Abstract
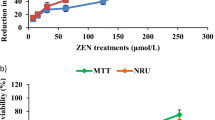
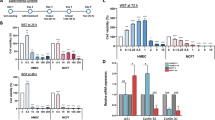
This study aimed to investigate the in vitro damage induced by ochratoxin A (OTA) in BME-UV1 and MDCK epithelial cells. Both cells lines were treated with OTA (0 up to 10 μg/mL), and cell viability (MTT assay), membrane stability (lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assay) and apoptotic cell rate (Tunel assay) were investigated. Further, the effect of the incubation with OTA has been evaluated at DNA level by the determination of DNA integrity, by the quantification of DNA adduct formation (8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG)) and by the assessment of the global DNA methylation status (5-methyl-cytosine (5-mC)). The obtained results showed that after 24 h of OTA treatment, BME-UV1 cell viability was reduced in a dose-dependent way. OTA significantly (P < 0.05) increased LDH release in BME-UV1 cells at all concentrations tested. OTA (1.25 μg/mL) induced 35 % LDH release in MDCK cells (P < 0.05). A significant (P < 0.05) change in percentages of apoptotic BME-UV1 (10 ± 0.86) and MDCK (25 ± 0.88) cells was calculated when the cells were co-incubated with OTA. The level of 8-OHdG adduct formation was significantly (P < 0.05) increased in BME-UV1 cells treated with 1.25 μg/mL of OTA. The results of the present study suggest that a different mechanism of action may occur in these cell lines.

Study results overview




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali R, Mittelstaedt RA, Shaddock JG, DinG W, Bhalli JA, Khan QM, et al. Comparative analysis of micronuclei and DNA damage induced by ochratoxin A in two mammalian cell lines. Mutat Res. 2011;723:58–64.
Anninou N, Chatzaki E, Papachristou F, Pitiakoudis M, Simopoulos C. Mycotoxins’ activity at toxic and sub-toxic concentrations: differential cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of single and combined administration of sterigmatocystin, ochratoxin a and citrinin on the hepatocellular cancer cell line Hep3B. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014;11:1855–72.
Baldi A, Losio MN, Cheli F, Rebucci R, Sangalli L, Fusi E, et al. Evaluation of the protective effects of α-tocopherol and retinol against ochratoxin A cytotoxicity. Br J Nutr. 2004;91:507–12.
Cheli F, Fusi E, Baldi A. Cell-based models for mycotoxin screening and toxicity evaluation: an update. World Mycotoxin J. 2014;7:153–66.
Cheli F, Giromini C, Baldi A. Mycotoxin mechanisms of action and health impact: in vitro or in vivo tests, that is the question. World Mycotoxin J. 2015;8:573–89.
Cheng KC, Cahill DS, Kasai H, Nishimura S, Loeb LA. 8-Hydroxyguanine, an abundant form of oxidative DNA damage, causes G----T and A----C substitutions. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:166–72.
Costa S, Utan A, Cervellati R, Speroni E, Guerra MC. Catechins: natural free-radical scavengers against ochratoxin A-induced cell damage in a pig kidney cell line (LLC-PK1). Food Chem Toxicol. 2007;10:1910–7.
Costa S, Utan A, Speroni E, Cervellati R, Piva G, Prandini A, et al. Oxidative stress induced by ochratoxin A in LLC-PK1 cell line and the chemoprotective effects of carnosic acid. World Mycotoxin J. 2008;1:469–74.
Cui J, Xing L, Li Z, Wu S, Wang J, Liu J, et al. Ochratoxin A induces G2 phase arrest in human gastric epithelium GES-1 cells in vitro. Toxicol Lett. 2010;193:152–8.
European Food Safety Authority. Opinion of the scientific panel on contaminants in the food chain on a request from the commission related to ochratoxin A in food. (Question n° EFSA-Q-2005-154). EFSA J. 2006. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2006.365.
Faucet V, Pfohl-Leszkowicz A, Dai J, Castegnaro M, Manderville RA. Evidence for covalent DNA adduction by ochratoxin A following chronic exposure to rat and subacute exposure to pig. Chem Res Toxicol. 2004;17:1289–96.
Fink-Gremmels J. Mycotoxins in cattle feeds and carry-over to dairy milk: a review. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2008;25:172–80.
Fusi E, Rebucci R, Pecorini C, Rossi L, D’Ambrosio F, Baldi A. Evaluation of the damage induced by ochratoxin A and the protective role of α-tocopherol in cultured bovine mammary epithelial cells. Vet Res Commun. 2008;32:343–5.
Gekle M, Schwerdt G, Freudinger R, Mildenberger S, Wilflingseder D, Pollack V, et al. Ochratoxin A induces JNK activation and apoptosis in MDCK-C7 cells at nanomolar concentrations. J Pharmacol Exp The. 2000;293:837–44.
