Abstract
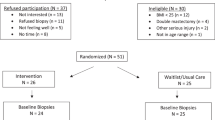
We conducted a phase II feasibility study of a 6-month behavioral weight loss intervention in postmenopausal overweight and obese women at increased risk for breast cancer and the effects of weight loss on anthropomorphic, blood, and benign breast tissue biomarkers. 67 women were screened by random peri-areolar fine-needle aspiration, 27 were registered and 24 participated in the interventional phase. The 24 biomarker evaluable women had a median baseline BMI of 34.2 kg/m2 and lost a median of 11 % of their initial weight. Significant tissue biomarker modulation after the 6-month intervention was noted for Ki-67 (if restricted to the 15 women with any Ki-67 at baseline, p = 0.041), adiponectin to leptin ratio (p = 0.003); and cyclin B1 (p = 0.001), phosphorylated retinoblastoma (p = 0.005), and ribosomal S6 (p = 0.004) proteins. Favorable modulation for serum markers was observed for sex hormone-binding globulin (p < 0.001), bioavailable estradiol (p < 0.001), bioavailable testosterone (p = 0.033), insulin (p = 0.018), adiponectin (p = 0.001), leptin (p < 0.001), the adiponectin to leptin ratio (p < 0.001), C-reactive protein (p = 0.002), and hepatocyte growth factor (p = 0.011). When subdivided by <10 or >10 % weight loss, change in percent total body and android (visceral) fat, physical activity, and the majority of the serum and tissue biomarkers were significantly modulated only for women with >10 % weight loss from baseline. Some factors such as serum PAI-1 and breast tissue pS2 (estrogen-inducible gene) mRNA were not significantly modulated overall but were when considering only those with >10 % weight loss. In conclusion, a median weight loss of 11 % over 6 months resulted in favorable modulation of a number of anthropomorphic, breast tissue and serum risk and mechanistic markers. Weight loss of 10 % or more should likely be the goal for breast cancer risk reduction studies in obese women.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang Z, Hankinson SE, Colditz GA et al (1997) Dual effects of weight and weight gain on breast cancer risk. JAMA 278:1407–1411
Ahn J, Schatzkin A, Lacey JV Jr, Albanes D, Ballard-Barbash R, Adams KF et al (2007) Adiposity, adult weight change, and postmenopausal breast cancer risk. Arch Intern Med 167:2091–2102
Harvie M, Howell A, Vierkant RA, Kumar N, Cerhan JR, Kelemen LE et al (2005) Association of gain and loss of weight before and after menopause with risk of postmenopausal breast cancer in the Iowa women’s health study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:656–661
Lahmann PH, Schulz M, Hoffmann K, Boeing H, Tjønneland A, Olsen A et al (2005) Long-term weight change and breast cancer risk: the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC). Br J Cancer 93:582–589
Eliassen AH, Colditz GA, Rosner B, Willett WC, Hankinson SE (2006) Adult weight change and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer. JAMA 296:193–201
Manders P, Pijpe A, Hooning MJ, Kluijt I, Vasen HF, Hoogerbrugge N et al (2011) Body weight and risk of breast cancer in BRCA1/2 mutation carriers. Breast Cancer Res Treat 126:193–202
Subbaramaiah K, Howe LR, Bhardwaj P, Du B, Gravaghi C, Yantiss RK et al (2011) Obesity is associated with inflammation and elevated aromatase expression in the mouse mammary gland. Cancer Prev Res 4:329–346
Subbaramaiah K, Morris PG, Zhou ZK, Morrow M, Du B, Giri D et al (2012) Increased levels of COX-2 and prostaglandin E2 contribute to elevated aromatase expression in inflamed breast tissue of obese women. Cancer Discov 2:356–365
Endogenous Hormones and Breast Cancer Collaborative Group, Key TJ, Appleby PN, Reeves GK, Roddam AW, Helzlsouer KJ, Alberg AJ et al (2011) Circulating sex hormones and breast cancer risk factors in postmenopausal women: reanalysis of 13 studies. Br J Cancer 105:709–722
Morris PG, Hudis CA, Morrow M, Falcone DJ, Zhou XK (2011) Inflammation and increased aromatase expression occur in the breast tissue of obese women with breast cancer. Cancer Prev Res 4:1021–1029
