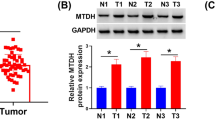
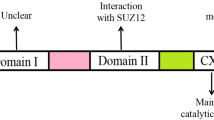
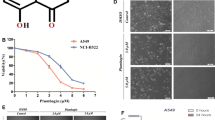
Abstract
Wogonin is a flavonoid compound extracted from Scutellaria baicalensis and is well known as a benzodiazepine receptor ligand with anxiolytic effects. Many recent studies have demonstrated that wogonin modulates angiogenesis, proliferation, invasion, and tumor progress in various cancer tissues. We further explored the mechanism of action of wogonin on cervical cancer cells that contain or lack human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA. Wogonin was cytotoxic to HPV 16 (+) cervical cancer cells, SiHa and CaSki, but not to HPV-negative cells. We demonstrated that wogonin induced apoptosis by suppressing the expressions of the E6 and E7 viral oncogenes in HPV-infected cervical cancer CaSki and SiHa cells. The modulation of p53 and protein retinoblastoma (pRb) were also triggered by the suppression of E6 and E7 expressions. However, p53 was not altered in HPV-negative cervical cancer C33A cells. Moreover, wogonin modulated the mitochondrial membrane potential and the expression of pro- and anti-apoptotic factors such as Bax and Bcl-2. Wogonin also provoked the cleavage of caspase-3, caspase-9, and poly ADP ribose polymerase. After transfection of siRNAs to target E6 and E7, additional restoration of p53 and pRb was not induced, but processing of caspases and PARP was increased compared with wogonin treatment alone. Together, our findings demonstrated that wogonin effectively promotes apoptosis by downregulating E6 and E7 expressions and promoting intrinsic apoptosis in human cervical cancer cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cdk:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase
- FITC:
-
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
- HPV:
-
Human papillomavirus
- HRP:
-
Horseradish-peroxidase
- PARP:
-
Poly ADP ribose polymerase
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- PMS:
-
Phenazine methosulfate
- Rb:
-
Retinoblastoma
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
References
Butz K, Geisen C, Ullmann A, Spitkovsky D, Hoppe-Seyler F. Cellular responses of HPV-positive cancer cells to genotoxic anti-cancer agents: repression of E6/E7-oncogene expression and induction of apoptosis. Int J Cancer. 1996;68:506–13.
Chen S, Gao J, Halicka HD, Traganos F, Darzynkiewicz Z. Down-regulation of androgen-receptor and PSA by phytochemicals. Int J Oncol. 2008;32:405–11.
Choo CK, Ling MT, Suen CK, Chan KW, Kwong YL. Retrovirus-mediated delivery of HPV16 E7 antisense RNA inhibited tumorigenicity of CaSki cells. Gynecol Oncol. 2000;78:293–301.
Crook T, Tidy JA, Vousden KH. Degradation of p53 can be targeted by HPV E6 sequences distinct from those required for p53 binding and trans-activation. Cell. 1991;3:547–56.
DeFilippis RA, Goodwin EC, Wu L, DiMaio D. Endogenous human papillomavirus E6 and E7 proteins differentially regulate proliferation, senescence, and apoptosis in HeLa cervical carcinoma cells. J Virol. 2003;77:1551–63.
Doorbar J. Molecular biology of human papillomavirus infection and cervical cancer. Clin Sci (Lond). 2006;110:525–41.
Fiandalo MV, Kyprianou N. Caspase control: protagonists of cancer cell apoptosis. Exp Oncol. 2012;34:165–75.
Galluzzi L, Morselli E, Kepp O, Tajeddine N, Kroemer G. Targeting p53 to mitochondria for cancer therapy. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:1949–55.
Gao J, Morgan WA, Sanchez-Medina A, Corcoran O. The ethanol extract of Scutellaria baicalensis and the active compounds induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis including upregulation of p53 and Bax in human lung cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011;254:221–8.
