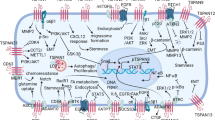
Abstract
Tetraspanin CD82 suppresses the progression and metastasis of a wide range of solid malignant tumors. However, its roles in tumorigenesis and hematopoietic malignancy remain unclear. Ubiquitously expressed CD82 restrains cell migration and cell invasion by modulating both cell-matrix and cell-cell adhesiveness and confining outside-in pro-motility signaling. This restraint at least contributes to, if not determines, the metastasis-suppressive activity and, also likely, the physiological functions of CD82. As a modulator of cell membrane heterogeneity, CD82 alters microdomains, trafficking, and topography of the membrane by changing the membrane molecular landscape. The functional activities of membrane molecules and the cytoskeletal interaction of the cell membrane are subsequently altered, followed by changes in cellular functions. Given its pathological and physiological importance, CD82 is a promising candidate for clinically predicting and blocking tumor progression and metastasis and also an emerging model protein for mechanistically understanding cell membrane organization and heterogeneity.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AML:
-
Acute myelogenous leukemia
- CAM:
-
Cell adhesion molecule
- EC:
-
Endothelial cells
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- ESC:
-
Endometrial stromal cell
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HGF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
- HIF:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor
- HPC:
-
Hematopoietic progenitor cell
- LEL:
-
Large extracellular loop
- LOH:
-
Loss of heterozygosity
- MM:
-
Multiple myeloma
- TEM:
-
Tetraspanin-enriched microdomain
References
Chiang, A. C., & Massague, J. (2008). Molecular basis of metastasis. The New England Journal of Medicine, 359(26), 2814–2823. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0805239.
Valastyan, S., & Weinberg, R. A. (2011). Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell, 147(2), 275–292. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.024.
Dong, J. T., Lamb, P. W., Rinker-Schaeffer, C. W., Vukanovic, J., Ichikawa, T., Isaacs, J. T., et al. (1995). KAI1, a metastasis suppressor gene for prostate cancer on human chromosome 11p11.2. Science, 268(5212), 884–886.
Zoller, M. (2009). Tetraspanins: push and pull in suppressing and promoting metastasis. Nature Reviews Cancer, 9(1), 40–55. doi:10.1038/nrc2543.
Liu, W. M., & Zhang, X. A. (2006). KAI1/CD82, a tumor metastasis suppressor. Cancer Letters, 240(2), 183–194. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2005.08.018.
Tonoli, H., & Barrett, J. C. (2005). CD82 metastasis suppressor gene: a potential target for new therapeutics? Trends in Molecular Medicine, 11(12), 563–570. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2005.10.002.
Miranti, C. K. (2009). Controlling cell surface dynamics and signaling: how CD82/KAI1 suppresses metastasis. Cellular Signalling, 21(2), 196–211. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.08.023.
Malik, F. A., Sanders, A. J., & Jiang, W. G. (2009). KAI-1/CD82, the molecule and clinical implication in cancer and cancer metastasis. Histology and Histopathology, 24(4), 519–530.
Tsai, Y. C., & Weissman, A. M. (2011). Dissecting the diverse functions of the metastasis suppressor CD82/KAI1. FEBS Letters, 585(20), 3166–3173. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2011.08.031.
Jackson, P., Marreiros, A., & Russell, P. J. (2005). KAI1 tetraspanin and metastasis suppressor. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 37(3), 530–534. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2004.08.009.
Lee, J. H., Seo, Y. W., Park, S. R., Kim, Y. J., & Kim, K. K. (2003). Expression of a splice variant of KAI1, a tumor metastasis suppressor gene, influences tumor invasion and progression. Cancer Research, 63(21), 7247–7255.
Strausberg, R. L., Feingold, E. A., Grouse, L. H., Derge, J. G., Klausner, R. D., Collins, F. S., et al. (2002). Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99(26), 16899–16903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899.
Wang, H., Zhang, W., Zhao, J., Zhang, L., Liu, M., Yan, G., et al. (2012). N-Glycosylation pattern of recombinant human CD82 (KAI1), a tumor-associated membrane protein. Journal of Proteomics, 75(4), 1375–1385. doi:10.1016/j.jprot.2011.11.013.
Bari, R., Zhang, Y. H., Zhang, F., Wang, N. X., Stipp, C. S., Zheng, J. J., et al. (2009). Transmembrane interactions are needed for KAI1/CD82-mediated suppression of cancer invasion and metastasis. The American Journal of Pathology, 174(2), 647–660. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2009.080685.