Hagelberg S, Hult K, Fuchs R. Toxicokinetics of ochratoxin A in several species and its plasma‐binding properties. J Appl Toxicol. 1989;9:91–6.
Kamp HG, Eisenbrand G, Schlatter J, Würth K, Janzowski C, Ochratoxin A. Induction of (oxidative) DNA damage, cytotoxicity and apoptosis in mammalian cell lines and primary cells. Toxicology. 2005;206:413–25.
Kasai H. Analysis of a form of oxidative DNA damage, 8-hydroxy-2 X -deoxyguanosine, as a marker of cellular oxidative stress during carcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 1997;387:147–63.
Klarić MŠ, Želježić D, Rumora L, Peraica M, Pepeljnjak S, Domijan AM. A potential role of calcium in apoptosis and aberrant chromatin forms in porcine kidney PK15 cells induced by individual and combined ochratoxin A and citrinin. Arch Toxicol. 2012;86:97–107.
Kouadio JH, Dano SD, Moukha S, Mobio TA, Creppy EE. Effects of combinations of Fusarium mycotoxins on the inhibition of macromolecular synthesis, malondialdehyde levels, DNA methylation and fragmentation, and viability in Caco-2 cells. Toxicon. 2007;49:306–17.
Liu J, Wang Y, Cui J, Xing L, Shen H, Wu S, et al. Ochratoxin A induces oxidative DNA damage and G1 phase arrest in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro. Toxicol Lett. 2012;211:164–71.
Mally A, Dekant W. DNA adduct formation by ochratoxin A: review of the available evidence. Food Addit Contam. 2005;22 Suppl 1:65–74.
Obrecht-Pflumio S, Dirheimer G. In vitro DNA and dGMP adducts formation caused by ochratoxin A. Chem Biol Interact. 2000;127:29–44.
Palli D, Miraglia M, Saieva C, Masala G, Cava E, Colatosti M, et al. Serum levels of ochratoxin A in healthy adults in Tuscany: correlation with individual characteristics and between repeat measurements. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1999;8:265–9.
Palma N, Cinelli S, Sapora O, Wilson SH, Dogliotti E. Ochratoxin A-induced mutagenesis in mammalian cells is consistent with the production of oxidative stress. Chem Res Toxicol. 2007;20:1031–7.
Pfohl-Leszkowicz A, Manderville RA. An update on direct genotoxicity as a molecular mechanism of ochratoxin a carcinogenicity. Chem Res Toxicol. 2012;25:252–62.
Pfohl-Leszkowicz A, Manderville RA, Ochratoxin A. An overview on toxicity and carcinogenicity in animals and humans. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2007;51:61–99.
Rutigliano L, Valentini L, Martino NA, Pizzi F, Zanghì A, Dell’Aquila ME, et al. Ochratoxin A at low concentrations inhibits in vitro growth of canine umbilical cord matrix mesenchymal stem cells through oxidative chromatin and DNA damage. Reprod Toxicol. 2015;57:121–9.
SAS. User’s Guide: Statistics, Release 9.4 Cary: SAS Inst. Inc; 2013.
Schwerdt G, Freudinger R, Mildenberger S, Silbernagl S, Gekle M. The nephrotoxin ochratoxin A induces apoptosis in cultured human proximal tubule cells. Cell Biol Toxicol. 1999;15:405–15.
Sorrenti V, Di Giacomo C, Acquaviva R, Barbagallo I, Bognanno M, Galvano F. Toxicity of ochratoxin A and its modulation by antioxidants: a review. Toxins. 2013;5:1742–66.
Stojković R, Hult K, Gamulin S, PleStina R. High affinity binding of ochratoxin A to plasma constituents. Biochem Int. 1984;9:33–8.
Yang S, Zhang H, De Saeger S, De Boevre M, Sun F, Zhang S, et al. In vitro and in vivo metabolism of ochratoxin A: a comparative study using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole/time-of-flight hybrid mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;3579–3589.
Zavizion B, Van Duffelen M, Schaeffer W, Politis I. Establishment and characterization of a bovine mammary epithelial cell line with unique properties. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Animal. 1996;32(3):138–48.
Zheng J, Zhang Y, Xu W, Luo Y, Hao J, Shen XL, et al. Zinc protects HepG2 cells against the oxidative damage and DNA damage induced by ochratoxin A. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013;268:123–31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giromini, C., Rebucci, R., Fusi, E. et al. Cytotoxicity, apoptosis, DNA damage and methylation in mammary and kidney epithelial cell lines exposed to ochratoxin A. Cell Biol Toxicol 32, 249–258 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-016-9332-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-016-9332-2