Hammarstedt A, Graham TE (2012) Kahn BB (2012) Adipose tissue dysregulation and reduced insulin sensitivity in non-obese individuals with enlarged abdominal adipose cells. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 4(1):42
Coelho M, Oliveira T, Fernandes R (2013) Biochemistry of adipose tissue: an endocrine organ. Arch Med Sci 9:191–200
Schairer C, Hill D, Sturgeon SR, Fears T, Pollak M, Mies C, Ziegler RG, Hoover RN, Sherman ME (2004) Serum concentrations of IGF-I, IGFBP-3 and c-peptide and risk of hyperplasia and cancer of the breast in postmenopausal women. Int J Cancer 108:773–779
Probst-Hensch NM, Steiner JH, Schraml P, Varga Z, Zürrer-Härdi U, Storz M, Korol D, Fehr MK, Fink D, Pestalozzi BC, Lütolf UM, Theurillat JP, Moch H (2010) IGFBP2 and IGFBP3 protein expressions in human breast cancer: association with hormonal factors and obesity. Clin Cancer Res 16:1025–1032
Hursting SD, Digiovanni J, Dannenberg AJ, Azrad M, Leroith D, Demark-Wahnefried W, Kakarala M, Brodie A, Berger NA (2012) Obesity, energy balance, and cancer: new opportunities for prevention. Cancer Prev Res 5:1260–1272
Bruning PF, Bonfrer JM, van Noord PA, Hart AA, Jong-Bakker M, Nooijen WJ (1992) Insulin resistance and breast-cancer risk. Int J Cancer 52:511–516
Sieri S, Pala V, Brighenti F, Pellegrini N, Muti P, Micheli A et al (2007) Dietary glycemic index, glycemic load, and the risk of breast cancer in an Italian prospective cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr 86:1160–1166
Tworoger SS, Eliassen AH, Kelesidis T et al (2007) Plasma adiponectin concentrations and risk of incident breast cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:1510–1516
Vona-Davis L, Rose DP (2007) Adipokines as endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine factors in breast cancer risk and progression. Endocr Relat Cancer 14:189–206
Becker S, Dossus L, Kaaks R (2009) Obesity related hyperinsulinaemia and hyperglycaemia and cancer development. Arch Physiol Biochem 115:86–96
Maccio A, Madeddu C, Mantovani G (2009) Adipose tissue as target organ in the treatment of hormone-dependent breast cancer: new therapeutic perspectives. Obes Rev 10:660–670
Taliaferro-Smith L, Nagalingam A, Zhong D, Zhou W, Saxena NK, Sharma D (2009) LKB1 is required for adiponectin-mediated modulation of AMPK-S6 K axis and inhibition of migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 28:2621–2633
Grossmann ME, Ray A, Nkhata KJ, Malakhov DA, Rogozina OP, Dogan S, Cleary MP (2010) Obesity and breast cancer: status of leptin and adiponectin in pathological processes. Cancer Metastasis Rev 29:641–653
Roberts DL, Dive C, Renehan AG (2010) Biological mechanisms linking obesity and cancer risk: new perspectives. Ann Rev Med 61:301–316
Mazzali G, Di Francesco V, Zoico E, Fantin F, Zamboni G, Benati C, Bambara V, Negri M, Bosello O, Zamboni M (2006) Interrelations between fat distribution, muscle lipid content, adipocytokines, and insulin resistance: effect of moderate weight loss in older women. Am J Clin Nutr 84:1193–1199
Harvie MN, Bokhari S, Shenton A, Ashcroft L, Evans G, Swindell R, Howell A (2007) Adult weight gain and central obesity in women with and without a family history of breast cancer: a case control study. Fam Cancer 6:287–294
Zamboni M, Di Francesco V, Garbin U, Fratta Pasini A, Mazzali G, Stranieri C, Zoico E, Fantin F, Bosello O, Cominacini L (2007) Adiponectin gene expression and adipocyte NF-kappaB transcriptional activity in elderly overweight and obese women: inter-relationships with fat distribution, hs-CRP, leptin and insulin resistance. Int J Obes 31:1104–1109
Karelis AD (2011) Obesity: to be obese: does it matter if you are metabolically healthy? Nat Rev Endocrinol 7:699–700
Shuster A, Patlas M, Pinthus JH, Mourtzakis M (2012) The clinical importance of visceral adiposity: a critical review of methods for visceral adipose tissue analysis. Br J Radiol 85:1–10
