Abstract
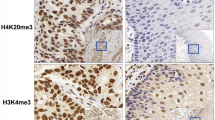
Repressive histone tail modifications have been associated with molecular breast cancer subtypes. We investigated whether histone 3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3) and histone 3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) were associated with tumor features and subtypes while adjusting for prospectively collected reproductive and lifestyle breast cancer risk factors. We have tissue microarray data with immunohistochemical marker information on 804 incident cases of invasive breast cancer diagnosed from 1976–2000 in the Nurses’ Health Study. Tissue microarray sections were stained for global H3K9me3 and H3K27me3, and scored into four categories. Multivariate odds ratios (OR) and 95 % confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using logistic regression models for tumor features and subtypes, adjusting for breast cancer risk factors. While there were no significant associations between H3K9me3 and tumor features, H3K27me3 was significantly associated with lower grade tumors compared to high grade tumors in the multivariate model (OR = 1.95, 95 % CI 1.35–2.81, p = 0.0004). H3K27me3 was suggestively associated with estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) tumors (OR = 1.47, 95 % CI 0.97–2.23, p = 0.07). In subtype analyses, H3K27me3 was positively associated with the luminal A subtype compared to all other subtypes (OR = 1.42, 95 % CI 1.14–1.77, p = 0.002), and was inversely associated with HER2-type (OR = 0.58, 95 % CI 0.37–0.91, p = 0.02) and basal-like breast cancer (OR = 0.52, 95 % CI 0.36–0.76, p = 0.0006). In the largest immunohistochemical examination of H3K9me3 and H3K27me3 in breast cancer, we found that H3K27me3 positivity, but not H3K9me3, was associated with lower grade tumors and the luminal A subtype after adjusting for reproductive and lifestyle breast cancer risk factors.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- BRCA1:
-
Breast cancer 1
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CK5/6:
-
Cytokeratin 5/6
- DAB:
-
Diaminobenzidine
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- EZH2:
-
Enhancer of zeste homolog 2
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- FFPE:
-
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded
- H3:
-
Histone 3
- H3K9me3:
-
Histone 3 lysine 9 trimethylation
- H3K27me3:
-
Histone 3 lysine 27 trimethylation
- HER2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- NHS:
-
Nurses’ Health Study
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- PMH:
-
Post-menopausal hormone
- PR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- PRC2:
-
Polycomb repressive complex 2
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- TMA:
-
Tissue microarray
- TNBC:
-
Triple-negative breast cancer
References
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Thorsen T, Quist H, Matese JC, Brown PO, Botstein D, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL (2001) Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(19):10869–10874
Polyak K (2011) Heterogeneity in breast cancer. J Clin Invest 121(10):3786–3788. doi:10.1172/jci60534
