Abstract
Purpose
Mammographic density is an established risk factor for breast cancer; however, the relation to tumor pathological parameters including the androgen receptor and molecular subtypes has not been extensively studied.
Methods
In the Malmö Diet and Cancer Study, 733 invasive breast cancers were diagnosed from 1991 to 2007. Mammographic density was defined qualitatively. Tumor biomarker information including estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor, androgen receptor (AR), human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2), and Ki67 was collected. Surrogate molecular subtypes were defined as luminal A, luminal B, HER2 positive and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Results
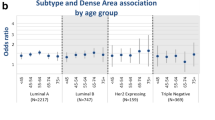
Among the 632 tumors with mammographic and pathological information, 352 tumors were screening-detected and 280 clinically detected. Higher mammographic density was associated with ER-negative tumors [ORadj 1.93 (1.04–3.59)] and TNBC [ORadj 2.44 (1.01–5.89), luminal A reference], in clinically detected breast cancer. Similarly, higher mammographic density was associated with AR-negative tumors [ORadj 1.77 (0.80–3.93)] in clinically detected breast cancer, though the evidence for this association was weak.
Conclusions
In clinically detected breast cancer, but not in screening-detected, higher mammographic density was associated with ER-negative tumors including TNBC. This study highlights the need for taking mode of detection into consideration when addressing mammographic density and tumor biomarkers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCormack VA, dos Santos Silva I (2006) Breast density and parenchymal patterns as markers of breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 15(6):1159–1169. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-06-0034
Yaghjyan L, Colditz GA, Collins LC, Schnitt SJ, Rosner B, Vachon C, Tamimi RM (2011) Mammographic breast density and subsequent risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women according to tumor characteristics. J Natl Cancer Inst 103(15):1179–1189. doi:10.1093/jnci/djr225
Ciatto S, Visioli C, Paci E, Zappa M (2004) Breast density as a determinant of interval cancer at mammographic screening. Br J Cancer 90(2):393–396. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601548
Mandelson MT, Oestreicher N, Porter PL, White D, Finder CA, Taplin SH, White E (2000) Breast density as a predictor of mammographic detection: comparison of interval- and screen-detected cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst 92(13):1081–1087
Olsen AH, Bihrmann K, Jensen MB, Vejborg I, Lynge E (2009) Breast density and outcome of mammography screening: a cohort study. Br J Cancer 100(7):1205–1208. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604989
Huo CW, Chew GL, Britt KL, Ingman WV, Henderson MA, Hopper JL, Thompson EW (2014) Mammographic density—a review on the current understanding of its association with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 144(3):479–502. doi:10.1007/s10549-014-2901-2
Joensuu H, Lehtimaki T, Holli K, Elomaa L, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T, Kataja V, Anttila A, Lundin M, Isola J, Lundin J (2004) Risk for distant recurrence of breast cancer detected by mammography screening or other methods. JAMA J Am Med Assoc 292(9):1064–1073. doi:10.1001/jama.292.9.1064
Bertrand KA, Tamimi RM, Scott CG, Jensen MR, Pankratz VS, Visscher D, Norman A, Couch F, Shepherd J, Fan B, Chen YY, Ma L, Beck AH, Cummings SR, Kerlikowske K, Vachon CM (2013) Mammographic density and risk of breast cancer by age and tumor characteristics. Breast Cancer Res 15(6):R104. doi:10.1186/bcr3570
Sartor H, Borgquist S, Hartman L, Zackrisson S (2015) Do pathological parameters differ with regard to breast density and mode of detection in breast cancer? The Malmo Diet and Cancer Study. Breast 24(1):12–17. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2014.10.006
Antoni S, Sasco AJ, dos Santos Silva I, McCormack V (2013) Is mammographic density differentially associated with breast cancer according to receptor status? A meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 137(2):337–347
