Abstract
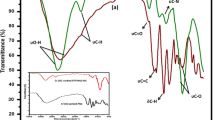
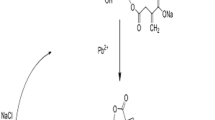
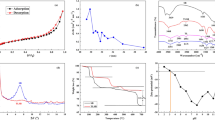
Due to environmental concerns and decreasing global resources, removing aqueous heavy metals from industrial wastewaters is important for ecological sustainability. In this work, the removal of vanadium from a synthetic aqueous solution using bisphosphonate nanocelluloses was studied. Bisphoshonate nanocellulose was obtained from periodate oxidized and sodium alendronate aminated wood cellulose fibers using a mechanical disintegration method. Depending on the reaction condition, long flexible nanofibrillated celluloses or shorter rigid cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) were obtained. The most efficient removal of vanadium was obtained at low solution pH (2 and 3), which is most likely due to the complexation of vanadium with bisphosphonate groups and the electrostatic interaction between cationic vanadium species and anionic acid groups. Based on the Langmuir isotherm, a maximum adsorption capacity of 1.98 mmol/g was attained with the CNCs that had 0.32 mmol/g of bisphosphonate content. The adsorption kinetic of vanadium was modeled and found to follow a pseudo-second-order model.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abon M, Volta J-C (1997) Vanadium phosphorus oxides for n-butane oxidation to maleic anhydride. Appl Catal Gen 157:173–193. doi:10.1016/S0926-860X(97)00016-1
Alexandrescu L, Syverud K, Gatti A, Chinga-Carrasco G (2013) Cytotoxicity tests of cellulose nanofibril-based structures. Cellulose 20:1765–1775. doi:10.1007/s10570-013-9948-9
Anirudhan TS, Jalajamony S, Divya L (2009) Efficiency of amine-modified poly(glycidyl methacrylate)-grafted cellulose in the removal and recovery of vanadium(V) from aqueous solutions. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:2118–2124. doi:10.1021/ie8000869
Arvidsson R, Nguyen D, Svanström M (2015) Life cycle assessment of cellulose nanofibrils production by mechanical treatment and two different pretreatment processes. Environ Sci Technol. doi:10.1021/acs.est.5b00888
Bailey SE, Olin TJ, Bricka RM, Adrian DD (1999) A review of potentially low-cost sorbents for heavy metals. Water Res 33:2469–2479. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00475-8
Cai G-B, Zhao G-X, Wang X-K, Yu S-H (2010) Synthesis of polyacrylic acid stabilized amorphous calcium carbonate nanoparticles and their application for removal of toxic heavy metal ions in water. J Phys Chem C 114:12948–12954. doi:10.1021/jp103464p
Carrillo CA, Laine J, Rojas OJ (2014) Microemulsion systems for fiber deconstruction into cellulose nanofibrils. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:22622–22627. doi:10.1021/am5067332
Chen L-F, Liang H-W, Lu Y et al (2011) Synthesis of an attapulgite clay@carbon nanocomposite adsorbent by a hydrothermal carbonization process and their application in the removal of toxic metal ions from water. Langmuir 27:8998–9004. doi:10.1021/la2017165
Crans DC, Holder AA, Saha TK et al (2007) Chelation of vanadium(V) by difluoromethylene bisphosphonate, a structural analogue of pyrophosphate. Inorg Chem 46:6723–6732. doi:10.1021/ic062484r
Dangerfield EM, Gulab SA, Plunkett CH et al (2010) A fast, efficient and stereoselective synthesis of hydroxy-pyrrolidines. Carbohydr Res 345:1360–1365. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2010.03.016
Domingo JL (1996) Vanadium: a review of the reproductive and developmental toxicity. Reprod Toxicol 10:175–182. doi:10.1016/0890-6238(96)00019-6
Dufresne A (2013) Nanocellulose: a new ageless bionanomaterial. Mater Today 16:220–227. doi:10.1016/j.mattod.2013.06.004
Eriksen KM, Karydis DA, Boghosian S, Fehrmann R (1995) Deactivation and compound formation in sulfuric-acid catalysts and model systems. J Catal 155:32–42. doi:10.1006/jcat.1995.1185