Nagira, M., Imai, T., Ishikawa, I., Uwabe, K. I., & Yoshie, O. (1994). Mouse homologue of C33 antigen (CD82), a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily: complementary DNA, genomic structure, and expression. Cellular Immunology, 157(1), 144–157. doi:10.1006/cimm.1994.1212.
Shiwu, W. U., Lan, Y., Wenqing, S., Lei, Z., & Yisheng, T. (2012). Expression and clinical significance of CD82/KAI1 and E-cadherin in non-small cell lung cancer. Archives of Iranian Medicine, 15(11), 707–712.
Knoener, M., Krech, T., Puls, F., Lehmann, U., Kreipe, H., & Christgen, M. (2012). Limited value of KAI1/CD82 protein expression as a prognostic marker in human gastric cancer. Disease Markers, 32(6), 337–342. doi:10.3233/DMA-2012-0896.
Yang, J. M., Peng, Z. H., Si, S. H., Liu, W. W., Luo, Y. H., & Ye, Z. Y. (2008). KAI1 gene suppresses invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma MHCC97-H cells in vitro and in animal models. Liver International, 28(1), 132–139. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2007.01620.x.
Scarpino, S., Duranti, E., Giglio, S., Di Napoli, A., Galafate, D., Del Bufalo, D., et al. (2013). Papillary carcinoma of the thyroid: high expression of COX-2 and low expression of KAI-1/CD82 are associated with increased tumor invasiveness. Thyroid, 23(9), 1127–1137. doi:10.1089/thy.2011.0421.
Zhang, B., Liu, W., Li, L., Lu, J., Liu, M., Sun, Y., et al. (2013). KAI1/CD82 and cyclin D1 as biomarkers of invasion, metastasis and prognosis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, 6(6), 1060–1067.
Xu, J. H., Guo, X. Z., Ren, L. N., Shao, L. C., & Liu, M. P. (2008). KAI1 is a potential target for anti-metastasis in pancreatic cancer cells. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 14(7), 1126–1132.
Richardson, M. M., Jennings, L. K., & Zhang, X. A. (2011). Tetraspanins and tumor progression. Clinical and Experimental Metastasis, 28(3), 261–270. doi:10.1007/s10585-010-9365-5.
Yang, X., Wei, L. L., Tang, C., Slack, R., Mueller, S., & Lippman, M. E. (2001). Overexpression of KAI1 suppresses in vitro invasiveness and in vivo metastasis in breast cancer cells. Cancer Research, 61(13), 5284–5288.
Nishioka, C., Ikezoe, T., Furihata, M., Yang, J., Serada, S., Naka, T., et al. (2013). CD34(+)/CD38(-) acute myelogenous leukemia cells aberrantly express CD82 which regulates adhesion and survival of leukemia stem cells. International Journal of Cancer, 132(9), 2006–2019. doi:10.1002/ijc.27904.
Burchert, A., Notter, M., Dietrich Menssen, H., Schwartz, S., Knauf, W., Neubauer, A., et al. (1999). CD82 (KAI1), a member of the tetraspan family, is expressed on early haemopoietic progenitor cells and up-regulated in distinct human leukaemias. British Journal of Haematology, 107(3), 494–504.
Termini, C. M., Cotter, M. L., Marjon, K. D., Buranda, T., Lidke, K. A., & Gillette, J. M. (2014). The membrane scaffold CD82 regulates cell adhesion by altering alpha4 integrin stability and molecular density. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 25(10), 1560–1573. doi:10.1091/mbc.E13-11-0660.
Nishioka, C., Ikezoe, T., Yang, J., Nobumoto, A., Kataoka, S., Tsuda, M., et al. (2014). CD82 regulates STAT5/IL-10 and supports survival of acute myelogenous leukemia cells. International Journal of Cancer, 134(1), 55–64. doi:10.1002/ijc.28348.
Geradts, J., Maynard, R., Birrer, M. J., Hendricks, D., Abbondanzo, S. L., Fong, K. M., et al. (1999). Frequent loss of KAI1 expression in squamous and lymphoid neoplasms. An immunohistochemical study of archival tissues. The American Journal of Pathology, 154(6), 1665–1671. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65422-3.
Ferrer, M., Yunta, M., & Lazo, P. A. (1998). Pattern of expression of tetraspanin antigen genes in Burkitt lymphoma cell lines. Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 113(3), 346–352.
Wheeler, D. L., Barrett, T., Benson, D. A., Bryant, S. H., Canese, K., Chetvernin, V., et al. (2007). Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Research, 35(Database issue), D5–D12. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl1031.
Cheadle, C., Vawter, M. P., Freed, W. J., & Becker, K. G. (2003). Analysis of microarray data using Z score transformation. The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, 5(2), 73–81. doi:10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60455-2.
