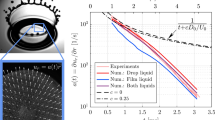
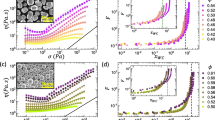
Abstract
We conduct rheological characterization of nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) suspensions, a highly non-Newtonian complex fluid, at several concentrations. Special care is taken to cope with the prevalent problems of time scale issues, wall depletion and confinement effects. We do this by combining the wide-gap vane geometry, extremely long measurement times, and modeling. We take into account the wide-gap related stress heterogeneity by extending upon mainstream methods and apply a gap correction. Furthermore, we rationalize the experimental data through a simple viscous structural model. With these tools we find that, owing to the small size of the particles subjected to Brownian motion, the NFC suspensions exhibit a critical shear rate, where the flow curve experiences a turning point. This makes the steady state of these suspensions at low shear rates non-unique. To optimize various mixing and pumping applications, such history dependent tendency of NFC suspensions to shear band needs to be taken into account.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agoda-Tandjawa G, Durand S, Berot S, Blassel C, Gaillard C, Garnier C, Doublier JL (2010) Rheological characterization of microfibrillated cellulose suspensions after freezing. Carbohydr Polym 80(3):677–686
Ahola S, Myllytie P, Österberg M, Teerinen T, Laine J (2008) Effect of polymer adsorption on cellulose nanofibril water binding capacity and aggregation. BioResources 3(4):1315–1328
Ancey C (2005) Solving the Couette inverse problem using a wavelet-vaguelette decomposition. J Rheol 49(2):441–460
Barnes HA (1995) A review of the slip (wall depletion) of polymer solutions, emulsions and particle suspensions in viscometers: its cause, character, and cure. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 56(3):221–251
Barnes HA (2000) Measuring the viscosity of large-particle (and flocculated) suspensions: a note on the necessary gap size of rotational viscometers. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 94(2):213–217
Bennington CPJ, Kerekes RJ, Grace JR (1990) The yield stress of fibre suspensions. Can J Chem Eng 68(5):748–757
Berli CLA, Quemada D (2000) Rheological modeling of microgel suspensions involving solid-liquid transition. Langmuir 16(21):7968–7974
Björkman U (2006) The metarheology of crowded fibre suspensions. Ann Trans Nordic Rheol Soc 14:69
Bonn D, Denn MM (2009) Yield stress fluids slowly yield to analysis. Science 324(5933):1401–1402
Buscall R (2010) Letter to the editor: wall slip in dispersion rheometry. J Rheol 54(6):1177–1183
Cohen SD, Hindmarsh AC (1996) CVODE, a stiff/nonstiff ODE solver in C. Comp Phys 10:138–143
Coussot P (2005) Rheometry of pastes, suspensions, and granular materials: applications in industry and environment. Wiley, Hoboken
Coussot P, Ovarlez G (2010) Physical origin of shear-banding in jammed systems. Eur Phys J E 33(3):183–188
Coussot P, Nguyen Q, Huynh HT, Bonn D (2002a) Avalanche behavior in yield stress fluids. Phys Rev Lett 88(17):175501
Coussot P, Nguyen QD, Huynh HT, Bonn D (2002b) Viscosity bifurcation in thixotropic, yielding fluids. J Rheol 46(3):573–589
Coussot P, Roussel N, Jarny S, Chanson H (2005) Continuous or catastrophic solid-liquid transition in jammed systems. Phys Fluids 17(1):011704
Damani R, Powell RL, Hagen N (1993) Viscoelastic characterization of medium consistency pulp suspensions. Can J Chem Eng 71(5):676–684
Derakhshandeh B, Hatzikiriakos SG, Bennington CPJ (2010) Rheology of pulp suspensions using ultrasonic doppler velocimetry. Rheologica Acta 49(11–12):1127–1140
Divoux T, Tamarii D, Barentin C, Manneville S (2010) Transient shear banding in a simple yield stress fluid. Phys Rev Lett 104(20):208301