Mason C, Katzmarzyk PT (2010) Waist circumference thresholds for the prediction of cardiometabolic risk: is measurement site important? Eur J Clin Nutr 64:862–867
Byers T, Sedjo RL (2011) Does intentional weight loss reduce cancer risk? Diabetes Obes Metab 12:1063–1072
Sjöström L, Gummesson A, Sjöström CD, Narbro K, Peltonen M, Wedel H, Bengtsson C, Bouchard C, Carlsson B, Dahlgren S, Jacobson P, Karason K, Karlsson J, Larsson B, Lindroos AK, Lönroth H, Näslund I, Olbers T, Stenlöf K, Torgerson J, Carlsson LM; Swedish Obese Subjects Study (2009) Effects of bariatric surgery on cancer incidence in obese patients in Sweden (Swedish Obese Subjects Study): a prospective, controlled intervention trial. Lancet Oncol 10:653–662
Sjöström L, Gummesson A, Sjöström CD, Narbro K, Peltonen M, Wedel H, Bengtsson C, Bouchard C, Carlsson B, Dahlgren S, Jacobson P, Karason K, Karlsson J, Larsson B, Lindroos AK, Lönroth H, Näslund I, Olbers T, Stenlöf K, Torgerson J, Carlsson LM; Swedish Obese Subjects Study (1998) Executive summary of the clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults. Arch Intern Med 158:1867–1885
Parker ED, Folsom AR (2003) Intentional weight loss and incidence of obesity related cancers: the Iowa Women’s Health Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 27:1447–1452
Leblanc ES, O’Connor E, Whitlock EP, Patnode CD, Kapka T (2011) Effectiveness of primary care-relevant treatments for obesity in adults: a systematic evidence review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern Med 155:434–447
Moyer VA, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (2012) Screening for and management of obesity in adults: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med 157:373–378
Donnelly JE, Smith BK, Dunn L, Mayo MM, Jacobsen DJ, Stewart EE, Gibson C, Sullivan DK (2007) Comparison of a phone vs clinic approach to achieve 10 % weight loss. Int J Obes 31:1270–1276
Fabian CJ, Kimler BF, Zalles CM, Klemp JR, Kamel S, Zeiger S, Mayo MS (2000) Short-term prediction of breast cancer by random peri-areolar fine needle aspiration cytology and Gail risk. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:1217–1227
Fabian CJ, Kimler BF, Zalles CM, Klemp JR, Petroff BK, Khan QJ, Sharma P, Setchell KD, Zhao X, Phillips TA, Metheny T, Hughes JR, Yeh HW, Johnson KA (2010) Reduction in Ki-67 in benign breast tissue of high-risk women with the lignan secoisolariciresinol diglycoside. Cancer Prev Res 3:1342–1350
Masood S, Frykberg ER, McLellan GL, Scalapino MC, Mitchum DG, Bullard JB (1990) Prospective evaluation of radiologically directed fine-needle aspiration biopsy of nonpalpable breast lesions. Cancer 66:1480–1487
Khan QJ, Kimler BF, Clark J, Metheny T, Zalles CM, Fabian CJ (2005) Ki-67 expression in benign breast ductal cells obtained by random periareolar fine needle aspiration. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:786–789
National Task Force on the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity, Dieting and the development of eating disorders in overweight and obese adults (2000) Arch Intern Med 160:2581–2589
Vermeulen A, Verdonck G (1992) Representativeness of a single point plasma testosterone level for the long term hormonal milieu in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 74:939–942
Phillips TA, Fabian CJ, Kimler BF, Petroff BK (2013) Assessment of RNA in human breast tissue sampled by random periareolar fine needle aspiration and ductal lavage and processed as fixed or frozen specimens. Reprod Biol 13:75–81
Hennessy BT, Lu Y, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Carey MS, Myhre S, Ju Z, Davies MA, Liu W, Coombes K, Meric-Bernstam F, Bedrosian I, McGahren M, Agarwal R, Zhang F, Overgaard J, Alsner J, Neve RM, Kuo WL, Gray JW, Borresen-Dale AL, Mills GB (2010) A technical assessment of the utility of reverse phase protein arrays for the study of the functional proteome in non-microdissected human breast cancers. Clin Proteomics 6:129–151
Moore T, Beltran L, Carbajal S, Strom S, Traag J, Hursting SD, DiGiovanni J (2008) Dietary energy balance modulates signaling through the Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin pathways in multiple epithelial tissues. Cancer Prev Res 1:65–76