Drucker, L., Tohami, T., Tartakover-Matalon, S., Zismanov, V., Shapiro, H., Radnay, J., et al. (2006). Promoter hypermethylation of tetraspanin members contributes to their silencing in myeloma cell lines. Carcinogenesis, 27(2), 197–204. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgi209.
Tohami, T., Drucker, L., Shapiro, H., Radnay, J., & Lishner, M. (2007). Overexpression of tetraspanins affects multiple myeloma cell survival and invasive potential. FASEB Journal, 21(3), 691–699. doi:10.1096/fj.06-6610com.
Zismanov, V., Lishner, M., Tartakover-Matalon, S., Radnay, J., Shapiro, H., & Drucker, L. (2009). Tetraspanin-induced death of myeloma cell lines is autophagic and involves increased UPR signalling. British Journal of Cancer, 101(8), 1402–1409. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605291.
Lishner, M., Zismanov, V., Tohami, T., Tartakover-Matalon, S., Elis, A., & Drucker, L. (2008). Tetraspanins affect myeloma cell fate via Akt signaling and FoxO activation. Cellular Signalling, 20(12), 2309–2316. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.08.018.
Zismanov, V., Drucker, L., Attar-Schneider, O., Matalon, S. T., Pasmanik-Chor, M., & Lishner, M. (2012). Tetraspanins stimulate protein synthesis in myeloma cell lines. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 113(7), 2500–2510. doi:10.1002/jcb.24126.
Yang, X., Welch, D. R., Phillips, K. K., Weissman, B. E., & Wei, L. L. (1997). KAI1, a putative marker for metastatic potential in human breast cancer. Cancer Letters, 119(2), 149–155.
Yang, X., Wei, L., Tang, C., Slack, R., Montgomery, E., & Lippman, M. (2000). KAI1 protein is down-regulated during the progression of human breast cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, 6(9), 3424–3429.
Stark, A. M., Tongers, K., Maass, N., Mehdorn, H. M., & Held-Feindt, J. (2005). Reduced metastasis-suppressor gene mRNA-expression in breast cancer brain metastases. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology, 131(3), 191–198. doi:10.1007/s00432-004-0629-9.
Malik, F. A., Sanders, A. J., Jones, A. D., Mansel, R. E., & Jiang, W. G. (2009). Transcriptional and translational modulation of KAI1 expression in ductal carcinoma of the breast and the prognostic significance. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 23(2), 273–278.
Mooez, S., Malik, F. A., Kayani, M. A., Rashid, R., Zahid, A., & Khan, A. (2011). Expressional alterations and transcript isoforms of metastasis suppressor genes (KAI1 and KiSS1) in breast cancer patients. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 12(10), 2785–2791.
Christgen, M., Bruchhardt, H., Ballmaier, M., Krech, T., Langer, F., Kreipe, H., et al. (2008). KAI1/CD82 is a novel target of estrogen receptor-mediated gene repression and downregulated in primary human breast cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 123(10), 2239–2246. doi:10.1002/ijc.23806.
Huang, H., Groth, J., Sossey-Alaoui, K., Hawthorn, L., Beall, S., & Geradts, J. (2005). Aberrant expression of novel and previously described cell membrane markers in human breast cancer cell lines and tumors. Clinical Cancer Research, 11(12), 4357–4364. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2107.
Christgen, M., Christgen, H., Heil, C., Krech, T., Langer, F., Kreipe, H., et al. (2009). Expression of KAI1/CD82 in distant metastases from estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Cancer Science, 100(9), 1767–1771. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01231.x.
Huang, C. I., Kohno, N., Ogawa, E., Adachi, M., Taki, T., & Miyake, M. (1998). Correlation of reduction in MRP-1/CD9 and KAI1/CD82 expression with recurrences in breast cancer patients. The American Journal of Pathology, 153(3), 973–983.
Son, B. H., Choi, J. S., & Lee, J. H. (2005). Prognostic values of KAI1 and survivin expression in an infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the breast. Pathology, 37(2), 131–136.
Malik, F. A., Sanders, A. J., Kayani, M. A., & Jiang, W. G. (2009). Effect of expressional alteration of KAI1 on breast cancer cell growth, adhesion, migration and invasion. Cancer Genomics Proteomics, 6(4), 205–213.
Bandyopadhyay, S., Zhan, R., Chaudhuri, A., Watabe, M., Pai, S. K., Hirota, S., et al. (2006). Interaction of KAI1 on tumor cells with DARC on vascular endothelium leads to metastasis suppression. Nature Medicine, 12(8), 933–938. doi:10.1038/nm1444.
