Abstract
Purpose
The transcription factors ZEB1 and ZEB2 mediate epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastatic progression in numerous malignancies including breast cancer. ZEB1 and ZEB2 drive EMT through transcriptional repression of cell–cell junction proteins and members of the tumor suppressive miR200 family. However, in estrogen receptor positive (ER +) breast cancer, the role of ZEB2 as an independent driver of metastasis has not been fully investigated.
Methods
In the current study, we induced exogenous expression of ZEB2 in ER + MCF-7 and ZR-75–1 breast cancer cell lines and examined EMT gene expression and metastasis using dose–response qRT-PCR, transwell migration assays, proliferation assays with immunofluorescence of Ki-67 staining. We used RNA sequencing to identify pathways and genes affected by ZEB2 overexpression. Finally, we treated ZEB2-overexpressing cells with 17β-estradiol (E2) or ICI 182,780 to evaluate how ZEB2 affects estrogen response.
Results
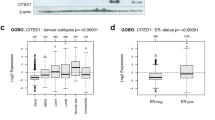
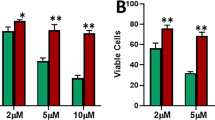
Contrary to expectation, we found that ZEB2 did not increase canonical epithelial nor decrease mesenchymal gene expressions. Furthermore, ZEB2 overexpression did not promote a mesenchymal cell morphology. However, ZEB1 and ZEB2 protein expression induced significant migration of MCF-7 and ZR-75-1 breast cancer cells in vitro and MCF-7 xenograft metastasis in vivo. Transcriptomic (RNA sequencing) pathway analysis revealed alterations in estrogen signaling regulators and pathways, suggesting a role for ZEB2 in endocrine sensitivity in luminal A breast cancer. Expression of ZEB2 was negatively correlated with estrogen receptor complex genes in luminal A patient tumors. Furthermore, treatment with 17β-estradiol (E2) or the estrogen receptor antagonist ICI 182,780 had no effect on growth of ZEB2-overexpressing cells.
Conclusion
ZEB2 is a multi-functional regulator of drug sensitivity, cell migration, and metastasis in ER + breast cancer and functions through non-canonical mechanisms.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kohler BA, Sherman RL, Howlander N, Jemal A, Ryerson AB, Henry KA, Boscoe FP, Cronin KA, Lake A, Noone AM et al (2015) Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2011, featuring incidence of breast cancer subtypes by race/ethnicity, poverty, and state. J Natl Cancer Inst 107(6):djv048.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2018) Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin 68:7–30
Guo F, Kuo Y-f, Shih YCT, Giordano SH, Berenson AB (2018) Trends in breast cancer mortality by stage at diagnosis among young women in the United States. Cancer 124(17):3500–3509
Hashmi AA, Aijaz S, Khan SM, Mahboob R, Irfan M, Zafar NI, Nisar M, Siddiqui M, Edhi MM, Faridi N et al (2018) Prognostic parameters of luminal A and luminal B intrinsic breast cancer subtypes of Pakistani patients. World J Surg Oncol 16(1).
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, Van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA et al (2000) Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 406:747–752
Meisel JL, Venur VA, Gnant M & Carey L (2018) Evolution of targeted therapy in breast cancer: where precision medicine began. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 78–86.
Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL (2009) Biological determinants of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 9:631
Giulliano M, Schifp R, Osborne CK, Trivedi MV (2011) Biological mechanisms and clinical implications of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Breast 20(Suppl 3):S42–S49
Hiscox S, Gee J, Nicholson RI (2007) Endocrine resistance and breast cancer invasion. In: Mansel RE, Fodstad O, Jiang WG (Eds.) Metastasis of Breast Cancer. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands.
Yuan J, Liu M, Yang L, Tu G, Zhu Q, Chen M, Cheng H, Lou H, Fu W, Li Z, Yang G (2015) Acquisition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in the tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cell: a new role for G protein-coupled estrogen receptor in mediating tamoxifen resistance through cancer-associated fibroblast-derived fibronectin and beta1-integrin signaling pathway in tumor cells. Breast Cancer Res 17(1):69
Kalluri R, Weinberg RA (2009) The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest 119:1420–1428
Savagner PP (2010) The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) phenomenon. Ann Oncol 21(Suppl 7):vii89-vii92.
Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R (2014) Molecular mechanisms of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15(3):178–196
Thiery JP, Acloqque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 139(5):871–890
Welch DR, Hurst DR (2019) Defining the hallmarks of metastasis. Cancer Res 79(12).
