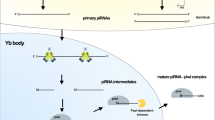
Abstract
With the length of about 26–31 nt, PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA) is a small non-coding RNA (ncRNA) that interacts with PIWI proteins to form the piRNA silencing complex (piRISC). PIWI is a subfamily of Argonaute, and piRNA must bind to PIWI to exert its regulatory role. Current studies indicated that piRNA and PIWI are significantly abnormally expressed in gastric, breast, kidney, colon, and lung cancers, and are involved in the initiation, progression, and metastasis of cancers, which may be the potential diagnostic tools, prognostic markers, and therapeutic targets for cancers. By reviewing piRNA recent studies, this research summarized the mechanism of piRNA generation and the functions of piRNA/PIWI in gastric, breast, kidney, colon, and lung cancers, providing a reference value for further piRNA research.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferreira, H. J., & Esteller, M. (2018). Non-coding RNAs, epigenetics, and cancer: tying it all together. Cancer Metastasis Reviews, 37(1), 55–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-017-9715-8.
Xiao, Y., & Ke, A. (2016). PIWI takes a giant step. Cell, 167(2), 310–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.09.043.
Rodriguez-Leal, D., Castillo-Cobian, A., Rodriguez-Arevalo, I., & Vielle-Calzada, J. P. (2016). A primary sequence analysis of the ARGONAUTE protein family in plants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 1347. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01347.
Russell, S. J., & LaMarre, J. (2018). Transposons and the PIWI pathway: genome defense in gametes and embryos. Reproduction, 156(4), R111–r124. https://doi.org/10.1530/rep-18-0218.
Theron, E., Maupetit-Mehouas, S., Pouchin, P., Baudet, L., Brasset, E., & Vaury, C. (2018). The interplay between the Argonaute proteins Piwi and Aub within Drosophila germarium is critical for oogenesis, piRNA biogenesis and TE silencing. Nucleic Acids Research, 46(19), 10052–10065. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky695.
Weng, W., Li, H., & Goel, A. (2019). Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) and cancer: emerging biological concepts and potential clinical implications. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta. Reviews on Cancer, 1871(1), 160–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2018.12.005.
Chalbatani, G. M., Dana, H., Memari, F., Gharagozlou, E., Ashjaei, S., Kheirandish, P., Marmari, V., Mahmoudzadeh, H., Mozayani, F., Maleki, A. R., Sadeghian, E., Nia, E. Z., Miri, S. R., Nia, N. Z., Rezaeian, O., Eskandary, A., Razavi, N., Shirkhoda, M., & Rouzbahani, F. N. (2019). Biological function and molecular mechanism of piRNA in cancer. Pract Lab Med, 13, e00113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plabm.2018.e00113.
Trzybulska, D., Vergadi, E., & Tsatsanis, C. (2018). miRNA and other non-coding RNAs as promising diagnostic markers. Ejifcc, 29(3), 221–226.
Krishnan, P., & Damaraju, S. (2018). The challenges and opportunities in the clinical application of noncoding RNAs: the road map for miRNAs and piRNAs in cancer diagnostics and prognostics. Int J Genomics, 2018, 5848046. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5848046.
Zhang, Y., Liu, W., Li, R., Gu, J., Wu, P., Peng, C., et al. (2018). Structural insights into the sequence-specific recognition of Piwi by Drosophila Papi. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115(13), 3374–3379. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1717116115.
Goriaux, C., Desset, S., Renaud, Y., Vaury, C., & Brasset, E. (2014). Transcriptional properties and splicing of the flamenco piRNA cluster. EMBO Reports, 15(4), 411–418. https://doi.org/10.1002/embr.201337898.
Andersen, P. R., Tirian, L., Vunjak, M., & Brennecke, J. (2017). A heterochromatin-dependent transcription machinery drives piRNA expression. Nature, 549(7670), 54–59. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23482.
Dennis, C., Zanni, V., Brasset, E., Eymery, A., Zhang, L., Mteirek, R., Jensen, S., Rong, Y. S., & Vaury, C. (2013). “Dot COM”, a nuclear transit center for the primary piRNA pathway in Drosophila. PLoS One, 8(9), e72752. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0072752.
