Abstract
Background
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) is a serine-threonine protein kinase, discovered as a regulator of glycogen synthase. GSK-3 may regulate the expression of SERCA-2a potentially affecting myocardial contractility. It is known to phosphorylate and inhibit IRS-1, thus disrupting insulin signalling. This study aimed to determine whether myocardial GSK-3 protein and its substrate proteins are dysregulated in obesity and insulin resistance, and whether chronic GSK-3 inhibition can prevent or reverse this.
Methods
Weight matched male Wistar rats were rendered obese by hyperphagia using a special diet (DIO) for 16 weeks and compared to chow fed controls. Half of each group was treated with the GSK-3 inhibitor CHIR118637 (30 mg/kg/day) from week 12 to16 of the diet period. Biometric and biochemical parameters were measured and protein expression determined by Western blotting and specific antibodies. Ca2+ATPase activity was determined spectrophotometrically. Cardiomyocytes were prepared by collagenase perfusion and insulin stimulated 2-deoxy-glucose uptake determined.
Results
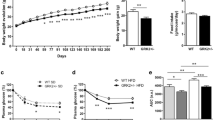
DIO rats were significantly heavier than controls, associated with increased intra-peritoneal fat and insulin resistance. GSK-3 inhibition did not affect weight but improved insulin resistance, also on cellular level. It had no effect on GSK-3 expression but elevated its phospho/total ratio and elevated IRS-2 expression. Obesity lowered SERCA-2a expression and activity while GSK-3 inhibition alleviated this. The phospho/total ratio of phospholamban underscored inhibition of SERCA-2a in obesity. In addition, signs of myocardial hypertrophy were observed in treated control rats.
Conclusion
GSK-3 inhibition could not reverse all the detrimental effects of obesity but may be harmful in normal rat hearts. It regulates IRS-2, SERCA-2a and phospholamban expression but not IRS-1.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hemmings BA, Yellowlees D, Kernohan JC, Cohen P. Purification of glycogen synthase kinase 3 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Co-purification with the activation factor(FA) of the (Mg-ATP) dependent protein phosphatase. Eur J Biochem. 1981;119:443–51.
Embi N, Rylatt DB, Cohen P. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Separation from cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase and phosphorylase kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107:519–27.
Huisamen B, Lochner A. GSK-3 protein and the heart: friend or foe? SAHeart. 2010;7:48–57.
Woodgett JR. Judging a protein by more than its name: GSK-3. Sci STKE. 2001;2001(100):re12.
Ciaraldi TP, Nikoulina SE, Bandukwala RA, Carter L, Henry RR. Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 alpha in insulin action in cultured human skeletal muscle cells. Endocrinology. 2007;148:4393–9.
Woodgett JR. Molecular cloning and expression of glycogen synthase kinase-3/factor A. EMBO J. 1990;9:2431–8.
Doble BW, Woodgett JR. GSK-3: tricks of the trade for a multi-tasking kinase. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:1175–86.
Parker PJ, Caudwell FB, Cohen P. Glycogen synthase from rabbit skeletal muscle; effect of insulin on the state of phosphorylation of the seven phosphoserine residues in vivo. Eur J Biochem. 1983;130:227–34.
Mora A, Sakamoto K, McManus EJ, Alessi DR. Role of the PDK-1-PKB-GSK-3 pathway in regulating glycogen synthase and glucose uptake in the heart. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:3632–8.
Eldar-Finkelman H, Argast GM, Foord O, Fischer EH, Krebs EG. Expression and characterization of glycogen synthase kinase-3 mutants and their effect on glycogen synthase activity in intact cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93(19):10228–33.
Michael A, Haq S, Chen X, Hsich E, Cui L, Walters B, et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta regulates growth, calcium homeostasis, and diastolic function in the heart. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:21383–93.
Omar MA, Wang L, Clanachan AS. Cardioprotection by GSK-3 inhibition: role of enhanced glycogen synthesis and attenuation of calcium overload. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;86(3):478–86.
Takeda N. Cardiac disturbances in diabetes mellitus. Pathophysiology. 2010;17:83–8.
Asahi M, Nakayama H, Tada M, Otsu K. Regulation of sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+ adenosine triphosphatase by phospholamban and sarcolipin: implication for cardiac hypertrophy and failure. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2003;13:152–7.
Huisamen B, Dietrich D, Blackhurst D, Flepisi B, Lochner A. Early cardiovascular changes occurring in diet-induced obese, insulin resistant rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012;368:37–45.
Huisamen B, Pêrel SJC, Friedrich SO, Salie R, Strijdom H, Lochner A. AngII receptor antagonism improves nitric oxide production, eNOS and PKB expression in hearts from a rat model of insulin resistance. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;349:21–31.
Huisamen B, Genis A, Lochner A. Pre-treatment with a DPP-4 inhibitor is infarct sparing in hearts from obese, pre-diabetic rats. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2011;25:13–20.
Henriksen EJ, Dokken BB. Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Curr Drug Targets. 2006;7:1435–41.
Cline GW, Johnson K, Regittnig W, Perret P, Tozzo E, Xiao L, et al. Effects of a novel glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor on insulin-stimulated glucose metabolism in Zucker diabetic fatty (fa/fa) rats. Diabetes. 2002;51:2903–10.
Meijer L, Flajolet M, Greengard P. Pharmacological inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase 3. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004;25:471–80.