Aigner K, Dampier B, Descovich L, Mikula M, Sultan A, Schreiber M, Mikulits W, Brabletz T, Strand D, Obrist P et al (2007) The transcription factor ZEB1 (deltaEF1) promotes tumour cell dedifferentiation by repressing master regulators of epithelial polarity. Oncogene 26(49):6979–6988
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G, Kang Y (2008) The miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer cell migration by directly targeting of E-cadherin transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem 283:14910–14914
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N, Bert AG, Wang J, Shannon MF, Goodall GJ (2008) A double-negative feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the microRNA-200 family regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 68:7846–7854
Kurahara H, Takao S, Maemura K, Mataki Y, Kuwahata T, Maeda K, Ding Q, Sakoda M, Iino S, Ishigami S et al (2012) Epithelial–mesenchymal transition and mesenchymal–epithelial transition via regulation of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2 expression in pancreatic cancer. J Surg Oncol 105:655–661
Voutsadakis IA (2016) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and regulation of EMT factors by steroid nuclear receptors in breast cancer: A review and in silico investigation. J Clin Med 5(1):11
Vandewalle C, Comijn J, De Craene B, Vermassen P, Bruyneel E, Andersen H, Tulchinsky E, Van Roy F, Berx G (2005) SIP1/ZEB2 induces EMT by repressing genes of different epithelial cell–cell junctions. Nucleic Acids Res 33:6566–6578
Rhodes LV, Antoon JW, Muir SE, Elliott S, Beckman BS, Burow ME (2010) Effects of human mesenchymal stem cells on ER-positive human breast carcinoma cells mediated through ER-SDF-1/CXCR4 crosstalk. Mol Cancer 9:295
Rhodes LV, Tate CR, Segar HC, Burks HE, Phamduy TB, Hoang V, Elliott S, Gilliam D, Pounder FN, Anbalagan M et al (2014) Suppression of triple-negative breast cancer metastasis by pan-DAC inhibitor panobinostat via inhibition of ZEB family of EMT master regulators. Breast Cancer Res Treat 145:593–604
Martin EC, Rhodes LV, Elliott S, Krebs AE, Nephew KP, Flemington EK, Collins-Burow BM, Burow ME (2014) microRNA regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin expression and activity controls estrogen receptor function and RAD001 sensitivity. Mol Cancer 13:229
Miller DFB, Yan PS, Buechlein A, Rodriguez BA, Yilmaz AS, Goel S, Lin H, Collins-Burow B, Rhodes LV, Braun C, Pradeep S et al (2013) A new method for stranded whole transcriptome RNA-seq. Methods (San Diego, Calif.) 63:126–134.
Jezequel P, Campone M, Gouraud W, Guerin-Charbonnel C, Leux C, Ricolleau G, Campion L (2012) bc-GenExMiner: an easy-to-use online platform for gene prognostic analyses in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 131:765–775
Jézéquel P, Gouraud W, Ben Azzouz F, Guérin-Charbonnel C, Juin P, Lasla H, Campone M (2021) bc-GenExMiner 4.5: new mining module computes breast cancer differential gene expression analyses. Database (Oxford) baab007
Sánchez-Tillό E, Siles L, De Barrios O, Cuatrecasas M, Vaquero EC, Castells A, Postigo A (2011) Expanding roles of ZEB factors in tumorigenesis and tumor progression. Am J Cancer Res 1:897–912
Hill L, Browne G, Tulchinsky E (2013) ZEB/miR-200 feedback loop: at the crossroads of signal transduction in cancer. Int J Cancer 132:745–754
Friedl P, Gilmour D (2009) Collective cell migration in morphogenesis, regeneration and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:445–457
Friedl P, Locker J, Sahai E, Segall JE (2012) Classifying collective cancer cell invasion. Nat Cell Biol 14:777–783
Yilmaz M, Christofori G (2010) Mechanisms of motility in metastasizing cells. Mol Cancer Res 8:629–642
Yilmaz M, Christofori G, Lehembre F (2007) Distinct mechanisms of tumor invasion and metastasis. Trends Mol Med 13:535–541
Qi S, Song Y, Peng Y, Wang H, Long H, Yu X et al (2012) ZEB2 mediates multiple pathways regulating cell proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis in glioma. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038842
Marino M, Galluzzo P, Ascenzi P (2006) Estrogen signaling multiple pathways to impact gene transcription. Curr Genomics 7:497–508
Saha Roy S, Vadlamudi RK (2012) Role of estrogen receptor signaling in breast cancer metastasis. Int J Breast Cancer 2012:654698.