Larochelle, A., Gillette, J. M., Desmond, R., Ichwan, B., Cantilena, A., Cerf, A., et al. (2012). Bone marrow homing and engraftment of human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells is mediated by a polarized membrane domain. Blood, 119(8), 1848–1855. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-08-371583.
Abe, M., Sugiura, T., Takahashi, M., Ishii, K., Shimoda, M., & Shirasuna, K. (2008). A novel function of CD82/KAI-1 on E-cadherin-mediated homophilic cellular adhesion of cancer cells. Cancer Letters, 266(2), 163–170. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.02.058.
Liu, W. M., Zhang, F., Moshiach, S., Zhou, B., Huang, C., Srinivasan, K., et al. (2012). Tetraspanin CD82 inhibits protrusion and retraction in cell movement by attenuating the plasma membrane-dependent actin organization. PloS One, 7(12), e51797. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0051797.
Lee, H. A., Park, I., Byun, H. J., Jeoung, D., Kim, Y. M., & Lee, H. (2011). Metastasis suppressor KAI1/CD82 attenuates the matrix adhesion of human prostate cancer cells by suppressing fibronectin expression and beta1 integrin activation. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 27(5), 575–586. doi:10.1159/000329979.
Jee, B. K., Lee, J. Y., Lim, Y., Lee, K. H., & Jo, Y. H. (2007). Effect of KAI1/CD82 on the beta1 integrin maturation in highly migratory carcinoma cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 359(3), 703–708. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.159.
Ruseva, Z., Geiger, P. X., Hutzler, P., Kotzsch, M., Luber, B., Schmitt, M., et al. (2009). Tumor suppressor KAI1 affects integrin alphavbeta3-mediated ovarian cancer cell adhesion, motility, and proliferation. Experimental Cell Research, 315(10), 1759–1771. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.01.007.
Wei, Q., Zhang, F., Richardson, M. M., Roy, N. H., Rodgers, W., Liu, Y., et al. (2014). CD82 restrains pathological angiogenesis by altering lipid raft clustering and CD44 trafficking in endothelial cells. Circulation, 130(17), 1493–1504. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.011096.
Guo, X. Z., Xu, J. H., Liu, M. P., Kleeff, J., Ho, C. K., Ren, L. N., et al. (2005). KAI1 inhibits anchorage-dependent and -independent pancreatic cancer cell growth. Oncology Reports, 14(1), 59–63.
Lu, D., Wang, W. X., Xu, Y. Q., Jiang, Q. Y., & Yang, Y. (2007). Inhibitory effect of KAI1 gene on breast cancer cell growth in vitro. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 29(8), 580–583.
Tsai, Y. C., Mendoza, A., Mariano, J. M., Zhou, M., Kostova, Z., Chen, B., et al. (2007). The ubiquitin ligase gp78 promotes sarcoma metastasis by targeting KAI1 for degradation. Nature Medicine, 13(12), 1504–1509. doi:10.1038/nm1686.
Lee, J. H., Bae, J. A., Lee, J. H., Seo, Y. W., Kho, D. H., Sun, E. G., et al. (2010). Glycoprotein 90K, downregulated in advanced colorectal cancer tissues, interacts with CD9/CD82 and suppresses the Wnt/beta-catenin signal via ISGylation of beta-catenin. Gut, 59(7), 907–917. doi:10.1136/gut.2009.194068.
Nishioka, C., Ikezoe, T., Takeuchi, A., Nobumoto, A., Tsuda, M., & Yokoyama, A. (2015). The novel function of CD82 and its impact on BCL2L12 via AKT/STAT5 signal pathway in acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Leukemia. doi:10.1038/leu.2015.219.
Mine, M., Yamaguchi, K., Sugiura, T., Chigita, S., Yoshihama, N., Yoshihama, R., et al. (2015). miR-203 inhibits Frizzled-2 expression via CD82/KAI1 expression in human lung carcinoma cells. PLoS One, 10(7), e0131350. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0131350.
Chigita, S., Sugiura, T., Abe, M., Kobayashi, Y., Shimoda, M., Onoda, M., et al. (2012). CD82 inhibits canonical Wnt signalling by controlling the cellular distribution of beta-catenin in carcinoma cells. International Journal of Oncology, 41(6), 2021–2028. doi:10.3892/ijo.2012.1671.
Chairoungdua, A., Smith, D. L., Pochard, P., Hull, M., & Caplan, M. J. (2010). Exosome release of beta-catenin: a novel mechanism that antagonizes Wnt signaling. The Journal of Cell Biology, 190(6), 1079–1091. doi:10.1083/jcb.201002049.
Odintsova, E., Voortman, J., Gilbert, E., & Berditchevski, F. (2003). Tetraspanin CD82 regulates compartmentalisation and ligand-induced dimerization of EGFR. Journal of Cell Science, 116(Pt 22), 4557–4566. doi:10.1242/jcs.00793.