Hanning JE, Saini HK, Murray MJ, Sv D, Davis MPA, Barker EM, et al. Lack of correlation between predicted and actual off-target effects of short-interfering RNAs targeting the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncogene. Br J Cancer. 2013;108:450–60.
Harrison LJ, Sia GL, Sim KY. 5,7-dihydroxy-8-methoxyflavone from Tetracera indica. Planta Med. 1994;60:493–4.
Hernandez AM, Colvin ES, Chen YC, Geiss SL, Eller LE, Fueger PT. Upregulation of p21 activates the intrinsic apoptotic pathway in beta cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2013. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00663.
Himeji M, Ohtsuki T, Fukazawa H, Tanaka M, Yazaki S, Ui S, et al. Difference of growth-inhibitory effect of Scutellaria baicalensis-producing flavonoid wogonin among human cancer cells and normal diploid cell. Cancer Lett. 2007;245:269–74.
Hoti N, Ma J, Tabassum S, Wang Y, Wu M. Triphenyl tin benzimidazolethiol, a novel antitumor agent, induces mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in human cervical cancer cells via suppression of HPV-18 encoded E6. J Biochem. 2003;134:521–8.
Huang KF, Zhang GD, Huang YQ, Diao Y. Wogonin induces apoptosis and down-regulates survivin in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells by modulating PI3K-AKT pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2012;12:334–41.
Huang ST, Wang CY, Yang RC, Chu CJ, Wu HT, Pang JH. Wogonin, an active compound in Scutellaria baicalensis, induces apoptosis and reduces telomerase activity in the HL-60 leukemia cells. Phytomedicine. 2010;17:47–54.
Hui KM, Huen MS, Wang HY, Zheng H, Sigel E, Baur R, et al. Anxiolytic effect of wogonin, a benzodiazepine receptor ligand isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. Biochem Pharmacol. 2002;64:1415–24.
Hui KM, Wang XH, Xue H. Interaction of flavones from the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis with the benzodiazepine site. Planta Med. 2000;66:91–3.
Jiang M, Milner J. Selective silencing of viral gene expression in HPV-positive human cervical carcinoma cells treated with siRNA, a primer of RNA interference. Oncogene. 2002;21:6041–8.
Kim SJ, Kim HJ, Kim HR, Lee SH, Cho SD, Choi CS, et al. Antitumor actions of baicalein and wogonin in HT-29 human colorectal cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2012;6:1443–9.
Lee DH, Lee TH, Jung CH, Kim YH. Wogonin induces apoptosis by activating the AMPK and p53 signaling pathways in human glioblastoma cells. Cell Signal. 2012;24:2216–25.
Lee DH, Rhee JG, Lee YJ. Reactive oxygen species up-regulate p53 and Puma; a possible mechanism for apoptosis during combined treatment with TRAIL and wogonin. Br J Pharmacol. 2009;157:1189–202.
Liu C, Li XW, Cui LM, Li LC, Chen LY, Zhang XW. Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by TTF1 from extract of herbal medicine. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:4875–82.
Munger K, Basile JR, Duensing S, Eichten A, Gonzalez SL, Grace M, et al. Biological activities and molecular targets of the human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein. Oncogene. 2001;20:7888–98.
Munger K, Howley PM. Human papillomavirus immortalization and transformation functions. Virus Res. 2002;89:213–28.
Munger K, Scheffner M, Huibregtse JM, Howley PM. Interactions of HPV E6 and E7 oncoproteins with tumour suppressor gene products. Cancer Surv. 1992;12:197–217.
Park BK, Heo MY, Park H, Kim HP. Inhibition of TPA-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression and skin inflammation in mice by wogonin, a plant flavone from Scutellaria radix. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001;425:153–7.
Piao HZ, Jin SA, Chun HS, Lee JC, Kim WK. Neuroprotective effect of wogonin: potential roles of inflammatory cytokines. Arch Pharm Res. 2004;27:930–6.
