Abstract
Objective
As some articles have highlighted the role of microRNA-92a (miR-92a) in myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury (MI/RI), this article aimed to investigate the effect of miR-92a on Sevoflurane (Sevo)-treated MI/RI via regulation of Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4).
Methods
An MI/RI rat model was established by ligating the left anterior descending coronary artery. The cardiac function, pathological changes of myocardial tissues, inflammatory response, oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in MI/RI rats were determined. KLF4 and miR-92a expression was detected in the myocardial tissue of rats, and the target relationship between miR-92a and KLF4 was confirmed.
Results
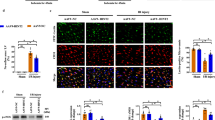
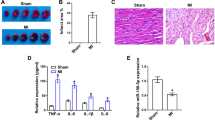
Sevo treatment alleviated myocardial damage, inflammatory response, oxidative stress response, and cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and improved cardiac function in MI/RI rats. miR-92a increased and KLF4 decreased in the myocardial tissue of MI/RI rats. KLF4 was targeted by miR-92a. Downregulation of miR-92a or upregulation of KLF4 further enhanced the effect of Sevo treatment on MI/RI.
Conclusion
This study suggests that depletion of miR-92a promotes upregulation of KLF4 to improve cardiac function, reduce cardiomyocyte apoptosis and further enhance the role of Sevo treatment in alleviating MI/RI.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Yu SY, et al. Knockdown of lncRNA AK139328 alleviates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury in diabetic mice via modulating miR-204-3p and inhibiting autophagy. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(10):4886–98.
Zou L, et al. Long noncoding RNA-MEG3 contributes to myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through suppression of miR-7-5p expression. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(8). https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20190210.
Zhang W, Li Y, Wang P. Long non-coding RNA-ROR aggravates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2018;51(6):e6555.
Ma N, et al. Trimetazidine protects against cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury via effects on cardiac miRNA21 expression, Akt and the Bcl2/Bax pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(5):4216–22.
Chen JG, et al. Inhibiting miR-155 protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via targeted regulation of HIF-1alpha in rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019;22(9):1050–8.
Xie XJ, et al. Suppression of microRNA-135b-5p protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in mice during sevoflurane anesthesia. Biosci Rep. 2017;37(3). https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20170186.
Yu H, et al. MiR-92a modulates proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion of osteosarcoma cell lines by targeting Dickkopf-related protein 3. Biosci Rep. 2019;39:4.
Qiao SG, et al. Sevoflurane postconditioning protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by restoring autophagic flux via an NO-dependent mechanism. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019;40(1):35–45.
Huang HT, et al. MiR-92a regulates endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) by targeting GDF11 via activate SMAD2/3/FAK/Akt/eNOS pathway. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(20):563.
Cheng M, An S, Li J. CDKN2B-AS may indirectly regulate coronary artery disease-associated genes via targeting miR-92a. Gene. 2017;629:101–7.
Ye Y, et al. The role of microRNA in modulating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Physiol Genomics. 2011;43(10):534–42.
Zhang B, et al. MicroRNA-92a inhibition attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced myocardiocyte apoptosis by targeting Smad7. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e100298.
Liu H, et al. Inhibition of MiR-92a may protect endothelial cells after acute myocardial infarction in rats: role of KLF2/4. Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:2451–62.
Sakaizawa T, et al. Potential role of ASC, a Proapoptotic protein, for determining the Cisplatin susceptibility of lung Cancer cells. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2018;244(2):133–44.
Zhang Y, et al. Kruppel-like factor 4 transcriptionally regulates TGF-beta1 and contributes to cardiac myofibroblast differentiation. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e63424.
Yoshida T, et al. Kruppel-like factor 4 protein regulates isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy by modulating myocardin expression and activity. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(38):26107–18.
Ferdinandy P, Schulz R, Baxter GF. Interaction of cardiovascular risk factors with myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury, preconditioning, and postconditioning. Pharmacol Rev. 2007;59(4):418–58.
Qin X, et al. Exosomal miR-196a derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts confers cisplatin resistance in head and neck cancer through targeting CDKN1B and ING5. Genome Biol. 2019;20(1):12.
Qi Z, et al. Role of microRNA-145 in protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice by regulating expression of GZMK with the treatment of sevoflurane. J Cell Physiol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28323.
Tian ZQ, Jiang H, Lu ZB. MiR-320 regulates cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by ischemia-reperfusion injury by targeting AKIP1. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018;23:41.
Yu P, et al. Protective effect of Sevoflurane Postconditioning against cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury via ameliorating mitochondrial impairment, oxidative stress and rescuing Autophagic clearance. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0134666.
Hinkel R, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-92a protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in a large-animal model. Circulation. 2013;128(10):1066–75.
Liao X, et al. Distinct roles of resident and nonresident macrophages in nonischemic cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(20):E4661–9.
Jiang C, et al. The effects and mechanism of miR-92a and miR-126 on myocardial apoptosis in mouse ischemia-reperfusion model. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;70(3):1901–6.
Zhang Y, et al. Circulating endothelial microparticles and miR-92a in acute myocardial infarction. Biosci Rep. 2017;37(2). https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20170047.
Wang W, et al. Circulating microRNA-92a level predicts acute coronary syndrome in diabetic patients with coronary heart disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2019;18(1):22.
Zhu Z, et al. Kruppel-like factor 4 inhibits pancreatic Cancer epithelial-to-Mesenchymal transition and metastasis by Down-regulating Caveolin-1 expression. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(1):238–52.
Fan L, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced cell injury in ATDC5 cells via miR-92a/KLF4 mediation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;118:109180.
Liu PJ, et al. MiRNA-92a promotes cell proliferation and invasion through binding to KLF4 in glioma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(15):6612–20.
Wu J, et al. Sevoflurane postconditioning protects the myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury via activation of the JAK2-STAT3 pathway. PeerJ. 2017;5:e3196.
Cao J, et al. Sevoflurane post-conditioning reduces rat myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury through an increase in NOS and a decrease in phopshorylated NHE1 levels. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36(6):1529–37.
Dong J, et al. Effects of Sevoflurane pretreatment on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through the Akt/hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1alpha)/vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling pathway. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:3100–7.
Yu R, et al. Kruppel-like factor 4 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell growth and aggressiveness by stimulating transforming growth factor-beta1-meidated ERK/JNK/NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Tumour Biol. 2017;39(6):1010428317705574.
Wang L, et al. Role of Kruppel-like factor 4 in regulating inhibitor of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 in the progression of gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(5):6865–72.
Acknowledgements
We would like to give our sincere gratitude to the reviewers for their constructive comments.
Funding
This work was supported by Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine budget project (18LK055); the Special Project of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine in general hospital of Shanghai Health Committee (Grant Number ZHYY-ZXYJHZX-202023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Rong Lu and Guoliang Yan designed the study; Qianfu Wu, Fei He, Jiali Zheng and Hongjing Zhang conducted experimental studies; Haihui Wang, Chang Cheng and Panwei Hu performed data analysis; Qianfu Wu and Haihui Wang edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Statement
All animal experiments were in compliance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health. The protocol was approved by the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of School of Basic Medical Sciences, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Consent for Publication
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data and photographs.
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Qianfu Wu and Haihui Wang are co-first authors.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 14.3 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Q., Wang, H., He, F. et al. Depletion of microRNA-92a Enhances the Role of Sevoflurane Treatment in Reducing Myocardial Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury by Upregulating KLF4. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 37, 1053–1064 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-021-07303-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-021-07303-x