Danglot, L., Chaineau, M., Dahan, M., Gendron, M. C., Boggetto, N., Perez, F., et al. (2010). Role of TI-VAMP and CD82 in EGFR cell-surface dynamics and signaling. Journal of Cell Science, 123(Pt 5), 723–735. doi:10.1242/jcs.062497.
Odintsova, E., van Niel, G., Conjeaud, H., Raposo, G., Iwamoto, R., Mekada, E., et al. (2013). Metastasis suppressor tetraspanin CD82/KAI1 regulates ubiquitylation of epidermal growth factor receptor. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288(36), 26323–26334. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.439380.
Sridhar, S. C., & Miranti, C. K. (2006). Tetraspanin KAI1/CD82 suppresses invasion by inhibiting integrin-dependent crosstalk with c-Met receptor and Src kinases. Oncogene, 25(16), 2367–2378. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209269.
Todeschini, A. R., Dos Santos, J. N., Handa, K., & Hakomori, S. I. (2007). Ganglioside GM2-tetraspanin CD82 complex inhibits met and its cross-talk with integrins, providing a basis for control of cell motility through glycosynapse. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282(11), 8123–8133. doi:10.1074/jbc.M611407200.
Takahashi, M., Sugiura, T., Abe, M., Ishii, K., & Shirasuna, K. (2007). Regulation of c-Met signaling by the tetraspanin KAI-1/CD82 affects cancer cell migration. International Journal of Cancer, 121(9), 1919–1929. doi:10.1002/ijc.22887.
Mu, Z., Wang, H., Zhang, J., Li, Q., Wang, L., & Guo, X. (2008). KAI1/CD82 suppresses hepatocyte growth factor-induced migration of hepatoma cells via upregulation of Sprouty2. Science in China. Series C, Life Sciences, 51(7), 648–654. doi:10.1007/s11427-008-0086-1.
Lee, C. C., Putnam, A. J., Miranti, C. K., Gustafson, M., Wang, L. M., Vande Woude, G. F., et al. (2004). Overexpression of sprouty 2 inhibits HGF/SF-mediated cell growth, invasion, migration, and cytokinesis. Oncogene, 23(30), 5193–5202. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207646.
Xu, C., Zhang, Y. H., Thangavel, M., Richardson, M. M., Liu, L., Zhou, B., et al. (2009). CD82 endocytosis and cholesterol-dependent reorganization of tetraspanin webs and lipid rafts. FASEB Journal, 23(10), 3273–3288. doi:10.1096/fj.08-123414.
Khanna, P., Chung, C. Y., Neves, R. I., Robertson, G. P., & Dong, C. (2014). CD82/KAI expression prevents IL-8-mediated endothelial gap formation in late-stage melanomas. Oncogene, 33(22), 2898–2908. doi:10.1038/onc.2013.249.
Gabellini, C., Trisciuoglio, D., Desideri, M., Candiloro, A., Ragazzoni, Y., Orlandi, A., et al. (2009). Functional activity of CXCL8 receptors, CXCR1 and CXCR2, on human malignant melanoma progression. European Journal of Cancer, 45(14), 2618–2627. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2009.07.007.
Delaguillaumie, A., Harriague, J., Kohanna, S., Bismuth, G., Rubinstein, E., Seigneuret, M., et al. (2004). Tetraspanin CD82 controls the association of cholesterol-dependent microdomains with the actin cytoskeleton in T lymphocytes: relevance to co-stimulation. Journal of Cell Science, 117(Pt 22), 5269–5282. doi:10.1242/jcs.01380.
Charrin, S., Manie, S., Thiele, C., Billard, M., Gerlier, D., Boucheix, C., et al. (2003). A physical and functional link between cholesterol and tetraspanins. European Journal of Immunology, 33(9), 2479–2489. doi:10.1002/eji.200323884.
Todeschini, A. R., Dos Santos, J. N., Handa, K., & Hakomori, S. I. (2008). Ganglioside GM2/GM3 complex affixed on silica nanospheres strongly inhibits cell motility through CD82/cMet-mediated pathway. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(6), 1925–1930. doi:10.1073/pnas.0709619104.
Li, Y., Huang, X., Zhang, J., Li, Y., & Ma, K. (2013). Synergistic inhibition of cell migration by tetraspanin CD82 and gangliosides occurs via the EGFR or cMet-activated Pl3K/Akt signalling pathway. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 45(11), 2349–2358. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2013.08.002.
Zhang, X. A., & Huang, C. (2012). Tetraspanins and cell membrane tubular structures. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 69(17), 2843–2852. doi:10.1007/s00018-012-0954-0.