Divoux T, Grenard V, Manneville S (2013) Rheological hysteresis in soft glassy materials. Phys Rev Lett 110(1):018304
Dzuy NQ, Boger DV (1983) Yield stress measurement for concentrated suspensions. J Rheol 27(4):321–349
Dzuy NQ, Boger DV (1985) Direct yield stress measurement with the vane method. J Rheol 29(3):335–347
Eichhorn SJ, Dufresne A, Aranguren M, Marcovich NE, Capadona JR, Rowan SJ, Weder C, Thielemans W, Roman M, Renneckar S et al (2010) Review: current international research into cellulose nanofibres and nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 45(1):1–33
Eriksen O, Syverud K, Gregersen O (2008) The use of microfibrillated cellulose produced from kraft pulp as strength enhancer in TMP paper. Nordic Pulp Paper Res J 23(3):299–304
Fielding SM (2007) Complex dynamics of shear banded flows. Soft Matter 3(10):1262–1279
Fisher DT, Clayton SA, Boger DV, Scales PJ (2007) The bucket rheometer for shear stress-shear rate measurement of industrial suspensions. J Rheol 51(5):821–831
Fukuzumi H, Tanaka R, Saito T, Isogai A (2014) Dispersion stability and aggregation behavior of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils in water as a function of salt addition. Cellulose 21(3):1553–1559
Goyon J, Colin A, Ovarlez G, Ajdari A, Bocquet L (2008) Spatial cooperativity in soft glassy flows. Nature 454(7200):84–87
Hayaka F, Saito T, Isogai A (2013) Influence of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibril length on film properties. Carbohydr Polym 93(1):172–177
Heirman G, Vandewalle L, Van Gemert D, Wallevik O (2008) Integration approach of the couette inverse problem of powder type self-compacting concrete in a wide-gap concentric cylinder rheometer. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 150(2):93–103
Illa X, Puisto A, Lehtinen A, Mohtaschemi M, Alava MJ (2013) Transient shear banding in time-dependent fluids. Phys Rev E 87:022307
Iotti M, Gregersen ØW, Moe S, Lenes M (2011) Rheological studies of microfibrillar cellulose water dispersions. J Polym Environ 19(1):137–145
Ishii D, Saito T, Isogai A (2011) Viscoelastic evaluation of average length of cellulose nanofibers prepared by tempo-mediated oxidation. Biomacromolecules 12(3):548–550
Isogai A, Saito T, Fukuzumi H (2011) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. Nanoscale 3(1):71–85
Jones E, Oliphant T, Peterson P, et al. (2001) SciPy: open source scientific tools for Python.
Labanda J, Marco P, Llorens J (2004) Rheological model to predict the thixotropic behaviour of colloidal dispersions. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 249(1):123–126
Lasseuguette E, Roux D, Nishiyama Y (2008) Rheological properties of microfibrillar suspension of TEMPO-oxidized pulp. Cellulose 15(3):425–433
Lehtinen A, Puisto A, Illa X, Mohtaschemi M, Alava MJ (2013) Transient shear banding in viscoelastic maxwell fluids. Soft Matter 9:8041–8049
Lowys MP, Desbrieres J, Rinaudo M (2001) Rheological characterization of cellulosic microfibril suspensions. role of polymeric additives. Food Hydrocoll 15(1):25–32
Martin JD, Hu YT (2012) Transient and steady-state shear banding in aging soft glassy materials. Soft Matter 8(26):6940–6949
Mewis J, Wagner N (2009) Thixotropy. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 147:214–227
Mohtaschemi M, Dimic-Misic K, Puisto A, Korhonen M, Maloney T, Paltakari J, Alava MJ (2014a) Rheological characterization of fibrillated cellulose suspensions via bucket vane viscometer. Cellulose 21:1305–1312
Mohtaschemi M, Puisto A, Illa X, Alava MJ (2014b) Rheology dynamics of aggregating colloidal suspensions. Soft Matter 10:2971–2981
Møller PCF, Fall A, Bonn D (2009a) Origin of apparent viscosity in yield stress fluids below yielding. EPL (Europhys Lett) 87(3):38004