Dennis, C., Brasset, E., & Vaury, C. (2019). flam piRNA precursors channel from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in a temporally regulated manner along Drosophila oogenesis. Mob DNA, 10, 28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13100-019-0170-7.
Murota, Y., Ishizu, H., Nakagawa, S., Iwasaki, Y. W., Shibata, S., Kamatani, M. K., Saito, K., Okano, H., Siomi, H., & Siomi, M. C. (2014). Yb integrates piRNA intermediates and processing factors into perinuclear bodies to enhance piRISC assembly. Cell Reports, 8(1), 103–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.05.043.
Szakmary, A., Reedy, M., Qi, H., & Lin, H. (2009). The Yb protein defines a novel organelle and regulates male germline stem cell self-renewal in Drosophila melanogaster. The Journal of Cell Biology, 185(4), 613–627. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200903034.
Pandey, R. R., Homolka, D., Chen, K. M., Sachidanandam, R., Fauvarque, M. O., & Pillai, R. S. (2017). Recruitment of Armitage and Yb to a transcript triggers its phased processing into primary piRNAs in Drosophila ovaries. PLoS Genetics, 13(8), e1006956. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006956.
Ge, D. T., Wang, W., Tipping, C., Gainetdinov, I., Weng, Z., & Zamore, P. D. (2019). The RNA-binding ATPase, Armitage, couples piRNA amplification in Nuage to phased piRNA production on mitochondria. Molecular Cell, 74(5), 982–995 e986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.04.006.
Munafo, M., Manelli, V., Falconio, F. A., Sawle, A., Kneuss, E., Eastwood, E. L., et al. (2019). Daedalus and Gasz recruit Armitage to mitochondria, bringing piRNA precursors to the biogenesis machinery. Genes & Development, 33(13–14), 844–856. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.325662.119.
Ipsaro, J. J., Haase, A. D., Knott, S. R., Joshua-Tor, L., & Hannon, G. J. (2012). The structural biochemistry of Zucchini implicates it as a nuclease in piRNA biogenesis. Nature, 491(7423), 279–283. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11502.
Izumi, N., Shoji, K., Sakaguchi, Y., Honda, S., Kirino, Y., Suzuki, T., Katsuma, S., & Tomari, Y. (2016). Identification and functional analysis of the pre-piRNA 3′ trimmer in silkworms. Cell, 164(5), 962–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.01.008.
Hirakata, S., Ishizu, H., Fujita, A., Tomoe, Y., & Siomi, M. C. (2019). Requirements for multivalent Yb body assembly in transposon silencing in Drosophila. EMBO Rep, 20(7), e47708. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201947708.
Ishizu, H., Kinoshita, T., Hirakata, S., Komatsuzaki, C., & Siomi, M. C. (2019). Distinct and collaborative functions of Yb and Armitage in transposon-targeting piRNA biogenesis. Cell Rep, 27(6), 1822-1835.e1828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.04.029.
Cheng, J., Guo, J. M., Xiao, B. X., Miao, Y., Jiang, Z., Zhou, H., et al. (2011). piRNA, the new non-coding RNA, is aberrantly expressed in human cancer cells. Clinica Chimica Acta, 412(17–18), 1621–1625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2011.05.015.
Lin, X., Xia, Y., Hu, D., Mao, Q., Yu, Z., Zhang, H., et al. (2019). Transcriptomewide piRNA profiling in human gastric cancer. Oncology Reports. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2019.7073.
Martinez, V. D., Enfield, K. S. S., Rowbotham, D. A., & Lam, W. L. (2016). An atlas of gastric PIWI-interacting RNA transcriptomes and their utility for identifying signatures of gastric cancer recurrence. Gastric Cancer, 19(2), 660–665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-015-0487-y.
Lin, X., Xia, Y., Hu, D., Mao, Q., Yu, Z., Zhang, H., Li, C., Chen, G., Liu, F., Zhu, W., Shi, Y., Zhang, H., Zheng, J., Sun, T., Xu, J., Chao, H. H., Zheng, X., & Luο, X. (2019). Transcriptomewide piRNA profiling in human gastric cancer. Oncology Reports, 41(5), 3089–3099. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2019.7073.
