Abstract
Objective:The aim of this study was to investigate the associations between meat and fish consumption and APC mutation status and hMLH1 expression in colon and rectal cancer.
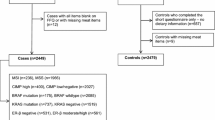
Methods:The associations were investigated in the Netherlands Cohort Study, and included 434 colon and 154 rectal cancer patients on whom case-cohort analyses (subcohort n = 2948) were performed.
Results:Total meat consumption was not associated with the endpoints studied. Meat product (i.e. processed meat) consumption showed a positive association with colon tumours harbouring a truncating APC mutation, whereas beef consumption was associated with an increased risk of colon tumours without a truncating APC mutation (incidence rate ratio (RR) highest versus lowest quartile of intake 1.61, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.96–2.71, p-trend = 0.04 and 1.58, 95% CI 1.10–2.25, p-trend = 0.01, respectively). Consumption of other meat (horsemeat, lamb, mutton, frankfurters and deep-fried meat rolls) was associated with an increased risk of rectal cancer without a truncating APC mutation (RR intake versus no intake 1.79, 95% CI 1.10–2.90). No associations were observed for meat consumption and tumours lacking hMLH1 expression.
Conclusions:Our data indicate that several types of meat may contribute differently to the aetiology of colon and rectal cancer, depending on APC mutation status but not hMLH1 expression of the tumour.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
JD Potter (1996) ArticleTitleNutrition and colorectal cancer Cancer Causes Control 7 IssueID1 127–146 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00115644 Occurrence Handle8850441
InstitutionalAuthorNameWorld Cancer Research Fund, American Institute for Cancer Research (1997) Food, nutrition and the prevention of cancer: A global perspective EditionNumber1 WCRF/AIRC Washington, DC
T Norat A Lukanova P Ferrari E Riboli (2002) ArticleTitleMeat consumption and colorectal cancer risk: Dose-response meta- analysis of epidemiological studies Int J Cancer 98 IssueID2 241–256 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ijc.10126 Occurrence Handle11857415
EK Wei E Giovannucci K Wu et al. (2004) ArticleTitleComparison of risk factors for colon and rectal cancer Int J Cancer 108 IssueID3 433–442 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ijc.11540 Occurrence Handle14648711
B. Iacopetta (2002) ArticleTitleAre there two sides to colorectal cancer? Int J Cancer 101 IssueID5 403–408 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ijc.10635 Occurrence Handle12216066
M Brink AF Goeij ParticleDe MP Weijenberg et al. (2003) ArticleTitleK-ras oncogene mutations in sporadic colorectal cancer in The Netherlands Cohort Study Carcinogenesis 24 IssueID4 703–710 Occurrence Handle10.1093/carcin/bgg009 Occurrence Handle12727799
M Lüchtenborg MP Weijenberg GM Roemen et al. (2004) ArticleTitleAPC mutations in sporadic colorectal carcinomas from The Netherlands Cohort Study Carcinogenesis 25 IssueID7 1219–1226 Occurrence Handle10.1093/carcin/bgh117 Occurrence Handle14976131
ER Fearon B Vogelstein (1990) ArticleTitleA genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis Cell 61 IssueID5 759–767 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-I Occurrence Handle2188735
SM Powell N Zilz Y Beazer-Barclay et al. (1992) ArticleTitleAPC mutations occur early during colorectal tumorigenesis Nature 359 IssueID6392 235–237 Occurrence Handle10.1038/359235a0 Occurrence Handle1528264
Y Miyoshi H Nagase H Ando et al. (1992) ArticleTitleSomatic mutations of the APC gene in colorectal tumors: mutation cluster region in the APC gene Human Mol Genet 1 IssueID4 229–233
S Cottrell D Bicknell L Kaklamanis WF Bodmer (1992) ArticleTitleMolecular analysis of APC mutations in familial adenomatous polyposis and sporadic colon carcinomas Lancet 340 IssueID8820 626–630 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0140-6736(92)92169-G Occurrence Handle1355210
M Miyaki M Konishi R Kikuchi-Yanoshita et al. (1994) ArticleTitleCharacteristics of somatic mutation of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene in colorectal tumors Cancer Res 54 IssueID11 3011–3020 Occurrence Handle8187091
K Yashima S Nakamori Y Murakami et al. (1994) ArticleTitleMutations of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene in the mutation cluster region: comparison of human pancreatic and colorectal cancers Int J Cancer 59 IssueID1 43–47 Occurrence Handle7927902
M Konishi R Kikuchi-Yanoshita K Tanaka et al. (1996) ArticleTitleMolecular nature of colon tumors in hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer, familial polyposis, and sporadic colon cancer Gastroenterology 111 IssueID2 307–317 Occurrence Handle10.1053/gast.1996.v111.pm8690195 Occurrence Handle8690195
C Filippo ParticleDe C Luceri G Caderni et al. (2002) ArticleTitleMutations of the APC gene in human sporadic colorectal cancers Scand J Gastroenterol 37 IssueID9 1048–1053 Occurrence Handle10.1080/003655202320378248 Occurrence Handle12374230