Yang XR, Chang-Claude J, Goode EL, Couch FJ, Nevanlinna H, Milne RL, Gaudet M, Schmidt MK, Broeks A, Cox A, Fasching PA, Hein R, Spurdle AB, Blows F, Driver K, Flesch-Janys D, Heinz J, Sinn P, Vrieling A, Heikkinen T, Aittomaki K, Heikkila P, Blomqvist C, Lissowska J, Peplonska B, Chanock S, Figueroa J, Brinton L, Hall P, Czene K, Humphreys K, Darabi H, Liu J, Van ‘t Veer LJ, van Leeuwen FE, Andrulis IL, Glendon G, Knight JA, Mulligan AM, O’Malley FP, Weerasooriya N, John EM, Beckmann MW, Hartmann A, Weihbrecht SB, Wachter DL, Jud SM, Loehberg CR, Baglietto L, English DR, Giles GG, McLean CA, Severi G, Lambrechts D, Vandorpe T, Weltens C, Paridaens R, Smeets A, Neven P, Wildiers H, Wang X, Olson JE, Cafourek V, Fredericksen Z, Kosel M, Vachon C, Cramp HE, Connley D, Cross SS, Balasubramanian SP, Reed MW, Dork T, Bremer M, Meyer A, Karstens JH, Ay A, Park-Simon TW, Hillemanns P, Arias Perez JI, Menendez Rodriguez P, Zamora P, Benitez J, Ko YD, Fischer HP, Hamann U, Pesch B, Bruning T, Justenhoven C, Brauch H, Eccles DM, Tapper WJ, Gerty SM, Sawyer EJ, Tomlinson IP, Jones A, Kerin M, Miller N, McInerney N, Anton-Culver H, Ziogas A, Shen CY, Hsiung CN, Wu PE, Yang SL, Yu JC, Chen ST, Hsu GC, Haiman CA, Henderson BE, Le Marchand L, Kolonel LN, Lindblom A, Margolin S, Jakubowska A, Lubinski J, Huzarski T, Byrski T, Gorski B, Gronwald J, Hooning MJ, Hollestelle A, van den Ouweland AM, Jager A, Kriege M, Tilanus-Linthorst MM, Collee M, Wang-Gohrke S, Pylkas K, Jukkola-Vuorinen A, Mononen K, Grip M, Hirvikoski P, Winqvist R, Mannermaa A, Kosma VM, Kauppinen J, Kataja V, Auvinen P, Soini Y, Sironen R, Bojesen SE, Orsted DD, Kaur-Knudsen D, Flyger H, Nordestgaard BG, Holland H, Chenevix-Trench G, Manoukian S, Barile M, Radice P, Hankinson SE, Hunter DJ, Tamimi R, Sangrajrang S, Brennan P, McKay J, Odefrey F, Gaborieau V, Devilee P, Huijts PE, Tollenaar RA, Seynaeve C, Dite GS, Apicella C, Hopper JL, Hammet F, Tsimiklis H, Smith LD, Southey MC, Humphreys MK, Easton D, Pharoah P, Sherman ME, Garcia-Closas M (2011) Associations of breast cancer risk factors with tumor subtypes: a pooled analysis from the Breast Cancer Association Consortium studies. J Natl Cancer Inst 103(3):250–263
Suzuki R, Orsini N, Mignone L, Saji S, Wolk A (2008) Alcohol intake and risk of breast cancer defined by estrogen and progesterone receptor status—a meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Int J Cancer 122(8):1832–1841
Tamimi RM, Colditz GA, Hazra A, Baer HJ, Hankinson SE, Rosner B, Marotti J, Connolly JL, Schnitt SJ, Collins LC (2012) Traditional breast cancer risk factors in relation to molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 131(1):159–167. doi:10.1007/s10549-011-1702-0
Millikan RC, Newman B, Tse CK, Moorman PG, Conway K, Dressler LG, Smith LV, Labbok MH, Geradts J, Bensen JT, Jackson S, Nyante S, Livasy C, Carey L, Earp HS, Perou CM (2008) Epidemiology of basal-like breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 109(1):123–139
Lakhani SR, Van De Vijver MJ, Jacquemier J, Anderson TJ, Osin PP, McGuffog L, Easton DF (2002) The pathology of familial breast cancer: predictive value of immunohistochemical markers estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, HER-2, and p53 in patients with mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2. J Clin Oncol 20(9):2310–2318
Foulkes WD, Stefansson IM, Chappuis PO, Begin LR, Goffin JR, Wong N, Trudel M, Akslen LA (2003) Germline BRCA1 mutations and a basal epithelial phenotype in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 95(19):1482–1485