Theodorou V, Stark R, Menon S, Carroll JS (2013) GATA3 acts upstream of FOXA1 in mediating ESR1 binding by shaping enhancer accessibility. Genome Res 23:12–22
Hurtado A, Holmes KA, Ross-Innes CS, Schmidt D, Carroll JS (2011) FOXA1 is a critical determinant of estrogen receptor function and endocrine response. Nat Genet 43:27–33
Mejlvang J, Kriajevska M, Vandewalle C, Chernova T, Saayan AE, Berx G, Mellon JK, Tulchinsky E (2007) Direct repression of cyclin D1 by SIP1 attenuates cell cycle progression in cells undergoing an epithelial mesenchymal transition. Mol Biol Cell 18:4615–4624
Dai YH, Tang YP, Zhu HY, Lv L, Chu Y, Zhou YQ, Hou JR (2012) ZEB2 promotes the metastasis of gastric cancer and modulates epithelial mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer cells. Dig Dis Sci 57:1253–1260
You J, Li Y, Fang N, Liu B, Zu L, Chang R, Li X, Zhou Q (2014) MiR-132 Suppresses the migration and invasion of lung cancer cells via targeting the EMT regulator ZEB2. PLOS One 9:e91827
Kong YH, Syed Zanaruddin SN, Lau SH, Ramanathan A, Kallarakkal TG, Vincent-Chong VK, Wan Mustafa WM, Abraham MT, Abdul Rahman ZA, Zain RB et al (2015) Co-expression of TWIST1 and ZEB2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma is associated with poor survival. PLOS One 10:e0134045
Wang Q, Jiang H, Deng X, Fang W, Guo S (2015) Expressions of ZEB2 and C-myc in epithelial ovarian cancer and their clinical significance Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 35:1765–9.
Brabletz S, Brabletz T (2010) The ZEB/miR-200 feedback loop—a motor of cellular plasticity in development and cancer? EMBO Rep 11:670–677
Comijn J, Berx G, Vermassen P, Verschueren K, Van Grunsven L, Bruyneel E, Mareel M, Huylebroeck D, Van Roy F (2001) The two-handed E box binding zinc finger protein SIP1 downregulates E-cadherin and induces invasion. Mol Cell 7:1267–1278
Miyoshi A, Kitajima Y, Sumi K, Sato K, Hagiwara A, Koga Y, Miyazaki K (2004) Snail and SIP1 increase cancer invasion by upregulating MMP family in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer 90:1265–1273
Tsai JH, Yang J (2013) Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in carcinoma metastasis. Genes Dev 27:2192–2206
Krakhmal NV, Zavyalova MV, Denisov EV, Vtorushin SV, Perelmuter VM (2015) Cancer invasion: patterns and mechanisms. Acta Naturae 7:17–28
Campbell K, Casanova J (2016) A common framework for EMT and collective cell migration. Development 143:4291–4300
Garg M (2017) Epithelial, mesenchymal and hybrid epithelial/mesenchymal phenotypes and their clinical relevance in cancer metastasis. Expert Rev Mol Med 19:e3.
Jolly MK, Boareto M, Huang B, Jia D, Lu M, Ben-Jacob E, Onuchic JN, Levine H (2015) Implications of the hybrid epithelial/mesenchymal phenotype in metastasis. Front Oncol 5:155
Tokunaga E, Hisamatsu Y, Tanaka K, Yamashita N, Saeki H, Oki E, Kitao H, Maehara Y (2014) Molecular mechanisms regulating the hormone sensitivity of breast cancer. Cancer Sci 105:1377–1383
Osborne CK, Schiff R (2011) Mechanisms of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Annu Rev Med 62:233–247
Albergaria A, Paredes J, Sousa B, Milanezi F, Carneiro V, Bastos J, Costa S, Viera D, Lopes N, Lam EW et al (2009) Expression of FOXA1 and GATA-3 in breast cancer: the prognostic significance in hormone receptor-negative tumours. Breast Cancer Res 11(3):R40
Hosoda M, Yamamoto M, Nakano K, Hatanaka KC, Takakuwa E, Hatanaka Y, Matsuno Y, Yamashita H (2014) Differential expression of progesterone receptor, FOXA1, GATA3, and p53 between pre- and postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 144:249–261
Hisamatsu Y, Tokunaga E, Yamashita N, Akiyoshi S, Okada S, Nakashima Y, Taketani K, Aishima S, Oda Y, Morita M, Maehara Y (2015) Impact of GATA-3 and FOXA1 expression in patients with hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer 22:520–528
Acknowledgements
Thank you to Dr. Van T. Hoang, PhD and the animal vivarium staff at Tulane University School of Medicine for their assistance with the in vivo experiments. High throughput sequencing was performed at the Center for Genomics and Bioinformatics at Indiana University, Bloomington.
Funding
This project was funded by the National Institutes of Health R01-CA174785-01A1 (BMC-B) and the National Institutes of Health R01-CA125806-02 (MEB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
All procedures involving these animals were conducted in compliance with State and Federal laws, standards of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, and guidelines established by the Tulane University Animal Care and Use Committee. The Tulane University Animal Care and Use Committee approved the use of animals in this specific study. The facilities and laboratory animal program of Tulane University are accredited by the Association for the Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burks, H.E., Matossian, M.D., Rhodes, L.V. et al. ZEB2 regulates endocrine therapy sensitivity and metastasis in luminal a breast cancer cells through a non-canonical mechanism. Breast Cancer Res Treat 189, 25–37 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-021-06256-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-021-06256-x