Abstract
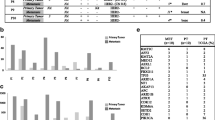
Women with contralateral breast cancer (CBC) have significantly worse prognosis compared to women with unilateral cancer. A possible explanation of the poor prognosis of patients with CBC is that in a subset of patients, the second cancer is not a new primary tumor but a metastasis of the first cancer that has potentially obtained aggressive characteristics through selection of treatment. Exome and whole-genome sequencing of solid tumors has previously been used to investigate the clonal relationship between primary tumors and metastases in several diseases. In order to assess the relationship between the first and the second cancer, we performed exome sequencing to identify somatic mutations in both first and second cancers, and compared paired normal tissue of 25 patients with metachronous CBC. For three patients, we identified shared somatic mutations indicating a common clonal origin thereby demonstrating that the second tumor is a metastasis of the first cancer, rather than a new primary cancer. Accordingly, these patients all developed distant metastasis within 3 years of the second diagnosis, compared with 7 out of 22 patients with non-shared somatic profiles. Genomic profiling of both tumors help the clinicians distinguish between true CBCs and subsequent metastases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Globocan 2008 [http://globocan.iarc.fr]
Brenner H, Engelsmann B, Stegmaier C, Ziegler H (1993) Clinical epidemiology of bilateral breast cancer. Cancer 72:3629–3635
Hartman M, Czene K, Reilly M, Adolfsson J, Bergh J, Adami H-O, Dickman PW, Hall P (2007) Incidence and prognosis of synchronous and metachronous bilateral breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 25:4210–4216
Janschek E, Kandioler-Eckersberger D, Ludwig C, Kappel S, Wolf B, Taucher S, Rudas M, Gnant M, Jakesz R (2001) Contralateral breast cancer: molecular differentiation between metastasis and second primary cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 67:1–8
Imyanitov EN, Suspitsin EN, Grigoriev MY, Togo AV, Kuligina ES, Belogubova EV, Pozharisski KM, Turkevich EA, Rodriquez C, Cornelisse CJ, Hanson KP, Theillet C (2002) Concordance of allelic imbalance profiles in synchronous and metachronous bilateral breast carcinomas. Int J Cancer 100:557–564
Brommesson S, Jönsson G, Strand C, Grabau D, Malmström P, Ringnér M, Fernö M, Hedenfalk I (2008) Tiling array-CGH for the assessment of genomic similarities among synchronous unilateral and bilateral invasive breast cancer tumor pairs. BMC Clin Pathol 8:6
Teixeira MR, Ribeiro FR, Torres L, Pandis N, Andersen JA, Lothe RA, Heim S (2004) Assessment of clonal relationships in ipsilateral and bilateral multiple breast carcinomas by comparative genomic hybridisation and hierarchical clustering analysis. Br J Cancer 91(4):775–782
Ding L, Ley TJ, Larson DE, Miller CA, Koboldt DC, Welch JS, Ritchey JK, Young MA, Lamprecht T, Mclellan MD, Mcmichael JF, Wallis JW, Lu C, Shen D, Harris CC, Dooling DJ, Fulton RS, Fulton LL, Chen K, Schmidt H, Kalicki-Veizer J, Magrini VJ, Cook L, Mcgrath SD, Vickery TL, Wendl MC, Heath S, Watson MA, Link DC, Tomasson MH et al (2012) Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by whole-genome sequencing. Nature 481:506–509
Ding L, Ellis MJ, Li S, Larson DE, Chen K, Wallis JW, Harris CC, Mclellan MD, Fulton RS, Fulton LL, Abbott RM, Hoog J, Dooling DJ, Koboldt DC, Schmidt H, Kalicki J, Zhang Q, Chen L, Lin L, Wendl MC, Mcmichael JF, Magrini VJ, Cook L, Mcgrath SD, Vickery TL, Appelbaum E, Deschryver K, Davies S, Guintoli T, Lin L et al (2010) Genome remodelling in a basal-like breast cancer metastasis and xenograft. Nature 464:999–1005
Van Allen EM, Foye A, Wagle N, Kim W, Carter SL, McKenna A, Simko JP, Garraway LA, Febbo PG (2013) Successful whole-exome sequencing from a prostate cancer bone metastasis biopsy. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 17:23–27
Haffner MC, Mosbruger T, Esopi DM, Fedor H, Heaphy CM, Walker DA, Adejola N, Gürel M, Hicks J, Meeker AK, Halushka MK, Simons JW, Isaacs WB, De Marzo AM, Nelson WG, Yegnasubramanian S (2013) Tracking the clonal origin of lethal prostate cancer. J Clin Invest 123:4918–4922
SeqPrep [https://github.com/jstjohn/SeqPrep]. Accessed 10 March 2014
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R (2009) 1000 genome project data processing subgroup: the sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079
Picard [http://picard.sourceforge.net]. version 1.85. Accessed 10 Feb 2013
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M, DePristo MA (2010) The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20:1297–1303
Cibulskis K, Lawrence MS, Carter SL, Sivachenko A, Jaffe D, Sougnez C, Gabriel SB, Meyerson M, Lander ES, Getz G (2013) Sensitive detection of somatic point mutations in impure and heterogeneous cancer samples. Nat Biotechnol 31:213–219
Network Cancer Genome Atlas (2012) Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 490:61–70
Banelli B, Casciano I, Di Vinci A, Gatteschi B, Levaggi A, Carli F, Bighin C, Salvi S, Allemanni G, Ghiorzo P, Pronzato P, Venturini M, Romani M, Del Mastro L (2010) Pathological and molecular characteristics distinguishing contralateral metastatic from new primary breast cancer. Ann Oncol 21:1237–1242
Bastien RR, guez-Lescure LR, Ebbert MT, Prat A, Rriz BM, Rowe L, Miller P, Ruiz-Borrego M, Anderson D, Lyons B, lvarez I, Dowell T, Wall D, Segu MN, Barley L, Boucher KM, Alba E, Pappas L, Davis CA, Aranda I, Fauron C, Stijleman IJ, Palacios J, Antón A, Carrasco E, Caballero RA, Ellis MJ, Nielsen TO, Perou CM, Astill M et al (2012) PAM50 breast cancer subtyping by RT-qPCR and concordance with standard clinical molecular markers. BMC Med Genomics 5(1):44
Ivshina AV, George J, Senko O, Mow B, Putti TC, Smeds J, Lindahl T, Pawitan Y, Hall P, Nordgren H, Wong JEL, Liu ET, Bergh J, Kuznetsov VA, Miller LD (2006) Genetic reclassification of histologic grade delineates new clinical subtypes of breast cancer. Cancer Res 66:10292–10301
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Science for Life Laboratory Stockholm Application lab for sequencing and Gabriela Prochazka, Anna Westring, Simon Sundling, and Heidi Talvitie for help with library preparation of the samples.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klevebring, D., Lindberg, J., Rockberg, J. et al. Exome sequencing of contralateral breast cancer identifies metastatic disease. Breast Cancer Res Treat 151, 319–324 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3403-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3403-6