Banerji S, Cibulskis K, Rangel-Escareno C, Brown KK, Carter SL, Frederick AM, Lawrence MS, Sivachenko AY, Sougnez C, Zou L, Cortes ML, Fernandez-Lopez JC, Peng S, Ardlie KG, Auclair D, Bautista-Pina V, Duke F, Francis J, Jung J, Maffuz-Aziz A, Onofrio RC, Parkin M, Pho NH, Quintanar-Jurado V, Ramos AH, Rebollar-Vega R, Rodriguez-Cuevas S, Romero-Cordoba SL, Schumacher SE, Stransky N, Thompson KM, Uribe-Figueroa L, Baselga J, Beroukhim R, Polyak K, Sgroi DC, Richardson AL, Jimenez-Sanchez G, Lander ES, Gabriel SB, Garraway LA, Golub TR, Melendez-Zajgla J, Toker A, Getz G, Hidalgo-Miranda A, Meyerson M (2012) Sequence analysis of mutations and translocations across breast cancer subtypes. Nature 486(7403):405–409. doi:10.1038/nature11154
Curtis C, Shah SP, Chin SF, Turashvili G, Rueda OM, Dunning MJ, Speed D, Lynch AG, Samarajiwa S, Yuan Y, Graf S, Ha G, Haffari G, Bashashati A, Russell R, McKinney S, Langerod A, Green A, Provenzano E, Wishart G, Pinder S, Watson P, Markowetz F, Murphy L, Ellis I, Purushotham A, Borresen-Dale AL, Brenton JD, Tavare S, Caldas C, Aparicio S (2012) The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature 486(7403):346–352. doi:10.1038/nature10983
Ellis MJ, Ding L, Shen D, Luo J, Suman VJ, Wallis JW, Van Tine BA, Hoog J, Goiffon RJ, Goldstein TC, Ng S, Lin L, Crowder R, Snider J, Ballman K, Weber J, Chen K, Koboldt DC, Kandoth C, Schierding WS, McMichael JF, Miller CA, Lu C, Harris CC, McLellan MD, Wendl MC, DeSchryver K, Allred DC, Esserman L, Unzeitig G, Margenthaler J, Babiera GV, Marcom PK, Guenther JM, Leitch M, Hunt K, Olson J, Tao Y, Maher CA, Fulton LL, Fulton RS, Harrison M, Oberkfell B, Du F, Demeter R, Vickery TL, Elhammali A, Piwnica-Worms H, McDonald S, Watson M, Dooling DJ, Ota D, Chang LW, Bose R, Ley TJ, Piwnica-Worms D, Stuart JM, Wilson RK, Mardis ER (2012) Whole-genome analysis informs breast cancer response to aromatase inhibition. Nature 486(7403):353–360. doi:10.1038/nature11143
Network CGA (2012) Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 490(7418):61–70. doi:10.1038/nature11412
Shah SP, Roth A, Goya R, Oloumi A, Ha G, Zhao Y, Turashvili G, Ding J, Tse K, Haffari G, Bashashati A, Prentice LM, Khattra J, Burleigh A, Yap D, Bernard V, McPherson A, Shumansky K, Crisan A, Giuliany R, Heravi-Moussavi A, Rosner J, Lai D, Birol I, Varhol R, Tam A, Dhalla N, Zeng T, Ma K, Chan SK, Griffith M, Moradian A, Cheng SW, Morin GB, Watson P, Gelmon K, Chia S, Chin SF, Curtis C, Rueda OM, Pharoah PD, Damaraju S, Mackey J, Hoon K, Harkins T, Tadigotla V, Sigaroudinia M, Gascard P, Tlsty T, Costello JF, Meyer IM, Eaves CJ, Wasserman WW, Jones S, Huntsman D, Hirst M, Caldas C, Marra MA, Aparicio S (2012) The clonal and mutational evolution spectrum of primary triple-negative breast cancers. Nature 486(7403):395–399. doi:10.1038/nature10933
Stephens PJ, Tarpey PS, Davies H, Van Loo P, Greenman C, Wedge DC, Nik-Zainal S, Martin S, Varela I, Bignell GR, Yates LR, Papaemmanuil E, Beare D, Butler A, Cheverton A, Gamble J, Hinton J, Jia M, Jayakumar A, Jones D, Latimer C, Lau KW, McLaren S, McBride DJ, Menzies A, Mudie L, Raine K, Rad R, Chapman MS, Teague J, Easton D, Langerod A, Lee MT, Shen CY, Tee BT, Huimin BW, Broeks A, Vargas AC, Turashvili G, Martens J, Fatima A, Miron P, Chin SF, Thomas G, Boyault S, Mariani O, Lakhani SR, van de Vijver M, van ‘t Veer L, Foekens J, Desmedt C, Sotiriou C, Tutt A, Caldas C, Reis-Filho JS, Aparicio SA, Salomon AV, Borresen-Dale AL, Richardson AL, Campbell PJ, Futreal PA, Stratton MR (2012) The landscape of cancer genes and mutational processes in breast cancer. Nature 486(7403):400–404. doi:10.1038/nature11017
