Abstract
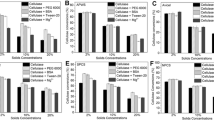
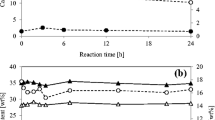
It has previously been shown that the improved digestibility of dilute acid pretreated corn stover is at least partially due to the removal of xylan and the consequent increase in accessibility of the cellulose to cellobiohydrolase enzymes. We now report on the impact that lignin removal has on the accessibility and digestibility of dilute acid pretreated corn stover. Samples of corn stover were subjected to dilute sulfuric acid pretreatment with and without simultaneous (partial) lignin removal. In addition, some samples were completely delignified after the pretreatment step using acidified sodium chlorite. The accessibility and digestibility of the samples were tested using a fluorescence-labeled cellobiohydrolase (Trichoderma reesei Cel7A) purified from a commercial cellulase preparation. Partial delignification of corn stover during dilute acid pretreatment was shown to improve cellulose digestibility by T. reesei Cel7A; however, decreasing the lignin content below 5% (g g−1) by treatment with acidified sodium chlorite resulted in a dramatic reduction in cellulose digestibility. Importantly, this effect was found to be enhanced in samples with lower xylan contents suggesting that the near complete removal of xylan and lignin may cause aggregation of the cellulose microfibrils resulting in decreased cellulase accessibility.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlgren PA, Goring DAI (1971) Removal of wood components during chlorite delignification of black spruce. Can J Chem 49:1272–1275. doi:10.1139/v71-207
Avgerinos GC, Wang DIC (1983) Selective solvent delignification for fermentation enhancement. Biotechnol Bioeng 25:67–83. doi:10.1002/bit.260250107
Barr BK, Hsieh YL, Ganem B, Wilson DB (1996) Identification of two functionally different classes of exocellulases. Biochemistry 35:586–592. doi:10.1021/bi9520388
Bernardez TD, Lyford K, Hogsett DA, Lynd LR (1993) Adsorption of Clostridium thermocellum cellulases onto pretreated mixed hardwood, avicel and lignin. Biotechnol Bioeng 42:899–907. doi:10.1002/bit.260420715
Black SK, Hames BR, Myers MD (1998) Method of separating lignocellulosic material into lignin, cellulose and dissolved sugars. US Pat 5:730–837
Chernoglazov VM, Ermolova OV, Klyosov AA (1988) Adsorption of high-purity endo-1, 4-β-glucanases from Trichoderma reesei on components of lignocellulosic materials: cellulose, lignin, and xylan. Enzyme Microb Tech 10:503–507. doi:10.1016/0141-0229(88)90029-4
Cowling EB (1975) Physical and chemical constraints in the hydrolysis of cellulose and lignocellulosic materials. Biotechnol Bioeng Symp 5:163–181
Davis MF, Schroeder HA, Maciel GE (1994) Solid-state C-13 nuclear-magnetic-resonance studies of wood decay. 2. White-rot decay of paper birch. Holzforschung 48:186–192
Ding S-Y, Himmel ME (2006) The maize primary cell wall microfibril: a new model derived from direct visualization. J Agric Food Chem 54:597–606. doi:10.1021/jf051851z
Doner LW, Irwin PL (1992) Assay of reducing end-groups in oligosaccharide homologs with 2, 2′-Bicinchoninate. Anal Biochem 202:50–53. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(92)90204-K
Dowe N, McMillan J (2001) SSF experimental protocols: lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis and fermentation. Laboratory analytical procedure. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO
Duchesne I, Hult E-L, Molin U, Daniel G, Iversen T, Lennholm H (2001) The influence of hemicellulose on fibril aggregation of kraft pulp fibres as revealed by FE-SEM and CP/MAS 13C-NMR. Cellulose 8:103–111. doi:10.1023/A:1016645809958
Eriksson T, Borjesson J, Tjerneld F (2002) Mechanism of surfactant effect in enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose. Enzyme Microb Technol 31:353–364. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(02)00134-5
Fan LT, Lee Y-H, Beardmore DH (1980) Mechanism of the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose: effects of major structural features of cellulose on enzymatic hydrolysis. Biotechnol Bioeng 22:177–199. doi:10.1002/bit.260220113
Fengel D, Wegener G (1984) Chemistry, ultrastructure, reactions. de Gruyter. New York and Berlin, Germany
Grethlein HE, Allen DC, Converse AO (1984) A comparative-study of the enzymatic-hydrolysis of acid-pretreated white-pine and mixed hardwood. Biotechnol Bioeng 26:1498–1505. doi:10.1002/bit.260261215
Grohmann K, Torget R, Himmel M (1985) Optimization of dilute acid pretreatment of biomass. Biotechnol Bioeng Symp 15:59–80