Gadd GM (2009) Biosorption: critical review of scientific rationale, environmental importance and significance for pollution treatment. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84:13–28. doi:10.1002/jctb.1999
Gupta S, Babu BV (2009) Utilization of waste product (tamarind seeds) for the removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions: equilibrium, kinetics, and regeneration studies. J Environ Manage 90:3013–3022. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.04.006
Habibi Y (2014) Key advances in the chemical modification of nanocelluloses. Chem Soc Rev 43:1519–1542. doi:10.1039/C3CS60204D
Hakim L, Sabarudin A, Oshita K et al (2008) Synthesis of cross-linked chitosan functionalized with threonine moiety and its application to on-line collection/concentration and determination of Mo, V and Cu. Talanta 74:977–985. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2007.08.012
Henriksson M, Henriksson G, Berglund LA, Lindström T (2007) An environmentally friendly method for enzyme-assisted preparation of microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) nanofibers. Eur Polym J 43:3434–3441. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2007.05.038
Herrick FW, Casebier RL, Hamilton JK, Sandberg KR (1983) Microfibrillated cellulose: morphology and accessibility. J Appl Polym Sci 37:797–813
Ho Y-S (2006) Second-order kinetic model for the sorption of cadmium onto tree fern: a comparison of linear and non-linear methods. Water Res 40:119–125. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.10.040
Ho YS, McKay G (1998) Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem Eng J 70:115–124. doi:10.1016/S0923-0467(98)00076-1
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. doi:10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Hokkanen S, Repo E, Sillanpää M (2013) Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by succinic anhydride modified mercerized nanocellulose. Chem Eng J 223:40–47. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2013.02.054
Jebali A, Ardakani SAY, Sedighi N, Hekmatimoghaddam S (2014) Nanocellulose conjugated with retinoic acid: its capability to adsorb aflatoxin B1. Cellulose 22:363–372. doi:10.1007/s10570-014-0475-0
Klemm D, Kramer F, Moritz S et al (2011) Nanocelluloses: a new family of nature-based materials. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:5438–5466. doi:10.1002/anie.201001273
Lazaridis NK, Jekel M, Zouboulis AI (2003) Removal of Cr(VI), Mo(VI), and V(V) ions from single metal aqueous solutions by sorption or nanofiltration. Sep Sci Technol 38:2201–2219. doi:10.1081/SS-120021620
Leung ACW, Hrapovic S, Lam E et al (2011) Characteristics and properties of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals prepared from a novel one-step procedure. Small 7:302–305. doi:10.1002/smll.201001715
Liao X-P, Tang W, Zhou R-Q, Shi B (2007) Adsorption of metal anions of vanadium(V) and chromium(VI) on Zr(IV)-impregnated collagen fiber. Adsorption 14:55–64. doi:10.1007/s10450-007-9045-1
Liimatainen H, Sirviö J, Haapala A et al (2011) Characterization of highly accessible cellulose microfibers generated by wet stirred media milling. Carbohydr Polym 83:2005–2010. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.11.007
Liu X, Hu Q, Fang Z et al (2009) Magnetic chitosan nanocomposites: a useful recyclable tool for heavy metal ion removal. Langmuir 25:3–8. doi:10.1021/la802754t
Liu P, Borrell PF, Božič M et al (2015) Nanocelluloses and their phosphorylated derivatives for selective adsorption of Ag+, Cu2+ and Fe3+ from industrial effluents. J Hazard Mater 294:177–185. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.04.001
Moskalyk RR, Alfantazi AM (2003) Processing of vanadium: a review. Miner Eng 16:793–805. doi:10.1016/S0892-6875(03)00213-9
Naeem A, Westerhoff P, Mustafa S (2007) Vanadium removal by metal (hydr)oxide adsorbents. Water Res 41:1596–1602. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.01.002