Garcia-Closas M, Hall P, Nevanlinna H, Pooley K, Morrison J, Richesson DA, Bojesen SE, Nordestgaard BG, Axelsson CK, Arias JI, Milne RL, Ribas G, Gonzalez-Neira A, Benitez J, Zamora P, Brauch H, Justenhoven C, Hamann U, Ko YD, Bruening T, Haas S, Dork T, Schurmann P, Hillemanns P, Bogdanova N, Bremer M, Karstens JH, Fagerholm R, Aaltonen K, Aittomaki K, von Smitten K, Blomqvist C, Mannermaa A, Uusitupa M, Eskelinen M, Tengstrom M, Kosma VM, Kataja V, Chenevix-Trench G, Spurdle AB, Beesley J, Chen X, Devilee P, van Asperen CJ, Jacobi CE, Tollenaar RA, Huijts PE, Klijn JG, Chang-Claude J, Kropp S, Slanger T, Flesch-Janys D, Mutschelknauss E, Salazar R, Wang-Gohrke S, Couch F, Goode EL, Olson JE, Vachon C, Fredericksen ZS, Giles GG, Baglietto L, Severi G, Hopper JL, English DR, Southey MC, Haiman CA, Henderson BE, Kolonel LN, Le Marchand L, Stram DO, Hunter DJ, Hankinson SE, Cox DG, Tamimi R, Kraft P, Sherman ME, Chanock SJ, Lissowska J, Brinton LA, Peplonska B, Hooning MJ, Meijers-Heijboer H, Collee JM, van den Ouweland A, Uitterlinden AG, Liu J, Lin LY, Yuqing L, Humphreys K, Czene K, Cox A, Balasubramanian SP, Cross SS, Reed MW, Blows F, Driver K, Dunning A, Tyrer J, Ponder BA, Sangrajrang S, Brennan P, McKay J, Odefrey F, Gabrieau V, Sigurdson A, Doody M, Struewing JP, Alexander B, Easton DF, Pharoah PD (2008) Heterogeneity of breast cancer associations with five susceptibility loci by clinical and pathological characteristics. PLoS Genet 4(4):1000054
Mizoo T, Taira N, Nishiyama K, Nogami T, Iwamoto T, Motoki T, Shien T, Matsuoka J, Doihara H, Ishihara S, Kawai H, Kawasaki K, Ishibe Y, Ogasawara Y, Komoike Y, Miyoshi S (2013) Effects of lifestyle and single nucleotide polymorphisms on breast cancer risk: a case-control study in Japanese women. BMC Cancer 13:565. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-565
Kawase T, Matsuo K, Suzuki T, Hiraki A, Watanabe M, Iwata H, Tanaka H, Tajima K (2009) FGFR2 intronic polymorphisms interact with reproductive risk factors of breast cancer: results of a case control study in Japan. Int J Cancer 125(8):1946–1952. doi:10.1002/ijc.24505
Cowper-Sal lari R, Zhang X, Wright JB, Bailey SD, Cole MD, Eeckhoute J, Moore JH, Lupien M (2012) Breast cancer risk-associated SNPs modulate the affinity of chromatin for FOXA1 and alter gene expression. Nat Genet 44(11):1191–1198. doi:10.1038/ng.2416
Holm K, Hegardt C, Staaf J, Vallon-Christersson J, Jonsson G, Olsson H, Borg A, Ringner M (2010) Molecular subtypes of breast cancer are associated with characteristic DNA methylation patterns. Breast Cancer Res 12(3):18
Easwaran H, Johnstone SE, Van Neste L, Ohm J, Mosbruger T, Wang Q, Aryee MJ, Joyce P, Ahuja N, Weisenberger D, Collisson E, Zhu J, Yegnasubramanian S, Matsui W, Baylin SB (2012) A DNA hypermethylation module for the stem/progenitor cell signature of cancer. Genome Res 22(5):837–849
Margueron R, Reinberg D (2011) The Polycomb complex PRC2 and its mark in life. Nature 469(7330):343–349
Holm K, Grabau D, Lovgren K, Aradottir S, Gruvberger-Saal S, Howlin J, Saal LH, Ethier SP, Bendahl PO, Stal O, Malmstrom P, Ferno M, Ryden L, Hegardt C, Borg A, Ringner M (2012) Global H3K27 trimethylation and EZH2 abundance in breast tumor subtypes. Mol Oncol 6(5):494–506. doi:10.1016/j.molonc.2012.06.002