Møller PCF, Fall A, Chikkadi V, Derks D, Bonn D (2009b) An attempt to categorize yield stress fluid behaviour. Philos Trans R Soc A 367(1909):5139–5155
Mosse WKJ, Boger DV, Garnier G (2012) Avoiding slip in pulp suspension rheometry. J Rheol 56(6):1517–1533
Okahisa Y, Yoshida A, Miyaguchi S, Yano H (2009) Optically transparent wood-cellulose nanocomposite as a base substrate for flexible organic light-emitting diode displays. Compos Sci Technol 69(11):1958–1961
Ovarlez G, Rodts S, Ragouilliaux A, Coussot P, Goyon J, Colin A (2008) Wide-gap Couette flows of dense emulsions: local concentration measurements, and comparison between macroscopic and local constitutive law measurements through magnetic resonance imaging. Phys Rev E 78(3):036307
Ovarlez G, Tocquer L, Bertrand F, Coussot P (2013) Rheopexy and tunable yield stress of carbon black suspensions. Soft Matter 9(23):5540–5549
Pääkkö M, Ankerfors M, Kosonen H, Nykänen A, Ahola S, Österberg M, Ruokolainen J, Laine J, Larsson PT, Ikkala O, Lindström T (2007) Enzymatic hydrolysis combined with mechanical shearing and high-pressure homogenization for nanoscale cellulose fibrils and strong gels. Biomacromolecules 8(6):1934–1941
Phillips RJ, Armstrong RC, Brown RA, Graham AL, Abbott JR (1992) A constitutive equation for concentrated suspensions that accounts for shear induced particle migration. Phys Fluids A 4:30–40
Roussel N, Le Roy R, Coussot P (2004) Thixotropy modelling at local and macroscopic scales. J Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech 117(2):85–95
Saarikoski E, Saarinen T, Salmela J, Seppälä J (2012) Flocculated flow of microfibrillated cellulose water suspensions: an imaging approach for characterisation of rheological behaviour. Cellulose 19(3):647–659
Saarinen T, Haavisto S, Sorvari A, Salmela J, Seppälä J (2013) The effect of wall depletion on the rheology of microfibrillated cellulose water suspensions by optical coherence tomography. Cellulose 21(3):1261–1275
Saito T, Nishiyama Y, Putaux JL, Vignon M, Isogai A (2006) Homogeneous suspensions of individualized microfibrils from tempo-catalyzed oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromolecules 7(6):1687–1691
Saito T, Kimura S, Nishiyama Y, Isogai A (2007) Cellulose nanofibers prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation of native cellulose. Biomacromolecules 8(8):2485–2491
Swerin A, Powell RL, Ödberg L (1992) Linear and nonlinear dynamic viscoelasticity of pulp fiber suspensions. Nordic Pulp Paper Res J 7(3):126–132
Teng H, Zhang J (2013) Modeling the viscoelasto-plastic behavior of waxy crude. Pet Sci 10(3):395–401
Turbak A, Snyder FW, Sandberg KR (1983) Microfibrillated cellulose, a new cellulose product: properties, uses and commercial potential. J Appl Polym Sci, Appl Polym Symp 37:815–827
Varanasi S, He R, Batchelor W (2013) Estimation of cellulose nanofibre aspect ratio from measurements of fibre suspension gel point. Cellulose 20(4):1885–1896
Yeow YL, Ko WC, Tang PPP (2000) Solving the inverse problem of Couette viscometry by Tikhonov regularization. J Rheol 44(6):1335–1351
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Effnet program in the Finnish Forest Cluster Ltd, and EU framework 7 program SUNPAP. Also, the support from the Academy of Finland through the COMP center of excellence and the project number 140268, within the framework of the International Doctoral Programme in Bioproducts Technology (PaPSaT) and Graduate School in Chemical Engineering (GSCE) are acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohtaschemi, M., Sorvari, A., Puisto, A. et al. The vane method and kinetic modeling: shear rheology of nanofibrillated cellulose suspensions. Cellulose 21, 3913–3925 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0409-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0409-x