Olsson A, Borgquist S, Butt S, Zackrisson S, Landberg G, Manjer J (2012) Tumour-related factors and prognosis in breast cancer detected by screening. Br J Surg 99(1):78–87. doi:10.1002/bjs.7757
Olsson A, Sartor H, Borgquist S, Zackrisson S, Manjer J (2014) Breast density and mode of detection in relation to breast cancer specific survival: a cohort study. BMC Cancer 14:229. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-14-229
Ding J, Warren R, Girling A, Thompson D, Easton D (2010) Mammographic density, estrogen receptor status and other breast cancer tumor characteristics. Breast J 16(3):279–289. doi:10.1111/j.1524-4741.2010.00907.x
Ghosh K, Brandt KR, Sellers TA, Reynolds C, Scott CG, Maloney SD, Carston MJ, Pankratz VS, Vachon CM (2008) Association of mammographic density with the pathology of subsequent breast cancer among postmenopausal women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 17(4):872–879. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-0559
Aiello EJ, Buist DS, White E, Porter PL (2005) Association between mammographic breast density and breast cancer tumor characteristics. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 14(3):662–668. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-04-0327
Gucalp A, Tolaney S, Isakoff SJ, Ingle JN, Liu MC, Carey LA, Blackwell K, Rugo H, Nabell L, Forero A, Stearns V, Doane AS, Danso M, Moynahan ME, Momen LF, Gonzalez JM, Akhtar A, Giri DD, Patil S, Feigin KN, Hudis CA, Traina TA, Translational Breast Cancer Research C (2013) Phase II trial of bicalutamide in patients with androgen receptor-positive, estrogen receptor-negative metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19(19):5505–5512. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3327
Hu R, Dawood S, Holmes MD, Collins LC, Schnitt SJ, Cole K, Marotti JD, Hankinson SE, Colditz GA, Tamimi RM (2011) Androgen receptor expression and breast cancer survival in postmenopausal women. Clin Cancer Res 17(7):1867–1874. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2021
Park S, Park H, Koo J, Yang W, Kim S, Park B-W (2012) Higher expression of androgen receptor is a significant predictor for better endocrine-responsiveness in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat 133(1):311–320. doi:10.1007/s10549-011-1950-z
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thürlimann B, Senn H-J, members P (2011) Strategies for subtypes—dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol 22(8):1736–1747. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr304
Boyd NF, Martin LJ, Yaffe MJ, Minkin S (2011) Mammographic density and breast cancer risk: current understanding and future prospects. Breast Cancer Res 13(6):223. doi:10.1186/bcr2942
Eriksson L, Hall P, Czene K, Dos Santos Silva I, McCormack V, Bergh J, Bjohle J, Ploner A (2012) Mammographic density and molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Br J Cancer 107(1):18–23. doi:10.1038/bjc.2012.234
Pollan M, Ascunce N, Ederra M, Murillo A, Erdozain N, Ales-Martinez JE, Pastor-Barriuso R (2013) Mammographic density and risk of breast cancer according to tumor characteristics and mode of detection: a Spanish population-based case–control study. Breast Cancer Res 15(1):R9. doi:10.1186/bcr3380
Manjer J, Carlsson S, Elmstahl S, Gullberg B, Janzon L, Lindstrom M, Mattisson I, Berglund G (2001) The Malmo Diet and Cancer Study: representativity, cancer incidence and mortality in participants and non-participants. Eur J Cancer Prev 10(6):489–499
Berglund G, Elmstahl S, Janzon L, Larsson SA (1993) The Malmo Diet and Cancer Study. Design and feasibility. J Intern Med 233(1):45–51
Manjer J, Elmstahl S, Janzon L, Berglund G (2002) Invitation to a population-based cohort study: differences between subjects recruited using various strategies. Scand J Public Health 30(2):103–112. doi:10.1080/14034940210133771
Lagerlund M, Sontrop J, Zackrisson S (2013) Do reproductive and hormonal risk factors for breast cancer associate with attendance at mammography screening? Cancer Causes Control 24(9):1687–1694. doi:10.1007/s10552-013-0243-8
Borgquist S, Anagnostaki L, Jirstrom K, Landberg G, Manjer J (2007) Breast tumours following combined hormone replacement therapy express favourable prognostic factors. Int J Cancer 120(10):2202–2207. doi:10.1002/ijc.22542