Cui, L., Lou, Y., Zhang, X., Zhou, H., Deng, H., Song, H., Yu, X., Xiao, B., Wang, W., & Guo, J. (2011). Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood from patients with gastric cancer using piRNAs as markers. Clinical Biochemistry, 44(13), 1050–1057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2011.06.004.
Cheng, J., Deng, H., Xiao, B., Zhou, H., Zhou, F., Shen, Z., & Guo, J. (2012). piR-823, a novel non-coding small RNA, demonstrates in vitro and in vivo tumor suppressive activity in human gastric cancer cells. Cancer Letters, 315(1), 12–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2011.10.004.
Wang, Y., Liu, Y., Shen, X., Zhang, X., Chen, X., Yang, C., & Gao, H. (2012). The PIWI protein acts as a predictive marker for human gastric cancer. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, 5(4), 315–325.
Gao, C. L., Sun, R., Li, D. H., & Gong, F. (2018). PIWI-like protein 1 upregulation promotes gastric cancer invasion and metastasis. Onco Targets Ther, 11, 8783–8789. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S186827.
Araujo, T., Khayat, A., Quintana, L., Calcagno, D., Mourao, R., Modesto, A., et al. (2018). Piwi like RNA-mediated gene silencing 1 gene as a possible major player in gastric cancer. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 24(47), 5338–5350. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i47.5338.
Hashim, A., Rizzo, F., Marchese, G., Ravo, M., Tarallo, R., Nassa, G., et al. (2014). RNA sequencing identifies specific PIWI-interacting small non-coding RNA expression patterns in breast cancer. Oncotarget, 5(20), 9901–9910. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2476.
Krishnan, P., Ghosh, S., Graham, K., Mackey, J. R., Kovalchuk, O., & Damaraju, S. (2016). Piwi-interacting RNAs and PIWI genes as novel prognostic markers for breast cancer. Oncotarget, 7(25), 37944–37956. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9272.
Huang, G., Hu, H., Xue, X., Shen, S., Gao, E., Guo, G., Shen, X., & Zhang, X. (2013). Altered expression of piRNAs and their relation with clinicopathologic features of breast cancer. Clinical & Translational Oncology, 15(7), 563–568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-012-0966-0.
Oner, C., Turgut Cosan, D., & Colak, E. (2016). Estrogen and androgen hormone levels modulate the expression of PIWI interacting RNA in prostate and breast cancer. PLoS One, 11(7), e0159044. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159044.
Tan, L., Mai, D., Zhang, B., Jiang, X., Zhang, J., Bai, R., Ye, Y., Li, M., Pan, L., Su, J., Zheng, Y., Liu, Z., Zuo, Z., Zhao, Q., Li, X., Huang, X., Yang, J., Tan, W., Zheng, J., & Lin, D. (2019). PIWI-interacting RNA-36712 restrains breast cancer progression and chemoresistance by interaction with SEPW1 pseudogene SEPW1P RNA. Molecular Cancer, 18(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0940-3.
Fu, A., Jacobs, D. I., Hoffman, A. E., Zheng, T., & Zhu, Y. (2015). PIWI-interacting RNA 021285 is involved in breast tumorigenesis possibly by remodeling the cancer epigenome. Carcinogenesis, 36(10), 1094–1102. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgv105.
Zhang, H., Ren, Y., Xu, H., Pang, D., Duan, C., & Liu, C. (2013). The expression of stem cell protein Piwil2 and piR-932 in breast cancer. Surgical Oncology, 22(4), 217–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suronc.2013.07.001.
Litwin, M., Szczepanska-Buda, A., Michalowska, D., Grzegrzolka, J., Piotrowska, A., Gomulkiewicz, A., et al. (2018). Aberrant expression of PIWIL1 and PIWIL2 and their clinical significance in ductal breast carcinoma. Anticancer Res, 38(4), 2021–2030. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.12441.