Bari, R., Guo, Q., Xia, B., Zhang, Y. H., Giesert, E. E., Levy, S., et al. (2011). Tetraspanins regulate the protrusive activities of cell membrane. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 415(4), 619–626. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.10.121.
Bass, R., Werner, F., Odintsova, E., Sugiura, T., Berditchevski, F., & Ellis, V. (2005). Regulation of urokinase receptor proteolytic function by the tetraspanin CD82. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280(15), 14811–14818. doi:10.1074/jbc.M414189200.
Jee, B. K., Park, K. M., Surendran, S., Lee, W. K., Han, C. W., Kim, Y. S., et al. (2006). KAI1/CD82 suppresses tumor invasion by MMP9 inactivation via TIMP1 up-regulation in the H1299 human lung carcinoma cell line. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 342(2), 655–661. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.01.153.
You, J., Madigan, M. C., Rowe, A., Sajinovic, M., Russell, P. J., & Jackson, P. (2012). An inverse relationship between KAI1 expression, invasive ability, and MMP-2 expression and activity in bladder cancer cell lines. Urologic Oncology, 30(4), 502–508. doi:10.1016/j.urolonc.2010.02.013.
Schroder, H. M., Hoffmann, S. C., Hecker, M., Korff, T., & Ludwig, T. (2013). The tetraspanin network modulates MT1-MMP cell surface trafficking. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 45(6), 1133–1144. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2013.02.020.
Arduise, C., Abache, T., Li, L., Billard, M., Chabanon, A., Ludwig, A., et al. (2008). Tetraspanins regulate ADAM10-mediated cleavage of TNF-alpha and epidermal growth factor. The Journal of Immunology , 181(10), 7002–7013.
Xu, D., Sharma, C., & Hemler, M. E. (2009). Tetraspanin12 regulates ADAM10-dependent cleavage of amyloid precursor protein. FASEB Journal, 23(11), 3674–3681. doi:10.1096/fj.09-133462.
Marreiros, A., Dudgeon, K., Dao, V., Grimm, M. O., Czolij, R., Crossley, M., et al. (2005). KAI1 promoter activity is dependent on p53, junB and AP2: evidence for a possible mechanism underlying loss of KAI1 expression in cancer cells. Oncogene, 24(4), 637–649. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208216.
Jackson, P., Ow, K., Yardley, G., Delprado, W., Quinn, D. I., Yang, J. L., et al. (2003). Downregulation of KAI1 mRNA in localised prostate cancer and its bony metastases does not correlate with p53 overexpression. Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases, 6(2), 174–181. doi:10.1038/sj.pcan.4500634.
Guo, C., Liu, Q. G., Zhang, L., Song, T., & Yang, X. (2009). Expression and clinical significance of p53, JunB and KAI1/CD82 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International, 8(4), 389–396.
Wu, J., Liang, S., Bergholz, J., He, H., Walsh, E. M., Zhang, Y., et al. (2014). DeltaNp63alpha activates CD82 metastasis suppressor to inhibit cancer cell invasion. Cell Death and Disease, 5, e1280. doi:10.1038/cddis.2014.239.
Kim, B., Boo, K., Lee, J. S., Kim, K. I., Kim, W. H., Cho, H. J., et al. (2010). Identification of the KAI1 metastasis suppressor gene as a hypoxia target gene. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 393(1), 179–184. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.01.118.
Nagao, K., & Oka, K. (2011). HIF-2 directly activates CD82 gene expression in endothelial cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 407(1), 260–265. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.03.017.
Dai, W., Wang, C., Wang, F., Wang, Y., Shen, M., Chen, K., et al. (2014). Anti-miR-197 inhibits migration in HCC cells by targeting KAI 1/CD82. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 446(2), 541–548. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.03.006.
Kim, Y. I., Shin, M. K., Lee, J. W., Chung, J. H., & Lee, M. H. (2009). Decreased expression of KAI1/CD82 metastasis suppressor gene is associated with loss of heterozygosity in melanoma cell lines. Oncology Reports, 21(1), 159–164.
Upheber, S., Karle, A., Miller, J., Schlaugk, S., Gross, E., & Reuning, U. (2015). Alternative splicing of KAI1 abrogates its tumor-suppressive effects on integrin alphavbeta3-mediated ovarian cancer biology. Cellular Signalling, 27(3), 652–662. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.11.028.
Gellersen, B., Briese, J., Oberndorfer, M., Redlin, K., Samalecos, A., Richter, D. U., et al. (2007). Expression of the metastasis suppressor KAI1 in decidual cells at the human maternal-fetal interface: regulation and functional implications. The American Journal of Pathology, 170(1), 126–139. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2007.060175.