Haw JF, Maciel GE, Schroeder HA (1984) C-13 nuclear magnetic-resonance spectrometric study of wood and wood pulping with cross polarization and magic-angle spinning. Anal Chem 56:1323–1329. doi:10.1021/ac00272a028
Ishizawa CI, Davis MF, Schell DF, Johnson DK (2007) Porosity and its effect on the digestibility of dilute sulfuric acid pretreated corn stover. J Agric Food Chem 55:2575–2581. doi:10.1021/jf062131a
Jeoh T, Ishizawa CI, Davis MF, Himmel ME, Adney WS, Johnson DK (2007) Cellulase digestibility of pretreated biomass is limited by cellulose accessibility. Biotechnol Bioeng 98:112–122. doi:10.1002/bit.21408
Meunier-Goddik L, Penner MH (1999) Enzyme-catalyzed saccharification of model celluloses in the presence of lignacious residues. J Agric Food Chem 47:346–351. doi:10.1021/jf980407b
Meunier-Goddik L, Bothwell M, Sangseethong K, Piyachomkwan K, Chung Y-C, Thammasouk K, Tanjo D, Penner MH (1999) Physicochemical properties of pretreated poplar feedstocks during simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. Enzyme Microb Technol 24:667–674. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(99)00003-4
Mooney CA, Mansfeld SD, Touhy MG, Saddler JN (1998) The effect of initial pore volume and lignin content on the enzymatic hydrolysis of softwoods. Bioresour Technol 64:113–119. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(97)00181-8
Oksanen T, Buchert J, Viikari L (1997) The role of hemicelluloses in the hornification of bleached kraft pulps. Holzforschung 51:355–360
Ooshima H, Burns DS, Converse AO (1990) Adsorption of cellulase from Trichoderma reesei on cellulose and lignacious residue in wood pretreated by dilute sulfuric acid with explosive decompression. Biotechnol Bioeng 36:446–452. doi:10.1002/bit.260360503
Palonen H, Tjerneld F, Zacchi G, Tenkanen M (2004) Adsorption of Trichoderma reesei CBH I and E.G II and their catalytic domains on steam pretreated softwood and isolated lignin. J Biotechnol 107:65–72. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2003.09.011
Schell D, Farmer J, Newman M, McMillan JD (2003) Dilute-sulfuric acid pretreatment of corn stover in pilot-scale reactor—investigation of yields, kinetics, and enzymatic digestibilities of solids. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 105–108:69–85. doi:10.1385/ABAB:105:1-3:69
Schroeder LR, Gentile VM, Atalla RH (1986) Nondegradative preparation of amorphous cellulose. J Wood Chem Technol 6:1–14. doi:10.1080/02773818608085213
Selig MJ, Viamajala S, Decker SR, Tucker MP, Himmel ME, Vinzant TB (2007) Deposition of lignin droplets produced during dilute acid pretreatment of maize stems retards enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Biotechnol Prog 23:1333–1339. doi:10.1021/bp0702018
Sheehan J, Himmel ME (1999) Enzymes, energy, and the environment: cellulase development in the emerging bioethanol industry. Biotechnol Prog 15:817–827. doi:10.1021/bp990110d
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D, Crocker D (2006) Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. Laboratory Analytical Procedure National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO
Ucar G, Fengel D (1988) Characterization of the acid pretreatment for the enzymatic hydrolysis of wood. Holzforschung 42:141–148
Vlasenko EY, Ding H, Labavitch JM, Shoemaker SP (1997) Enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated rice straw. Bioresour Technol 59:109–119. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(96)00169-1
Yang B, Wyman CE (2004) Effect of xylan and lignin removal by batch and flowthrough pretreatment on the enzymatic digestibility of corn stover cellulose. Biotechnol Bioeng 86:88–95. doi:10.1002/bit.20043
Yang B, Wyman CE (2006) BSA treatment to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose in lignin containing substrates. Biotechnol Bioeng 94:611–617. doi:10.1002/bit.20750
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Stuart Black for preparing the clean fractionation process samples, Dan Schell for providing the pilot-scale vertical reactor samples and the United States Department of Energy, Office of the Biomass Program for funding this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishizawa, C.I., Jeoh, T., Adney, W.S. et al. Can delignification decrease cellulose digestibility in acid pretreated corn stover?. Cellulose 16, 677–686 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-009-9313-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-009-9313-1