Zhang X, Giovannucci EL, Wu K, Smith-Warner SA, Fuchs CS, Pollak M, Willett WC, Ma J (2012) Magnesium intake, plasma C-peptide, and colorectal cancer incidence in US women: a 28-year follow-up study. Br J Cancer 106(7):1335–1341. doi:10.1038/bjc.2012.76
Collins LC, Cole KS, Marotti JD, Hu R, Schnitt SJ, Tamimi RM (2011) Androgen receptor expression in breast cancer in relation to molecular phenotype: results from the Nurses’ Health Study. Mod Pathol 24(7):924–931. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2011.54
Razzaghi H, Troester MA, Gierach GL, Olshan AF, Yankaskas BC, Millikan RC (2013) Association between mammographic density and basal-like and luminal A breast cancer subtypes. Breast Cancer Res 15(5):R76
Phipps AI, Malone KE, Porter PL, Daling JR, Li CI (2008) Reproductive and hormonal risk factors for postmenopausal luminal, HER-2-overexpressing, and triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer 113(7):1521–1526
Islam T, Matsuo K, Ito H, Hosono S, Watanabe M, Iwata H, Tajima K, Tanaka H (2012) Reproductive and hormonal risk factors for luminal, HER2-overexpressing, and triple-negative breast cancer in Japanese women. Ann Oncol 23(9):2435–2441
Pellakuru LG, Iwata T, Gurel B, Schultz D, Hicks J, Bethel C, Yegnasubramanian S, De Marzo AM (2012) Global levels of H3K27me3 track with differentiation in vivo and are deregulated by MYC in prostate cancer. Am J Pathol 181(2):560–569
Rogenhofer S, Kahl P, Mertens C, Hauser S, Hartmann W, Buttner R, Muller SC, von Ruecker A, Ellinger J (2012) Global histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27) methylation levels and their prognostic relevance in renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int 109(3):459–465
Simpson JF, Gray R, Dressler LG, Cobau CD, Falkson CI, Gilchrist KW, Pandya KJ, Page DL, Robert NJ (2000) Prognostic value of histologic grade and proliferative activity in axillary node-positive breast cancer: results from the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Companion Study, EST 4189. J Clin Oncol 18(10):2059–2069
Contesso G, Mouriesse H, Friedman S, Genin J, Sarrazin D, Rouesse J (1987) The importance of histologic grade in long-term prognosis of breast cancer: a study of 1,010 patients, uniformly treated at the Institut Gustave-Roussy. J Clin Oncol 5(9):1378–1386
Sotiriou C, Wirapati P, Loi S, Harris A, Fox S, Smeds J, Nordgren H, Farmer P, Praz V, Haibe-Kains B, Desmedt C, Larsimont D, Cardoso F, Peterse H, Nuyten D, Buyse M, Van de Vijver MJ, Bergh J, Piccart M, Delorenzi M (2006) Gene expression profiling in breast cancer: understanding the molecular basis of histologic grade to improve prognosis. J Natl Cancer Inst 98(4):262–272
Kallioniemi OP, Blanco G, Alavaikko M, Hietanen T, Mattila J, Lauslahti K, Koivula T (1987) Tumour DNA ploidy as an independent prognostic factor in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 56(5):637–642
Pal B, Bouras T, Shi W, Vaillant F, Sheridan JM, Fu N, Breslin K, Jiang K, Ritchie ME, Young M, Lindeman GJ, Smyth GK, Visvader JE (2013) Global changes in the mammary epigenome are induced by hormonal cues and coordinated by Ezh2. Cell Rep 3(2):411–426
Collett K, Eide GE, Arnes J, Stefansson IM, Eide J, Braaten A, Aas T, Otte AP, Akslen LA (2006) Expression of enhancer of zeste homologue 2 is significantly associated with increased tumor cell proliferation and is a marker of aggressive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12(4):1168–1174