Elebro K, Butt S, Dorkhan M, Jernström H, Borgquist S (2014) Age at first childbirth and oral contraceptive use are associated with risk of androgen receptor-negative breast cancer: the Malmö Diet and Cancer Cohort. Cancer Causes Control. doi:10.1007/s10552-014-0394-2
Collett K, Stefansson IM, Eide J, Braaten A, Wang H, Eide GE, Thoresen SO, Foulkes WD, Akslen LA (2005) A basal epithelial phenotype is more frequent in interval breast cancers compared with screen detected tumors. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 14(5):1108–1112. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-04-0394
Dawood S (2010) Triple-negative breast cancer. Drugs 70(17):2247–2258. doi:10.2165/11538150-000000000-00000
Yang W-T, Dryden M, Broglio K, Gilcrease M, Dawood S, Dempsey P, Valero V, Hortobagyi G, Atchley D, Arun B (2008) Mammographic features of triple receptor-negative primary breast cancers in young premenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat 111(3):405–410. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9810-6
Luck AA, Evans AJ, James JJ, Rakha EA, Paish EC, Green AR, Ellis IO (2008) Breast carcinoma with basal phenotype: mammographic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 191(2):346–351. doi:10.2214/AJR.07.2659
Franquet T, De Miguel C, Cozcolluela R, Donoso L (1993) Spiculated lesions of the breast: mammographic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 13(4):841–852
Ghosh K, Brandt KR, Reynolds C, Scott CG, Pankratz VS, Riehle DL, Lingle WL, Odogwu T, Radisky DC, Visscher DW, Ingle JN, Hartmann LC, Vachon CM (2012) Tissue composition of mammographically dense and non-dense breast tissue. Breast Cancer Res Treat 131(1):267–275. doi:10.1007/s10549-011-1727-4
Ogawa Y, Hai E, Matsumoto K, Ikeda K, Tokunaga S, Nagahara H, Sakurai K, Inoue T, Nishiguchi Y (2008) Androgen receptor expression in breast cancer: relationship with clinicopathological factors and biomarkers. Int J Clin Oncol 13(5):431–435. doi:10.1007/s10147-008-0770-6
Berg WA, Campassi C, Langenberg P, Sexton MJ (2000) Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System: inter- and intraobserver variability in feature analysis and final assessment. AJR Am J Roentgenol 174(6):1769–1777
Ciatto S, Houssami N, Apruzzese A, Bassetti E, Brancato B, Carozzi F, Catarzi S, Lamberini MP, Marcelli G, Pellizzoni R, Pesce B, Risso G, Russo F, Scorsolini A (2005) Categorizing breast mammographic density: intra- and interobserver reproducibility of BI-RADS density categories. Breast 14(4):269–275. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2004.12.004
Kerlikowske K, Grady D, Barclay J, Frankel SD, Ominsky SH, Sickles EA, Ernster V (1998) Variability and accuracy in mammographic interpretation using the American College of Radiology Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System. J Natl Cancer Inst 90(23):1801–1809
Nicholson BT, LoRusso AP, Smolkin M, Bovbjerg VE, Petroni GR, Harvey JA (2006) Accuracy of assigned BI-RADS breast density category definitions. Acad Radiol 13(9):1143–1149. doi:10.1016/j.acra.2006.06.005
Ooms EA, Zonderland HM, Eijkemans MJC, Kriege M, Mahdavian Delavary B, Burger CW, Ansink AC (2007) Mammography: interobserver variability in breast density assessment. Breast 16(6):568–576. doi:10.1016/j.breast.2007.04.007
Harvey JA, Gard CC, Miglioretti DL, Yankaskas BC, Kerlikowske K, Buist DS, Geller BA, Onega TL (2013) Reported mammographic density: film-screen versus digital acquisition. Radiology 266(3):752–758. doi:10.1148/radiol.12120221
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Anna Hwasser for excellent data management, Elise Nilsson for committed assistance with tumor tissue handling, and Lola Anagnostaki for assistance with pathology assessments. This work has received government funding for clinical research within the National Health Services.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sartor, H., Zackrisson, S., Elebro, K. et al. Mammographic density in relation to tumor biomarkers, molecular subtypes, and mode of detection in breast cancer. Cancer Causes Control 26, 931–939 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-015-0576-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-015-0576-6