Abstract
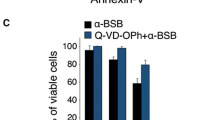
In this report, we have tested the cytotoxicity of two organotin (OT) compounds by flow cytometry on a panel of immortalized cancer cell lines of human and murine origin. Although the OT compounds exhibited varying levels of cytotoxicity, diphenylmethyltin chloride was more toxic than 1,4-bis (diphenylchlorostannyl)p-xylene on all cell lines tested. The OT compounds were found to be highly cytotoxic to lymphoma cell lines with lower toxicity toward the HeLa cervical cancer cell line. In order to discern the mechanism by which cell death was induced, additional experiments were conducted to monitor characteristic changes consistent with apoptosis and/or necrosis. Cell lines treated with the experimental compounds indicated that there was no consistent mode of cell death induction. However, both compounds induced apoptosis in the pro-B lymphocyte cell line, NFS-70. The work presented here also demonstrates that the two OT compounds possess selective cytotoxicity against distinct transformed cell lines.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATCC:
-
American Type Culture Collection
- Bis(Ph2SnCl)Xylene:
-
1,4-Bis (diphenylchlorostannyl)p-xylene
- CC50 :
-
Concentration that results in 50% cytotoxicity
- DBT:
-
Di-n-butyltin chloride
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- DPMT:
-
Diphenylmethyltin chloride
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- FACS:
-
Fluorescence-activated cell sorter
- FITC:
-
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- ID50 :
-
The 50% inhibitory dose
- IL-2:
-
Interleukin-2
- NK:
-
Natural killer
- OT:
-
Organotin
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- PS:
-
Phosphatidylserine
- PVC:
-
Polyvinyl chloride
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RPMI:
-
Roswell Park Memorial Institute
- TBT:
-
Tri-n-butyltin chloride
- TMT:
-
Trimethyltin
- TPT:
-
Triphenyltin
- TPT-CuCl2 :
-
Triphenyltin benzimidazolethiol copper chloride
References
Alzieu C, Sanjuan J, Deltreil P, Borel M. Tin contamination in Arcachon Bay: effects on oyster shell anomalies. Mar Pollut Bull. 1986;17:494.
Baggenstoss J. The fate of organotin compounds in a waste water treatment plant. Faculte de l’Environnement Naturel, Architectural et Construit (ENAC); Section Sciences et Ingenierie de l’Environnement (SIE); Laboratoire de chimie environnementale et ecotoxicologie (CECOTOX); Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland. 2004. http://www.sea.eawag.ch/inhalt/sites/projekte/pdf/Diploma_Thesis_JB_organotin.pdf. Accessed 12 Mar 2010.
Bailey SK, Davies IM. Tributyltin contamination in the Firth of Forth (1975–87). Sci Total Environ. 1988;76:185–92.
Brown AW, Aldridge WN, Street BW, Verschoyle RD. The behavioral and neuropathologic sequelae of intoxication by trimethyltin compounds in the rat. Am J Pathol. 1979;97:59–82.
Champ MA. A review of organotin regulatory strategies, pending actions, related costs and benefits. Sci Total Environ. 2000;258:21–71.
Chojnacki H. Quantum chemical studies on newly synthesized tin anticancer compounds. J Mol Struct. 2003;630:291–5.
Dylag M, Pruchnik H, Pruchnik F, Majkowska-Skrobek G, Ulaszewski S. Antifungal activity of organotin compounds with functionalized carboxylates evaluated by the microdilution bioassay in vitro. Med Mycol. 2010;48:373–83.
Elie BT, Levine C, Ubarretxena-Belandia I, Varela-Ramírez A, Aguilera RJ, Ovalle R, et al. Water-soluble phosphane–gold(I) complexes. Applications as recyclable catalysts in a three-component coupling reaction and as antimicrobial and anticancer agents. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2009;23:3421–30.
Fadok VA, Voelker DR, Campbell PA, Cohen JJ, Bratton DL, Henson PM. Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the surface of apoptotic lymphocytes triggers specific recognition and removal by macrophages. J Immunol. 1992;148:2207–16.
Feldman RG, White RF, Ikechukwu EI. Trimethyltin encephalopathy. Arch Neurol. 1993;50:1320–4.
Fent K. Ecotoxicology of organotin compounds. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1996;26:1–117.
Fortemps E, Amand G, Bomboir A, Lauwerys R, Laterre EC. Trimethyltin poisoning. Report of two cases. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1978;41:1–6.
