Abstract
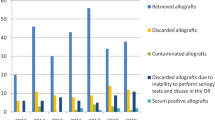
We analyzed the incidence and predisposing factors for overall discard rate after retrieval of 295 femoral head allografts. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the quality system of institutional bone banking and to ensure that we can provide high standard allografts with low infection rate. Audit of bone banking was conducted on 295 donors and 180 recipients. Of the 295 donated femoral heads 77 were discarded, giving an overall discard rate of 26.1 %. At retrieval, 37 allografts were positive, giving an overall contamination rate of 12.54 %. The organism most commonly identified was Staphylococcus species. Seven (2.37 %) of the 295 allografts failed the blood screening tests. Twelve allografts (4.06 %) were discarded because of suspected damage of the packaging or disuse during surgery. Due to donor death or inability to perform serology retests, 21 (7.11 %) allografts were discarded. In the postoperative survey an infection rate of 2.22 % was found. After 7 years of bone banking, our results show that overall discard rate and allograft related infection rate are in accordance with the international standards. The leading cause of allograft discarding was bacterial contamination influenced by the surgical team. We suggest stringent aseptic allograft handling during harvesting and thawing within highly concentrated antibiotic solution to reduce a possibility of its contamination.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Association of Tissue Banks (1992) Technical manual for tissue banking. AATB
Barnhart B, Allan DG, Milbrandt JC, Khardori N, Hall A, Barenfanger J (2009). Intra-operative culturing of donor allograft bone: a lack of clinical utility. U Pa Orthop J. http://upoj.org/site/files/v19/v19_10.pdf
Chiu CK, Lau PY et al (2004) Microbial contamination of femoral head allografts. Hong Kong Med J 10(6):401–405
Deijkers RLM, Bloem RM, Petit PLC, Brand R, Vehmeyer SBW, Veen MR (1997) Contamination of bone allografts: analysis of incidence and predisposing factors. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 79(1):161–166
EAMST, EATB (1997) Common standards for musculo-skeletal tissue banking. European Association for Musculo-skeletal Transplantation and European Association of Tissue Banks, Vienna
Hou CH, Yang RS (2005) Hospital-based allogenic bone bank—10-year experience. J Hosp Infect 59:41–45
Ibrahim T, Aswad MG, Dias JJ, Brown AR, Esler CN (2011) Long-term outcome of total hip replacement in patients with or without femoral head contamination. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 19(2):174–176
Ivory JP, Thomas IH (1993) Audit of a bone bank. J Bone Joint Surg Br 75:355–357
James LA, Ibrahim T, Esler CN (2004) Microbiological culture results for the femoral head. Are they important to the donor? J Bone Joint Surg Br 86(6):797–800
Journeaux SF, Johnson N, Bryce SL, Friedman SJ, Sommerville SM, Morgan DA (1999) Bacterial contamination rates during bone allograft retrieval. J Arthroplast 14(6):677–681
Kappe T, Cakir B, Mattes T, Reichel H, Flören M (2010) Infections after bone allograft surgery: a prospective study by a hospital bone bank using frozen femoral heads from living donors. Cell Tissue Bank 11:253–259
Meermans G, Roos J, Hofkens L, Cheyns P (2007) Bone banking in a community hospital. Acta Orthop Belg 73:754–759
Nielsen HT, Larsen S, Andersen M, Ovesen O (2001) Bone bank service in Odense, Denmark. Audit first ten years with bone banking at the Department of Orthopaedics, Odense University Hospital. Cell Tissue Bank 2:179–183
Phuong DT, Park KS, Hwang SY, Lee DH, Yoon TR (2013) Microbiological culture findings of the femoral heads as a prognostic factor in the total hip replacement surgery. Clin Orthop Surg 5(2):105–109. doi:10.4055/cios.2013.5.2.105
Pruss A, Seibold M, Benedix F et al (2003) Validation of the ‘‘Marburg bone bank system’’ for thermodisinfection of allogenic femoral head transplants using selected bacteria, fungi, and spores. Biologicals 31(4):287–294
Saies AD, Davidson DC (1990) Femoral head allograft bone banking. Aust N Z J Surg 60:267–270
Sommerville SM, Johnson N, Bryce SL et al (2000) Contamination of banked femoral head allograft: incidence, bacteriology and donor follow up. Aust N Z J Surg 70(7):480–484
Sutherland AG, Raafat A, Yates P et al (1997) Infection associated with the use of allograft bone from the North East Scotland Bone Bank. J Hosp Infect 35:215–222
The Canadian Council for Donation and Transplantation (CCDT) (2006) Evaluation of surgical bone banking and utilization in Canada. http://www.ccdt.ca. September 2006
Tomford WW, Thongphuasuk J, Mankin HJ, Ferraro MJ (1990) Frozen musculoskeletal allografts: a study of the clinical incidence and causes of infection associated with their use. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 72(8):1137–1143
van de Pol GJ, Sturm PD, van Loon CJ, Verhagen C, Schreurs BW (2007) Microbiological cultures of allografts of the femoral head just before transplantation. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89(9):1225–1228
Vehmeyer SBW, Slooff RMA, Bloem RM, Petit PLC (2002) Bacterial contamination of femoral head allografts from living donors. Acta Orthop Scand 73(2):165–170
Winter JM, Cowie AI, Wood DJ, Zheng MH (2005) Musculoskeletal tissue banking in Western Australia: review of the first ten years. ANZ J Surg 75(8):665–671
Zwitser E, van Royen B (2011) Quality control in hospital bone banking. In: Wide Spectra of Quality Control, (Ed Akyar I) In Tech 14: 259–260. http://www.intechopen.com/books/wide-spectra-of-quality-control/quality-control-in-hospital-bone-banking
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stepanovic, Z.L., Ristic, B.M. The effectiveness of bone banking in Central Serbia: audit of the first seven years. Cell Tissue Bank 15, 567–572 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-014-9426-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-014-9426-0