Wagman AS, Johnson KW, Bussiere DE. Discovery and development of GSK3 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10:1105–37.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54.
Feher JJ, Davis MD. Isolation of rat cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum with improved Ca2+ uptake and ryanodine binding. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1991;23:249–58.
Bers DM. Isolation and characterization of cardiac sarcolemma. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1979;555:131–6.
Fiske CH, Subbarow Y. The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J Biol Chem. 1925;66:375–400.
Donthi R, Huisamen B, Lochner A. The effect of vanadate and insulin on glucose transport in isolated adult rat cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2000;14:463–70.
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951;193:265–75.
Suarez J, Scott B, Dillmann WH. Conditional increase in SERCA2a protein is able to reverse contractile dysfunction and abnormal calcium flux in established diabetic cardiomyopathy. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008;295:R1439–45.
Eldar-Finkelman H, Licht-Murava A, Pietrokovski S, Eisenstein M. Substrate competitive GSK-3 inhibitors—strategy and implications. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1804;2010:598–603.
Martinez A. Preclinical efficacy on GSK-3 inhibitors: towards a future generation of powerful drugs. Med Res Rev. 2008;28:773–96.
Lee S, Yang WK, Song JH, Ra YM, Jeong JH, Choe W, et al. Anti-obesity effects of 3-hydroxychromone derivative, a novel small-molecule inhibitor of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013;85:965–76.
Abel ED, Litwin SE, Sweeney G. Cardiac remodeling in obesity. Physiol Rev. 2008;88:389–419.
Chess DJ, Stanley WC. Role of diet and fuel overabundance in the development and progression of heart failure. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;79:269–78.
Wolk R. Arrhythmogenic mechanisms in left ventricular hypertrophy. Europace. 2000;2:216–23.
Haq S, Choukroun G, Kang ZB, Ranu H, Matsui T, Rosenzweig A, et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta is a negative regulator of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Cell Biol. 2000;151:117–30.
Roach PJ. Control of glycogen synthase by hierarchal protein phosphorylation. FASEB J. 1990;4:2961–8.
Zhang W, DePaoli-Roach AA, Roach PJ. Mechanisms of multisite phosphorylation and inactivation of rabbit muscle glycogen synthase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993;304:219–25.
Shulman GI, Rothman DL, Jue T, Stein P, DeFronzo RA, Shulman RG. Quantitation of muscle glycogen synthesis in normal subjects and subjects with non-insulin-dependent diabetes by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:223–8.
Cline GW, Rothman DL, Magnusson I, Katz LD, Shulman GI. 13C-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies of hepatic glucose metabolism in normal subjects and subjects with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1994;94:2369–76.
Ring DB, Johnson KW, Henriksen EJ, Nuss JM, Goff D, Kinnick TR, et al. Selective glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitors potentiate insulin activation of glucose transport and utilization in vitro and in vivo. Diabetes. 2003;52:588–95.
Coghlan MP, Culbert AA, Cross DA, Corcoran SL, Yates JW, Pearce NJ, et al. Selective small molecule inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 modulate glycogen metabolism and gene transcription. Chem Biol. 2000;7:793–803.
Nikoulina SE, Ciaraldi TP, Mudaliar S, Carter L, Johnson K, Henry RR. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3 improves insulin action and glucose metabolism in human skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 2002;51:2190–8.
Gao HK, Yin Z, Zhou N, Feng XY, Gao F, Wang HC. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibition protects the heart from acute ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibition of inflammation and apoptosis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2008;52:286–92.
MacAulay K, Blair AS, Hajduch E, Terashima T, Baba O, Sutherland C, et al. Constitutive activation of GSK3 down-regulates glycogen synthase abundance and glycogen deposition in rat skeletal muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:9509–18.
Dihlmann S, Kloor M, Fallsehr C, Von Knebel DM. Regulation of Akt1 expression by beta-catenin/Tcf/Lef signalling in colorectal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:1503–12.
Henriksen EJ, Teachey MK. Short-term in vitro inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3 potentiates insulin signalling in type I skeletal muscle of Zucker diabetic Fatty rats. Metabolism. 2007;56:931–8.
Wade A. GSK-3 inhibitors and insulin receptor signalling in health, disease and therapeutics. Front Biosci. 2009;14:1558–70.
Ciaraldi TP, Carter L, Mudaliar S, Henry RR. GSK-3beta and control of glucose metabolism and insulin action in human skeletal muscle. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;315:153–8.
Araki E, Lipes MA, Patti ME, Brüning JC, Haag 3rd B, Johnson RS, et al. Alternative pathway of insulin signalling in mice with targeted disruption of the IRS-1 gene. Nature. 1994;372:186–90.
Vittorini S, Storti S, Parri MS, Cerillo AG, Clerico A. SERCA2a, phospholamban, sarcolipin, and ryanodine receptors gene expression in children with congenital heart defects. Mol Med. 2007;13:105–11.
James P, Inui M, Tada M, Chiesi M, Carafoli E. Nature and site of phospholamban regulation of the Ca2+ pump of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1989;342:90–2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flepisi, T.B., Lochner, A. & Huisamen, B. The Consequences of Long-Term Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Inhibition on Normal and Insulin Resistant Rat Hearts. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 27, 381–392 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-013-6467-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-013-6467-8