Gant VA, Wren MW, Rollins MS, Jeanes A, Hickok SS, Hall TJ. Three novel highly charged copper-based biocides: safety and efficacy against healthcare-associated organisms. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007;60:294–9.
Garg A, Bhosle NB. Butyltin compounds in the oyster, Saccostrea cucculata, from the west coast of India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2005;75:982–8.
Gennari A, Viviani B, Galli CL, Marinovich M, Pieters R, Corsini E. Organotins induce apoptosis by disturbance of [Ca2+]i and mitochondrial activity, causing oxidative stress and activation of caspases in rat thymocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2000;169:185–90.
Gielen M. Organotin compounds and their therapeutic potential: a report from the organometallic. Appl Organomet Chem. 2002;16:481–94.
Gielen M, Bouhdid A, Willem R, Bregadze VI, Ermanson LV, Tiekink ERT. X-ray structure of the dimeric bis[(1,7-dicarba-close-dodecaborane-1-carboxylato)-di-n-butyltin] oxide. J Organomet Chem. 1995;501:277–81.
Gomez FD, Apodaca P, Hollowa LN, Pannell KH, Whalen MM. Effect of a series of triorganotins on the immune function of human natural killer cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2007;23:18–24.
Gómez-Ruiz S, Kaluderović GN, Prashar S, Hey-Hawkins E, Erić A, Zizak Z, et al. Study of the cytotoxic activity of di and triphenyltin(IV) carboxylate complexes. J Inorg Biochem. 2008;102:2087–96.
Gui-bin J, Qun-fang Z, Bin H. Tin compounds and major trace metal elements in organotin-poisoned patient’s urine and blood measured by gas chromatography-flame photometric detector and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2000;65:277–84.
Gunasekar P, Li L, Prabhakaran K, Eybl V, Borowitz JL, Isom GE. Mechanisms of the apoptotic and necrotic actions of trimethyltin in cerebellar granule cells. Toxicol Sci. 2001;64:83–9.
Hadjikakou SK, Hadjiliadis N. Antiproliferative and anti-tumor activity of organotin compounds. Coord Chem Rev. 2009;253:235–49.
Hori T, Uchiyama T, Tsudo M, Umadome H, Ohno H, Fukuhara S, et al. Establishment of an interleukin 2-dependent human T cell line from a patient with T cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia who is not infected with human T cell leukemia/lymphoma virus. Blood. 1987;70:1069–72.
Hoti N, Zhu DE, Song Z, Wu Z, Tabassum S, Wu M. p53-dependent apoptotic mechanism of a new designer bimetallic compound tri-phenyl tin benzimidazolethiol copper chloride (TPT-CuCl2): in vivo studies in Wistar rats as well as in vitro studies in human cervical cancer cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;311:22–33.
Ito E, Yip KW, Katz D, Fonseca SB, Hedley DW, Chow S, et al. Potential use of cetrimonium bromide as an apoptosis-promoting anticancer agent for head and neck cancer. Mol Pharmacol. 2009;76:969–83.
Jamieson ER, Lippard SJ. Structure, recognition, and processing of cisplatin–DNA adducts. Chem Rev. 1999;99:2467–98.
Jones KH, Senft JA. An improved method to determine cell viability by simultaneous staining with fluorescein diacetate–propidium iodide. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985;33:77–9.
Kaluderovic GN, Kommera H, Hey-Hawkins E, Paschke R, Gomez-Ruiz S. Synthesis and biological applications of ionic triphenyltin(IV) chloride carboxylate complexes with exceptionally high cytotoxicity. Metallomics. 2010;2:419–28.
Kapoor RN, Apodaca P, Montes M, Gomez FD, Pannell KH. Mixed aryl–alkyl organotin compounds, Ar n MeSnCl3-n (Ar = RC6H4, R = H, ethyl, i-propyl, t-butyl; n-hexyl, n-octyl) and the effect of R upon antibiotic activity. Appl Organomet Chem. 2005;19:518–22.
Kim DK, Kim HT, Cho YB, Tai JH, Ahn JS, Kim TS, et al. Antitumor activity of cis-malonato[(4R, 5R)-4, 5-bis(aminomethyl)-2- isopropyl-1, 3-dioxolane]platinum(II), a new platinum analogue, as an anticancer agent. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1995;35:441–5.
Levinson C. Vinyl chloride: a case study of the new occupational health hazard. Geneva: International Chemical Federation; 1974. p. 15.
