, Ragauskas A (1997) Acidic group topochemistry and fibre-to-fibre specific bond strength. J Pulp Pap Sci 23(2):J59–J61
Bhardwaj NK, Hoang V, Nguyen KL (2007) A comparative study of the effect of refining on physical and electrokinetic properties of various cellulosic fibres. Bioresour Technol 98(8):1647–1654
Dang Z, Zhang J, Ragauskas AJ (2007) Characterizing TEMPO-mediated oxidation of ECF bleached softwood kraft pulps. Carbohydr Polym 70(3):310–317
Duker E, Lindström T (2008) On the mechanisms behind the ability of CMC to enhance paper strength. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 23(1):57–64
Etter MC (1990) Encoding and decoding hydrogen-bond patterns of organic compounds. Acc Chem Res 23(4):120–126
Fardim P, Durán N (2003) Modification of fibre surfaces during pulping and refining as analysed by SEM, XPS and ToF-SIMS. Colloids Surf A: Physicochem Eng Asp 223(1):263–276
Fatehi P, Tutus A, Xiao H (2009) Cationic-modified PVA as a dry strength additive for rice straw fibers. Bioresour Technol 100(2):749–755
Fatehi P, Kititerakun R, Ni Y, Xiao H (2010a) Synergy of CMC and modified chitosan on strength properties of cellulosic fiber network. Carbohydr Polym 80(1):208–214
Fatehi P, Liu X, Ni Y, Xiao H (2010b) Interaction of cationic modified poly vinyl alcohol with high yield pulp. Cellulose 17(5):1021–1031
Fujisawa S, Okita Y, Fukuzumi H, Saito T, Isogai A (2011) Preparation and characterization of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibril films with free carboxyl groups. Carbohydr Polym 84(1):579–583
Gharehkhani S, Sadeghinezhad E, Kazi SN, Yarmand H, Badarudin A, Safaei MR, Zubir MNM (2015) Basic effects of pulp refining on fiber properties—a review. Carbohydr Polym 115:785–803
González I, Alcalà M, Chinga-Carrasco G, Vilaseca F, Boufi S, Mutjé P (2014) From paper to nanopaper: evolution of mechanical and physical properties. Cellulose 21(4):2599–2609
Horvath AE, Lindström T, Laine J (2006) On the indirect polyelectrolyte titration of cellulosic fibers. Conditions for charge stoichiometry and comparison with ESCA. Langmuir 22(2):824–830
Hubbe MA (2006) Bonding between cellulosic fibers in the absence and presence of dry-strength agents—a review. Bioresources 1(2):281–318
Hubbe MA, Venditti RA, Rojas OJ (2007) What happens to cellulosic fibers during papermaking and recycling? A review. Bioresources 2(4):739–788
John MJ, Thomas S (2008) Biofibres and biocomposites. Carbohydr Polym 71(3):343–364
Kargl R, Mohan T, Bračič M, Kulterer M, Doliška A, Stana-Kleinschek K, Ribitsch V (2012) Adsorption of carboxymethyl cellulose on polymer surfaces: evidence of a specific interaction with cellulose. Langmuir 28(31):11440–11447
Kato KL, Cameron RE (1999) A review of the relationship between thermally-accelerated ageing of paper and hornification. Cellulose 6(1):23–40
Katz S, Beatson RP, Scallan AM (1984) The determination of strong and weak acidic groups in sulfite pulps. Sven Papperstidn 87:R48–R53
Kongdee A, Bechtold T, Burtscher E, Scheinecker M (2004) The influence of wet/dry treatment on pore structure-the correlation of pore parameters, water retention and moisture regain values. Carbohydr Polym 57(1):39–44
Laine J, Lindstrom T, Nordmark GG, Risinger G (2000) Studies on topochemical modification of cellulosic fibres Part 1. Chemical conditions for the attachment of carboxymethyl cellulose onto fibres. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 15(5):520–526
Lei M, Zhang H, Li J, Duan J (2013) Characteristics of poplar preconditioning followed by refining chemical treatment alkaline peroxide mechanical pulp fiber fractions and their effects on formation and properties of high-yield pulp containing paper. Ind Eng Chem Res 52(11):4083–4088
Li H, Zhang H, Li J, Du F (2014) Comparison of interfiber bonding ability of different poplar P-RC alkaline peroxide mechanical pulp (APMP) fiber fractions. BioResources 9(4):6019–6027
Li J, Liu Y, Duan C, Zhang H, Ni Y (2015) Mechanical pretreatment improving hemicelluloses removal from cellulosic fibers during cold caustic extraction. Bioresour Technol 192:501–506
Lowe RM, Page DH, Waterhouse JF, Hsieh J, Cheluka N, Ragauskas AJ (2007) Deformation behavior of wet lignocellulosic fibers. Holzforschung 61(3):261–266
Ma P, Fu S, Zhai H, Law K, Daneault C (2012) Influence of TEMPO-mediated oxidation on the lignin of thermomechanical pulp. Bioresour Technol 118:607–610