SH Kim Sh P Kaminker J Campisi (2002) ArticleTitleTelomeres, aging and cancer: in search of a happy ending Oncogene 21 IssueID4 503–511 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.onc.1205077 Occurrence Handle11850775
B Diergaarde WL Geloof Particlevan GN Muijen Particlevan FJ Kok E. Kampman (2003) ArticleTitleDietary factors and the occurrence of truncating APC mutations in sporadic colon carcinomas: a Dutch population-based study Carcinogenesis 24 IssueID2 283–90 Occurrence Handle10.1093/carcin/24.2.283 Occurrence Handle12584179
S Olschwang R Hamelin P Laurent-Puig et al. (1997) ArticleTitleAlternative genetic pathways in colorectal carcinogenesis Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94 IssueID22 12122–12127 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.94.22.12122 Occurrence Handle9342373
S Salahshor U Kressner L Pahlman B Glimelius G Lindmark A. Lindblom (1999) ArticleTitleColorectal cancer with and without microsatellite instability involves different genes Genes Chromosomes Cancer 26 IssueID3 247–252 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1098-2264(199911)26:3<247::AID-GCC9>3.0.CO;2-H Occurrence Handle10502323
WS Samowitz JA Holden K Curtin et al. (2001) ArticleTitleInverse relationship between Microsatellite Instability and K-ras and p53 Gene Alterations in Colon Cancer Am J Pathol 158 IssueID4 1517–1524 Occurrence Handle11290569
SN Thibodeau AJ French JM Cunningham et al. (1998) ArticleTitleMicrosatellite instability in colorectal cancer: different mutator phenotypes and the principal involvement of hMLH1 Cancer Res 58 IssueID8 1713–8
M Toyota T Ushijima H Kakiuchi et al. (1996) ArticleTitleGenetic alterations in rat colon tumors induced by heterocyclic amines Cancer 77 IssueID8 Suppl 1593–1597 Occurrence Handle8608549
SA Bingham R Hughes AJ Cross (2002) ArticleTitleEffect of white versus red meat on endogenous N-nitrosation in the human colon and further evidence of a dose response J Nutr 132 IssueID11 Suppl 3522S–3525S Occurrence Handle12421881
SS Mirvish J Haorah L Zhou ML Clapper KL Harrison AC Povey (2002) ArticleTitleTotal N-nitroso compounds and their precursors in hot dogs and in the gastrointestinal tract and feces of rats and mice: possible etiologic agents for colon cancer J Nutr 132 IssueID11 Suppl 3526S–3529S Occurrence Handle12421882
B Diergaarde H Braam GN Muijen Particlevan MJ Ligtenberg FJ Kok E Kampman (2003) ArticleTitleDietary factors and microsatellite instability in sporadic colon carcinomas Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 12 IssueID11 Pt 1 1130–1136 Occurrence Handle14652271
PA Brandt Particlevan den RA Goldbohm P ‘t Veer Particlevan A Volovics RJ Hermus F Sturmans (1990) ArticleTitleA large-scale prospective cohort study on diet and cancer in The Netherlands J Clin Epidemiol 43 IssueID3 285–295 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0895-4356(90)90009-E Occurrence Handle2313318
PA Brandt Particlevan den LJ Schouten RA Goldbohm E Dorant PM Hunen (1990) ArticleTitleDevelopment of a record linkage protocol for use in the Dutch Cancer Registry for Epidemiological Research Int J Epidemiol 19 IssueID3 553–8 Occurrence Handle2262247
RA Goldbohm PA Brandt Particlevan den P ‘t Veer Particlevan et al. (1994) ArticleTitleA prospective cohort study on the relation between meat consumption and the risk of colon cancer Cancer Res 54 IssueID3 718–723 Occurrence Handle8306333
RA Goldbohm PA Brandt Particlevan den HA Brants et al. (1994) ArticleTitleValidation of a dietary questionnaire used in a large-scale prospective cohort study on diet and cancer Eur J Clin Nutr 48 IssueID4 253–265 Occurrence Handle8039485
DY Lin LJ Wei (1989) ArticleTitleThe robust inference for the Cox Proportional Hazards Model JASA 84 IssueID408 1074–1078
D Schoenfeld (1982) ArticleTitlePartial residuals for the proportional hazards regression models Biometrika 69 IssueID1 239–241
MS Sandhu IR White K McPherson (2001) ArticleTitleSystematic review of the prospective cohort studies on meat consumption and colorectal cancer risk: a meta-analytical approach Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 10 IssueID5 439–446 Occurrence Handle11352852
R Fodde R Smits H Clevers (2001) ArticleTitleAPC, signal transduction and genetic instability in colorectal cancer Nat Rev Cancer 1 IssueID1 55–67 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35094067 Occurrence Handle11900252
M Brink MP Weijenberg AF Goeij Particlede et al. (2005) ArticleTitleMeat consumption and K-ras mutations in sporadic colon and rectal cancer in The Netherlands Cohort Study Br J Cancer 92 1310–1320 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.bjc.6602491 Occurrence Handle15812479
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lüchtenborg, M., Weijenberg, M.P., de Goeij, A.F.P.M. et al. Meat and Fish Consumption, APCGene Mutations and hMLH1 Expression in Colon and Rectal Cancer: a Prospective Cohort Study (The Netherlands). Cancer Causes Control 16, 1041–1054 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-005-0239-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-005-0239-0