Merkord J, Jonas L, Weber H, Kroning G, Nizze H, Hennighausen G. Acute interstitial pancreatitis in rats induced by dibutyltin dichloride (DBTC): pathogenesis and natural course of lesions. Pancreas. 1997;15:392–401.
Miyoshi N, Oubrahim H, Chock PB, Stadtman ER. Age-dependent cell death and the role of ATP in hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis and necrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:1727–31.
Moser VC. Rat strain- and gender-related differences in neurobehavioral screening: acute trimethyltin neurotoxicity. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1996;47:567–86.
Narayanan VL, Nasr M, Paull K. Computer assisted structure–antileukemic activity correlations of organotin compounds and initial exploration of their potential anti-HIV activity. In: Gielen M, editor. Tin-based anti-tumor drugs. New York: Springer; 1990. p. 200–17.
Ngan VK, Bellman K, Hill BT, Wilson L, Jordan MA. Mechanism of mitotic block and inhibition of cell proliferation by the semisynthetic Vinca alkaloids vinorelbine and its newer derivative vinflunine. Mol Pharmacol. 2001;60:225–32.
Park DM, Rich JN. Biology of glioma cancer stem cells. Mol Cells. 2009;28:7–12.
Pieters RH, Bol M, Seinen W, Penninks AH. Cellular and molecular aspects of organotin-induced thymus atrophy. Hum Exp Toxicol. 1994;13:876–9.
Piver WT. Organotin compounds: industrial applications and biological investigation. Environ Health Perspect. 1973;4:61–79.
Ross WD, Emmett EA, Steiner J, Tureen R. Neurotoxic effects of occupational exposure to organotins. Am J Psychiatry. 1981;138:1092–5.
Sen A, Chaudhuri TK. Synthesis and evaluation of dimethyl tin 4-cyclohexyl thiosemicarbazone as a novel antitumor agent. Exp Oncol. 2009;31:22–6.
Shaik N, Martinez A, Augustin I, Giovinazzo H, Varela-Ramirez A, Sanau M, et al. Synthesis of apoptosis-inducing iminophosphorane organogold(III) complexes and study of their interactions with biomolecular targets. Inorg Chem. 2009;48:1577–87.
Tamm I, Kikuchi T, Murphy JS. Serum enhances the cycling and survival of HeLa cells treated with 5, 6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1982;79:2569–73.
Thodupunoori SK, Alamudun IA, Cervantes-Lee F, Gomez FD G, Carrasco YP, Pannell KH. Synthesis, structures and preliminary biological screening of bis(diphenyl)chlorotin complexes and adducts: Ph2ClSnCH2RCH2SnClPh2, R = p-C6H4, CH2CH2. J Organomet Chem. 2006;691:1790–6.
Tian L, Sun Y, Li H, Zheng X, Cheng Y, Liu X, et al. Synthesis, characterization and biological activity of triorganotin 2-phenyl-1, 2, 3-triazole-4-carboxylates. J Inorg Biochem. 2005;99:1646–52.
Tomiyama K, Yamaguchi A, Kuriyama T, Arakawa Y. Analysis of mechanisms of cell death of T-lymphocytes induced by organotin agents. J Immunotoxicol. 2009;6:184–93.
Whalen MM, Loganathan BG, Kannan K. Immunotoxicity of environmentally relevant concentrations of butyltins on human natural killer cells in vitro. Environ Res. 1999;81:108–16.
Yip KW, Mao X, Au PY, Hedley DW, Chow S, Dalili S, et al. Benzethonium chloride: a novel anticancer agent identified by using a cell-based small-molecule screen. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:5557–69.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. S. Nagy for the generous gift of the Kit 225 cell line and to the staff of the UTEP’s Cell Culture and High Throughput Screening Core Facility for services and facilities provided. This work was supported by grant 5G12RR008124 to the Border Biomedical Research Center, granted to the University of Texas at El Paso from the National Center for Research Resources of the NIH. Y.P.C. was supported by the NIH-MARC*USTAR (5T34GM008048-25) and RISE (R25 GM069621-07) programs. Also, the authors thank Drs. Julia Bader for statistic analysis and Carolina Lema for critically reading the manuscript and help with organizing the bibliography.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 56 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varela-Ramirez, A., Costanzo, M., Carrasco, Y.P. et al. Cytotoxic effects of two organotin compounds and their mode of inflicting cell death on four mammalian cancer cells. Cell Biol Toxicol 27, 159–168 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-010-9178-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-010-9178-y