Gonzalez, M., Neufeld, J., Reimann, K., Wittmann, S., Samalecos, A., Wolf, A., et al. (2011). Expansion of human trophoblastic spheroids is promoted by decidualized endometrial stromal cells and enhanced by heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor and interleukin-1 beta. Molecular Human Reproduction, 17(7), 421–433. doi:10.1093/molehr/gar015.
Wei, X., Liu, S., Wang, X., & Yan, Q. (2012). CD82 expression alters with human endometrial cycles and affects the uterine endometrial receptivity in vitro. Experimental Biology and Medicine (Maywood, N.J.), 237(3), 254–262. doi:10.1258/ebm.2011.011309.
Meng, Y. H., Shao, J., Li, H., Hou, Y. L., Tang, C. L., Du, M. R., et al. (2012). CsA improves the trophoblasts invasiveness through strengthening the cross-talk of trophoblasts and decidual stromal cells mediated by CXCL12 and CD82 in early pregnancy. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, 5(4), 299–307.
Li, M. Q., Tang, C. L., Du, M. R., Fan, D. X., Zhao, H. B., Xu, B., et al. (2011). CXCL12 controls over-invasion of trophoblasts via upregulating CD82 expression in DSCs at maternal-fetal interface of human early pregnancy in a paracrine manner. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, 4(3), 276–286.
Li, M. Q., Hou, X. F., Shao, J., Tang, C. L., & Li, D. J. (2010). The DSCs-expressed CD82 controls the invasiveness of trophoblast cells via integrinbeta1/MAPK/MAPK3/1 signaling pathway in human first-trimester pregnancy. Biology of Reproduction, 82(5), 968–979. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.109.080739.
Li, M. Q., Hou, X. F., Lv, S. J., Meng, Y. H., Wang, X. Q., Tang, C. L., et al. (2011). CD82 gene suppression in endometrial stromal cells leads to increase of the cell invasiveness in the endometriotic milieu. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, 47(2), 195–208. doi:10.1530/JME-10-0165.
Gellersen, B., Wolf, A., Kruse, M., Schwenke, M., & Bamberger, A. M. (2013). Human endometrial stromal cell-trophoblast interactions: mutual stimulation of chemotactic migration and promigratory roles of cell surface molecules CD82 and CEACAM1. Biology of Reproduction, 88(3), 80. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.112.106724.
Spring, F. A., Griffiths, R. E., Mankelow, T. J., Agnew, C., Parsons, S. F., Chasis, J. A., et al. (2013). Tetraspanins CD81 and CD82 facilitate alpha4beta1-mediated adhesion of human erythroblasts to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. PloS One, 8(5), e62654. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062654.
Lin, G., Mela, A., Guilfoyle, E. M., & Goldman, J. E. (2009). Neonatal and adult O4(+) oligodendrocyte lineage cells display different growth factor responses and different gene expression patterns. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 87(15), 3390–3402. doi:10.1002/jnr.22065.
Mela, A., & Goldman, J. E. (2009). The tetraspanin KAI1/CD82 is expressed by late-lineage oligodendrocyte precursors and may function to restrict precursor migration and promote oligodendrocyte differentiation and myelination. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29(36), 11172–11181. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3075-09.2009.
Mela, A., & Goldman, J. E. (2013). CD82 blocks cMet activation and overcomes hepatocyte growth factor effects on oligodendrocyte precursor differentiation. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(18), 7952–7960. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5836-12.2013.
Risinger, J. I., Custer, M., Feigenbaum, L., Simpson, R. M., Hoover, S. B., Webster, J. D., et al. (2014). Normal viability of Kai1/Cd82 deficient mice. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 53(8), 610–624. doi:10.1002/mc.22009.
Choi, U. J., Jee, B. K., Lim, Y., & Lee, K. H. (2009). KAI1/CD82 decreases Rac1 expression and cell proliferation through PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in H1299 lung carcinoma cells. Cell Biochemistry and Function, 27(1), 40–47. doi:10.1002/cbf.1532.
Guan-Zhen, Y., Ying, C., Can-Rong, N., Guo-Dong, W., Jian-Xin, Q., & Jie-Jun, W. (2007). Reduced protein expression of metastasis-related genes (nm23, KISS1, KAI1 and p53) in lymph node and liver metastases of gastric cancer. International Journal of Experimental Pathology, 88(3), 175–183. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2613.2006.00510.x.
Chen, Z., Gu, S., Trojanowicz, B., Liu, N., Zhu, G., Dralle, H., et al. (2011). Down-regulation of TM4SF is associated with the metastatic potential of gastric carcinoma TM4SF members in gastric carcinoma. World Journal of Surgical Oncology, 9, 43. doi:10.1186/1477-7819-9-43.