Kleer CG, Cao Q, Varambally S, Shen R, Ota I, Tomlins SA, Ghosh D, Sewalt RG, Otte AP, Hayes DF, Sabel MS, Livant D, Weiss SJ, Rubin MA, Chinnaiyan AM (2003) EZH2 is a marker of aggressive breast cancer and promotes neoplastic transformation of breast epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(20):11606–11611. doi:10.1073/pnas.1933744100
Gong Y, Huo L, Liu P, Sneige N, Sun X, Ueno NT, Lucci A, Buchholz TA, Valero V, Cristofanilli M (2011) Polycomb group protein EZH2 is frequently expressed in inflammatory breast cancer and is predictive of worse clinical outcome. Cancer 117(24):5476–5484. doi:10.1002/cncr.26179
Alford SH, Toy K, Merajver SD, Kleer CG (2012) Increased risk for distant metastasis in patients with familial early-stage breast cancer and high EZH2 expression. Breast Cancer Res Treat 132(2):429–437. doi:10.1007/s10549-011-1591-2
Xu K, Wu ZJ, Groner AC, He HH, Cai C, Lis RT, Wu X, Stack EC, Loda M, Liu T, Xu H, Cato L, Thornton JE, Gregory RI, Morrissey C, Vessella RL, Montironi R, Magi-Galluzzi C, Kantoff PW, Balk SP, Liu XS, Brown M (2012) EZH2 oncogenic activity in castration-resistant prostate cancer cells is Polycomb-independent. Science 338(6113):1465–1469. doi:10.1126/science.1227604
van Engeland M, Herman JG (2010) Viewing the epigenetics of colorectal cancer through the window of folic acid effects. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 3(12):1509–1512. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0281
Fanelli M, Amatori S, Barozzi I, Soncini M, Dal Zuffo R, Bucci G, Capra M, Quarto M, Dellino GI, Mercurio C, Alcalay M, Viale G, Pelicci PG, Minucci S (2010) Pathology tissue-chromatin immunoprecipitation, coupled with high-throughput sequencing, allows the epigenetic profiling of patient samples. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(50):21535–21540
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Harvard/National Cancer Institute SPORE in Breast Cancer Career Development Award (1999P011116). MAH was supported by the National Institutes of Health Cancer Epidemiology Training Grant (NIH T32 CA09001). We would like to thank the participants and staff of the Nurses’ Health Study for their valuable contributions as well as the following state cancer registries for their help: AL, AZ, AR, CA, CO, CT, DE, FL, GA, ID, IL, IN, IA, KY, LA, ME, MD,MA, MI, NE, NH, NJ, NY, NC, ND, OH, OK, OR, PA, RI, SC, TN, TX, VA, WA, and WY. In addition, this study was approved by the Connecticut Department of Public Health (DPH) Human Investigations Committee. Certain data used in this publication were obtained from the DPH. The authors assume full responsibility for analyses and interpretation of these data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Standards
All data collection was conducted with approval of appropriate institutional review boards to protect human subjects with consent and data protection systems in place. Data analysis for this manuscript was conducted on de-identified data sets.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Healey, M.A., Hu, R., Beck, A.H. et al. Association of H3K9me3 and H3K27me3 repressive histone marks with breast cancer subtypes in the Nurses’ Health Study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 147, 639–651 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-014-3089-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-014-3089-1