Malti A, Edberg J, Granberg H et al (2016) Conducting polymers: an organic mixed ion-electron conductor for power electronics. Adv Sci. doi:10.1002/advs.201670006
Mao L, Law K, Claude D, Francois B (2008) Effects of carboxyl content on the characteristics of TMP long fibers. Ind Eng Chem Res 47(11):3809–3812
Miao Q, Chen L, Huang L, Tian C, Zheng L, Ni Y (2014a) A process for enhancing the accessibility and reactivity of hardwood kraft-based dissolving pulp for viscose rayon production by cellulase treatment. Bioresour Technol 154:109–113
Miao Q, Zhong G, Qin M, Chen L, Huang L (2014b) Influence of alkaline treatment and alkaline peroxide bleaching of aspen chemithermomechanical pulp on dissolved and colloidal substances. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(6):2544–2548
Miao Q, Tian C, Chen L, Huang L, Zheng L, Ni Y (2015) Combined mechanical and enzymatic treatments for improving the Fock reactivity of hardwood kraft-based dissolving pulp. Cellulose 22(1):803–809
Ni Y, He Z, Zhang H, Zhou Y (2011) Characteristics of high yield pulp and its effect on some typical wet-end issues. J Biobased Mater Biol 5(2):181–186
Nooy AEJ, Besemer AC, Bekkum H (1995) Highly selective nitroxyl radical-mediated oxidation of primary alcohol groups inwater-soluble glucans. Carbohydr Res 269(1):89–98
Öhman LO, Wågberg L, Malmgren K, Tjernström A (1997) Adsorption of aluminum (III) on cellulosic fibres in neutral to alkaline solutions: influence of charge and size of the particles formed. J Pulp Pap Sci 23(10):J467–J474
Page DH (1969) A theory for tensile strength of paper. Tappi J 52(4):674
Petit-Conil M, Cochaux A, De Choudens C (1994) Mechanical pulp characterization: a new and rapid method to evaluate fibre flexibility. Pap Puu 76(10):657–662
Rakkolainen M, Kontturi E, Isogai A, Enomae T, Blomstedt M, Vuorinen T (2009) Carboxymethyl cellulose treatment as a method to inhibit vessel picking tendency in printing of eucalyptus pulp sheets. Ind Eng Chem Res 48(4):1887–1892
Scallan AM (1983) The effect of acidic groups on the swelling of pulps: a review. Tappi J 66(11):73–75
Sezaki T, Hubbe MA, Heitmann JA, Argyropoulos DS (2006) Colloidal effects of acrylamide polyampholytes: part 2: adsorption onto cellulosic fibers. Colloids Surf A: Physicochem Eng Asp 289(1):89–95
Shen J, Song Z, Qian X, Ni Y (2011) A review on use of fillers in cellulosic paper for functional applications. Ind Eng Chem Res 50(2):661–666
Sim G, Alam MN, Godbout L, van de Ven T (2014) Structure of swollen carboxylated cellulose fibers. Cellulose 21(6):4595–4606
Sjöström E (1989) The origin of charge on cellulosic fibres. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 4(2):90–93
Wågberg L, Odberg L, Glad-Nordmark G (1989) Charge determination of porous substrates by polyelectrolyte adsorption. Part 1. Carboxymethylated, bleached cellulosic fibers. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 2:71–76
Wang B, Li R, He B, Li J (2011) The impacts of lignin coverage, relative bonded area, and fiber properties on sheet strength. Bioresources 6(4):4356–4369
Zaman M, Liu H, Xiao H, Chibante F, Ni Y (2013) Hydrophilic modification of polyester fabric by applying nanocrystalline cellulose containing surface finish. Carbohydr Polym 91(2):560–567
Zemljič LF, Stenius P, Laine J, Stana-Kleinschek K (2008) Topochemical modification of cotton fibres with carboxymethyl cellulose. Cellulose 15(2):315–321
Zhang H, He Z, Ni Y (2011) Improvement of high-yield pulp properties by using a small amount of bleached wheat straw pulp. Bioresour Technol 102(3):2829–2833
Zhang H, Zhao C, Li Z, Li J (2016a) The fiber charge measurement depending on the poly-DADMAC accessibility to cellulose fibers. Cellulose 23(1):163–173
Zhang H, Zeng X, Xie J, Li Z, Li H (2016b) Study on the sorption process of triclosan on cationic microfibrillated cellulose and its antibacterial activity. Carbohydr Polym 136:493–498
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 31370577).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, C., Zhang, H., Zeng, X. et al. Enhancing the inter-fiber bonding properties of cellulosic fibers by increasing different fiber charges. Cellulose 23, 1617–1628 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0941-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0941-y