Ilhan, O., Celik, S. Y., Han, U., & Onal, B. (2009). Use of KAI-1 as a prognostic factor in gastric carcinoma. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 21(12), 1369–1372. doi:10.1097/MEG.0b013e328323aac9.
Jiang, W. X., Song, B. G., Tang, R. Y., & Fang, J. P. (2008). Expression of nm23 and KAI1 and their clinical significance in gallbladder adenocarcinoma. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 30(6), 441–443.
Liu, X., Guo, X. Z., Zhang, W. W., Lu, Z. Z., Zhang, Q. W., Duan, H. F., et al. (2011). KAI1 inhibits HGF-induced invasion of pancreatic cancer by sphingosine kinase activity. Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International, 10(2), 201–208.
Rotterud, R., Fossa, S. D., & Nesland, J. M. (2007). Protein networking in bladder cancer: immunoreactivity for FGFR3, EGFR, ERBB2, KAI1, PTEN, and RAS in normal and malignant urothelium. Histology and Histopathology, 22(4), 349–363.
Ai, X., Zhang, X., Wu, Z., Ma, X., Ju, Z., Wang, B., et al. (2007). Expression of KAI1/CD82 and MRP-1/CD9 in transitional cell carcinoma of bladder. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology. Medical Sciences, 27(1), 79–82. doi:10.1007/s11596-007-0123-0.
Jackson, P., Rowe, A., & Grimm, M. O. (2007). An alternatively spliced KAI1 mRNA is expressed at low levels in human bladder cancers and bladder cancer cell lines and is not associated with invasive behaviour. Oncology Reports, 18(6), 1357–1363.
Rowe, A., & Jackson, P. (2006). Expression of KITENIN, a KAI1/CD82 binding protein and metastasis enhancer, in bladder cancer cell lines: relationship to KAI1/CD82 levels and invasive behaviour. Oncology Reports, 16(6), 1267–1272.
Ouyang, Y. W., Pan, X. L., Peng, Z. L., Qu, Y., & Zhang, H. Y. (2008). Expression of metastasis suppressor gene KAI1 in cervical carcinoma and infections of HPV16 E6, E7 and HPV18 E6/E7. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao. Yi Xue Ban, 39(3), 410–413.
Ouyang, Y. W., Pan, X. L., Qu, Y., Peng, Z. L., Wei, D. P., & Wang, X. (2008). Effect of metastasis suppressor gene KAI1 on the proliferation and invasive ability of cervical carcinoma cells. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao. Yi Xue Ban, 39(5), 753–756.
Park, J. J., Jin, Y. B., Lee, Y. J., Lee, J. S., Lee, Y. S., Ko, Y. G., et al. (2012). KAI1 suppresses HIF-1alpha and VEGF expression by blocking CDCP1-enhanced Src activation in prostate cancer. BMC Cancer, 12, 81. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-12-81.
Liu, W., Iiizumi-Gairani, M., Okuda, H., Kobayashi, A., Watabe, M., Pai, S. K., et al. (2011). KAI1 gene is engaged in NDRG1 gene-mediated metastasis suppression through the ATF3-NFkappaB complex in human prostate cancer. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286(21), 18949–18959. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.232637.
Tang, Y., Cheng, Y., Martinka, M., Ong, C. J., & Li, G. (2014). Prognostic significance of KAI1/CD82 in human melanoma and its role in cell migration and invasion through the regulation of ING4. Carcinogenesis, 35(1), 86–95. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgt346.
Gentleman, R. C., Carey, V. J., Bates, D. M., Bolstad, B., Dettling, M., Dudoit, S., et al. (2004). Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biology, 5(10), R80. doi:10.1186/gb-2004-5-10-r80.
Gautier, L., Cope, L., Bolstad, B. M., & Irizarry, R. A. (2004). affy—analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics, 20(3), 307–315. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btg405.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grant CA096991, AHA grant 13GRNT17040028, and OCAST grant HR13-207 to XAZ, and NIH 1U54GM104938 to JDW. XAZ is an Oklahoma TSET Cancer Research Scholar. We thank Ms. Kathy Kyler for English editing. Due to page limitations, we have cited the research articles published in and after 2006. For most studies published before 2006, we have cited Liu WM and Zhang XA, Cancer Letters, 2006, 240:183–194, and references can be found therein.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jin Feng, Chao Huang and Jonathan D. Wren contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, J., Huang, C., Wren, J.D. et al. Tetraspanin CD82: a suppressor of solid tumors and a modulator of membrane heterogeneity. Cancer Metastasis Rev 34, 619–633 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-015-9585-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-015-9585-x