Heng, Z. S. L., Lee, J. Y., Subhramanyam, C. S., Wang, C., Thanga, L. Z., & Hu, Q. (2018). The role of 17betaestradiolinduced upregulation of Piwilike 4 in modulating gene expression and motility in breast cancer cells. Oncology Reports, 40(5), 2525–2535. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6676.
Li, Y., Wu, X., Gao, H., Jin, J. M., Li, A. X., Kim, Y. S., Pal, S. K., Nelson, R. A., Lau, C. M., Guo, C., Mu, B., Wang, J., Wang, F., Wang, J., Zhao, Y., Chen, W., Rossi, J. J., Weiss, L. M., & Wu, H. (2015). Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) are dysregulated in renal cell carcinoma and associated with tumor metastasis and cancer-specific survival. Molecular Medicine, 21, 381–388. https://doi.org/10.2119/molmed.2014.00203.
Busch, J., Ralla, B., Jung, M., Wotschofsky, Z., Trujillo-Arribas, E., Schwabe, P., Kilic, E., Fendler, A., & Jung, K. (2015). Piwi-interacting RNAs as novel prognostic markers in clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 34, 61–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-015-0180-3.
Zhao, C., Tolkach, Y., Schmidt, D., Toma, M., Muders, M. H., Kristiansen, G., Müller, S. C., & Ellinger, J. (2019). Mitochondrial PIWI-interacting RNAs are novel biomarkers for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. World Journal of Urology, 37(8), 1639–1647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2575-1.
Iliev, R., Stanik, M., Fedorko, M., Poprach, A., Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P., Slaba, K., Svoboda, M., Fabian, P., Pacik, D., Dolezel, J., & Slaby, O. (2016). Decreased expression levels of PIWIL1, PIWIL2, and PIWIL4 are associated with worse survival in renal cell carcinoma patients. Onco Targets Ther, 9, 217–222. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S91295.
Iliev, R., Fedorko, M., Machackova, T., Mlcochova, H., Svoboda, M., Pacik, D., et al. (2016). Expression levels of PIWI-interacting RNA, piR-823, are deregulated in tumor tissue, blood serum and urine of patients with renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res, 36(12), 6419–6423. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.11239.
Stohr, C. G., Steffens, S., Polifka, I., Jung, R., Kahlmeyer, A., Ivanyi, P., et al. (2019). Piwi-like 1 protein expression is a prognostic factor for renal cell carcinoma patients. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1741. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-38254-3.
Mai, D., Ding, P., Tan, L., Zhang, J., Pan, Z., Bai, R., Li, C., Li, M., Zhou, Y., Tan, W., Zhou, Z., Li, Y., Zhou, A., Ye, Y., Pan, L., Zheng, Y., Su, J., Zuo, Z., Liu, Z., Zhao, Q., Li, X., Huang, X., Li, W., Wu, S., Jia, W., Zou, S., Wu, C., Xu, R. H., Zheng, J., & Lin, D. (2018). PIWI-interacting RNA-54265 is oncogenic and a potential therapeutic target in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Theranostics, 8(19), 5213–5230. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.28001.
Yin, J., Jiang, X. Y., Qi, W., Ji, C. G., Xie, X. L., Zhang, D. X., Cui, Z. J., Wang, C. K., Bai, Y., Wang, J., & Jiang, H. Q. (2017). piR-823 contributes to colorectal tumorigenesis by enhancing the transcriptional activity of HSF1. Cancer Science, 108(9), 1746–1756. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13300.
Yin, J., Qi, W., Ji, C. G., Zhang, D. X., Xie, X. L., Ding, Q., Jiang, X. Y., Han, J., & Jiang, H. Q. (2019). Small RNA sequencing revealed aberrant piRNA expression profiles in colorectal cancer. Oncology Reports, 42(1), 263–272. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2019.7158.
Weng, W., Liu, N., Toiyama, Y., Kusunoki, M., Nagasaka, T., Fujiwara, T., Wei, Q., Qin, H., Lin, H., Ma, Y., & Goel, A. (2018). Novel evidence for a PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA) as an oncogenic mediator of disease progression, and a potential prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. Molecular Cancer, 17(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0767-3.