Polier G, Ding J, Konkimalla BV, Eick D, Ribeiro N, Kohler R, et al. Wogonin and related natural flavones are inhibitors of CDK9 that induce apoptosis in cancer cells by transcriptional suppression of Mcl-1. Cell Death Dis. 2011;2:e182.
Roos WP, Kaina B. DNA damage-induced apoptosis: From specific DNA lesions to the DNA damage response and apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2012. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2012.01.007.
Sankaranarayanan R. Overview of cervical cancer in the developing world. FIGO 26th Annual Report on the Results of Treatment in Gynecological Cancer. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2006;95 Suppl 1:S205–10.
Sartorius U, Schmitz I, Krammer PH. Molecular mechanisms of death-receptor-mediated apoptosis. Chembiochem. 2001;2:20–9.
Scheffner M, Werness BA, Huibregtse JM, Levine AJ, Howley PM. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990;63:1129–36.
Sherr CJ. Cancer cell cycles. Science. 1996;274:1672–7.
Spierings D, McStay G, Saleh M, Bender C, Chipuk J, Maurer U, et al. Connected to death: the (unexpurgated) mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Science. 2005;310:66–7.
Tait SW, Green DR. Mitochondria and cell death: outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:621–32.
Tsai CF, Yeh WL, Huang SM, Tan TW, Lu DY. Wogonin induces reactive oxygen species production and cell apoptosis in human glioma cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:9877–92.
Wang W, Guo QL, You QD, Zhang K, Yang Y, Yu J, et al. The anticancer activities of wogonin in murine sarcoma S180 both in vitro and in vivo. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006;29:1132–7.
Wang X, Gorospe M, Huang Y, Holbrook NJ. p27Kip1 overexpression causes apoptotic death of mammalian cells. Oncogene. 1997;15:2991–7.
Westphal D, Dewson G, Czabotar PE, Kluck RM. Molecular biology of Bax and Bak activation and action. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813:521–31.
Yang L, Wang Q, Li D, Zhou Y, Zheng X, Sun H, et al. Wogonin enhances antitumor activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo through ROS-mediated downregulation of cFLIPL and IAP proteins. Apoptosis. 2013;18:618–26.
Yang L, Zhang HW, Hu R, Yang Y, Qi Q, Lu N, et al. Wogonin induces G1 phase arrest through inhibiting Cdk4 and cyclin D1 concomitant with an elevation in p21Cip1 in human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells. Biochem Cell Biol. 2009;87:933–42.
Yee C, Krishnan-Hewlett I, Baker CC, Schlegel R, Howley PM. Presence and expression of human papillomavirus sequences in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Am J Pathol. 1985;119:361–6.
Yu JS, Kim AK. Wogonin induces apoptosis by activation of ERK and p38 MAPKs signaling pathways and generation of reactive oxygen species in human breast cancer cells. Mol Cells. 2011;31:327–35.
Yun-Choi HS. Flavonoid components in plants of the genus Scutellaria. Korean Soc Pharmacogn. 1992;23:201–10.
zur Hausen H. Immortalization of human cells and their malignant conversion by high risk human papillomavirus genotypes. Semin Cancer Biol. 1999;9:405–11.
zur Hausen H. Papillomaviruses and cancer: from basic studies to clinical application. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:342–50.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant (A120833) from the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea. D.Y. and J.K were partially supported from Priority Research Centres Program (2012-0006686) and the Biodefense program (12-BD-02) from the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Republic of Korea, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
The effect of wogonin on cell cycle in cervical cancer cells. Cells were treated with 160 μM of wogonin for indicated time. CaSki and SiHa cervical cancer cells were fixed with 70 % ethanol and stained with PI. A total of 10,000 events were analyzed by flow cytometry (JPEG 10 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M.S., Bak, Y., Park, Y.S. et al. Wogonin induces apoptosis by suppressing E6 and E7 expressions and activating intrinsic signaling pathways in HPV-16 cervical cancer cells. Cell Biol Toxicol 29, 259–272 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-013-9251-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-013-9251-4