Namasivayam C, Sangeetha D (2006) Removal and recovery of vanadium(V) by adsorption onto ZnCl2 activated carbon: kinetics and isotherms. Adsorption 12:103–117. doi:10.1007/s10450-006-0373-3
Padilla-Rodríguez A, Hernández-Viezcas JA, Peralta-Videa JR et al (2015) Synthesis of protonated chitosan flakes for the removal of vanadium(III, IV and V) oxyanions from aqueous solutions. Microchem J 118:1–11. doi:10.1016/j.microc.2014.07.011
Parijaee M, Noaparast M, Saberyan K, Shafaie-Tonkaboni SZ (2014) Adsorption of vanadium(V) from acidic solutions by using octylamine functionalized magnetite nanoparticles as a novel adsorbent. Korean J Chem Eng 31:2237–2244. doi:10.1007/s11814-014-0179-z
Peacock CL, Sherman DM (2004) Vanadium(V) adsorption onto goethite (α-FeOOH) at pH 1.5–12: a surface complexation model based on ab initio molecular geometries and EXAFS spectroscopy. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:1723–1733. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2003.10.018
Pitkänen M, Kangas H, Laitinen O et al (2014) Characteristics and safety of nano-sized cellulose fibrils. Cellulose 21:3871–3886. doi:10.1007/s10570-014-0397-x
Qian S, Wang H, Huang G et al (2004) Studies of adsorption properties of crosslinked chitosan for vanadium(V), tungsten(VI). J Appl Polym Sci 92:1584–1588. doi:10.1002/app.20102
Rånby BG, Banderet A, Sillén LG (1949) Aqueous colloidal solutions of cellulose micelles. Acta Chem Scand 3:649–650. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.03-0649
Rengel Z (1999) Heavy metals as essential nutrients. Heavy metal stress in plants. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 231–251
Saito T, Nishiyama Y, Putaux J-L et al (2006) Homogeneous suspensions of individualized microfibrils from TEMPO-catalyzed oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromolecules 7:1687–1691. doi:10.1021/bm060154s
Schwarz K, Milne DB (1971) Growth effects of vanadium in the rat. Science 174:426–428. doi:10.1126/science.174.4007.426
Sirviö JA, Visanko M, Liimatainen H (2015a) Deep eutectic solvent system based on choline chloride-urea as a pre-treatment for nanofibrillation of wood cellulose. Green Chem 17:3401–3406. doi:10.1039/C5GC00398A
Sirviö JA, Hasa T, Ahola J et al (2015b) Phosphonated nanocelluloses from sequential oxidative-reductive treatment—physicochemical characteristics and thermal properties. Carbohydr Polym 133:524–532. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.06.090
Stafiej A, Pyrzynska K (2007) Adsorption of heavy metal ions with carbon nanotubes. Sep Purif Technol 58:49–52. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2007.07.008
Suopajärvi T, Liimatainen H, Karjalainen M et al (2015) Lead adsorption with sulfonated wheat pulp nanocelluloses. J Water Process Eng 5:136–142. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2014.06.003
Visanko M, Liimatainen H, Sirviö JA et al (2014) Amphiphilic cellulose nanocrystals from acid-free oxidative treatment: physicochemical characteristics and use as an oil-water stabilizer. Biomacromolecules 15:2769–2775. doi:10.1021/bm500628g
Wang T, Cheng Z, Wang B, Ma W (2012) The influence of vanadate in calcined Mg/Al hydrotalcite synthesis on adsorption of vanadium (V) from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 181–182:182–188. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2011.11.053
Zhang L, Liu X, Xia W, Zhang W (2014) Preparation and characterization of chitosan-zirconium(IV) composite for adsorption of vanadium(V). Int J Biol Macromol 64:155–161. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.11.040
Acknowledgments
Elisa Wirkkala is gratefully acknowledged for vanadium analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sirviö, J.A., Hasa, T., Leiviskä, T. et al. Bisphosphonate nanocellulose in the removal of vanadium(V) from water. Cellulose 23, 689–697 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0819-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0819-4