Sun, R., Gao, C. L., Li, D. H., Li, B. J., & Ding, Y. H. (2017). Expression status of PIWIL1 as a prognostic marker of colorectal cancer. Disease Markers, 2017, 1204937. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1204937.
Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P., Stitkovcova, K., Radova, L., Sachlova, M., Kosarova, Z., Slaba, K., et al. (2018). Circulating PIWI-interacting RNAs piR-5937 and piR-28876 are promising diagnostic biomarkers of colon cancer. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 27(9), 1019–1028. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-18-0318.
Tian, T., Li, X., & Zhang, J. (2019). mTOR signaling in cancer and mTOR inhibitors in solid tumor targeting therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030755.
Peng, L., Song, L., Liu, C., Lv, X., Li, X., Jie, J., Zhao, D., & Li, D. (2016). piR-55490 inhibits the growth of lung carcinoma by suppressing mTOR signaling. Tumour Biology, 37(2), 2749–2756. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4056-0.
Yao, J., Wang, Y. W., Fang, B. B., Zhang, S. J., & Cheng, B. L. (2016). piR-651 and its function in 95-D lung cancer cells. Biomed Rep, 4(5), 546–550. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2016.628.
Zhang, S. J., Yao, J., Shen, B. Z., Li, G. B., Kong, S. S., Bi, D. D., Pan, S. H., & Cheng, B. L. (2018). Role of piwi-interacting RNA-651 in the carcinogenesis of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncology Letters, 15(1), 940–946. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.7406.
Li, D., Luo, Y., Gao, Y., Yang, Y., Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Tan, S., Zhang, Y., Duan, J., & Yang, Y. (2016). piR-651 promotes tumor formation in non-small cell lung carcinoma through the upregulation of cyclin D1 and CDK4. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 38(3), 927–936. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2016.2671.
Reeves, M. E., Firek, M., Jliedi, A., & Amaar, Y. G. (2017). Identification and characterization of RASSF1C piRNA target genes in lung cancer cells. Oncotarget, 8(21), 34268–34282. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15965.
Reeves, M. E., Baldwin, M. L., Aragon, R., Baldwin, S., Chen, S. T., Li, X., Mohan, S., & Amaar, Y. G. (2012). RASSF1C modulates the expression of a stem cell renewal gene, PIWIL1. BMC Research Notes, 5, 239. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-5-239.
Reeves, M. E., Firek, M., Chen, S. T., & Amaar, Y. G. (2014). Evidence that RASSF1C stimulation of lung cancer cell proliferation depends on IGFBP-5 and PIWIL1 expression levels. PLoS One, 9(7), e101679. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0101679.
Xie, K., Zhang, K., Kong, J., Wang, C., Gu, Y., Liang, C., Jiang, T., Qin, N., Liu, J., Guo, X., Huo, R., Liu, M., Ma, H., Dai, J., & Hu, Z. (2018). Cancer-testis gene PIWIL1 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Medicine, 7(1), 157–166. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1248.
Abbreviations
ccRCC, clear cell renal cell carcinoma; CRC, colorectal cancer; ncRNA, non-coding RNA; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; PIC, pre-initiation complex; PICS, piRNA biogenesis and chromosome segregation; piRNA, PIWI-interacting RNA; piRISC, piRNA silencing complex; pre-piRNA, piRNA precursor; RCC, renal cell carcinoma; TEs, transposon elements; Zuc, Zucchini; HSF-1, heat shock transcription factor-1; MTOR, mammalian or mechanical target of rapamycin
Funding
This work was supported partly by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81541153); Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Department (2016A050503046, 2015A050502048 and 2016B030309002); The Public Service Platform of South China Sea for R&D Marine Biomedicine Resources (GDMUK201808); Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory Zhanjiang (ZJW-2019-07); Zhanjiang Science and technology Plan (2017A06012); Research Project of “Excellent Innovative Talent Support Program” of Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2018RCD13); and “Group-type” Special Supporting Project for Educational Talents in Universities (4SG19057G).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
All authors consent for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, B., Li, D., Du, L. et al. piRNAs: biogenesis and their potential roles in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 39, 567–575 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-020-09863-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-020-09863-0