Mason C, Xiao L, Duggan C, Imayama I, Foster-Schubert KE, Kong A, Campbell KL, Wang CY, Alfano CM, Blackburn GL, Pollack M, McTiernan A (2013) Effects of dietary weight loss and exercise on insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in postmenopausal women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 22:1457–1463
Sidle A, Palaty C, Dirks P, Wiggan O, Kiess M, Gill RM, Wong AK, Hamel PA (1996) Activity of the retinoblastoma family proteins, pRB, p107, and p130, during cellular proliferation and differentiation. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 31:237–271
García-Tuñón I, Ricote M, Ruiz A, Fraile B, Paniagua R, Royuela M (2006) Cell cycle control related proteins (p53, p21, and Rb) and transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta) in benign and carcinomatous (in situ and infiltrating) human breast: implications in malignant transformations. Cancer Invest 24:119–125
Khan S, Brougham CL, Ryan J, Sahrudin A, O’Neill G, Wall D, Curran C, Newell J, Kerin MJ (2013) Dwyer RM (2013) miR-379 regulates cyclin B1 expression and is decreased in breast cancer. PLoS One 8(7):e68753
Magnuson B, Ekim B, Fingar DC (2012) Regulation and function of ribosomal protein S6 kinase (S6 K) within mTOR signalling networks. Biochem J 441:1–21
Stanton AL, Bernaards CA, Ganz PA (2005) The BCPT symptom scales: a measure of physical symptoms for women diagnosed with or at risk for breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:448–456
Mendoza TR, Wang XS, Cleeland CS, Morrissey M, Johnson BA, Wendt JK, Huber SL (1999) The rapid assessment of fatigue severity in cancer patients: use of the Brief Fatigue Inventory. Cancer 85:1186–1196
Sloan JA, Loprinzi CL, Novotny PJ, Barton DL, Lavasseur BI, Windschitl H (2001) Methodologic lessons learned from hot flash studies. J Clin Oncol 19:4280–4290
Klempel MC, Varaday KA (2011) Reliability of leptin but not adiponectin as a biomarker for diet induced weight loss in humans. Nutr Rev 69:145–154
Campbell KL, Foster-Schubert KE, Alfano CM, Wang CC, Wang CY, Duggan CR, Mason C, Imayama I, Kong A, Xiao L, Bain CE, Blackburn GL, Stanczyk FZ, McTiernan (2012) Reduced-calorie dietary weight loss, exercise, and sex hormones in postmenopausal women: randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol 30:2314–2326
Imayama I, Ulrich CM, Alfano CM, Wang C, Xiao L, Wener MH, Campbell KL, Duggan C, Foster-Schubert KE, Kong A, Mason CE, Wang CY, Blackburn GL, Bain CE, Thompson HJ, McTiernan A (2012) Effects of a caloric restriction weight loss diet and exercise on inflammatory biomarkers in overweight/obese postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled trial. Cancer Res 72:2314–2326
Abbenhardt C, McTiernan A, Alfano CM, Wener MH, Campbell KL, Duggan C, Foster-Schubert KE, Kong A, Toriola AT, Potter JD, Mason C, Xiao L, Blackburn GL, Bain C, Ulrich CM (2013) Effects of individual and combined dietary weight loss and exercise interventions in postmenopausal women on adiponectin and leptin levels. J Intern Med 274:115–163
Grossmann ME, Ray A, Dogan S, Mizuno NK, Cleary MP (2008) Balance of adiponectin and leptin modulates breast cancer cell growth. Cell Res 18:1154–1156
Ollberding NJ, Kim Y, Shvetsov YB, Wilkens LR, Franke AA, Cooney RV, Maskarinec G, Hernandez BY, Henderson BE, Le Marchand L, Kolonel LN, Goodman MT (2013) Prediagnostic leptin, adiponectin, C-reactive protein, and the risk of postmenopausal breast cancer. Cancer Prev Res 6:188–195
Santen RJ, Boyd NF, Chlebowski RT, Cummings S, Cuzick J, Dowsett M, Easton D, Forbes JF, Key T, Hankinson SE, Howell A, Ingle J; Breast Cancer Prevention Collaborative Group (2007) Critical assessment of new risk factors for breast cancer: considerations for development of an improved risk prediction model. Endocr Relat Cancer 14:169–187
Prieto-Hontoria PL, Pérez-Matute P, Fernández-Galilea M, Bustos M, Martínez JA, Moreno-Aliaga MJ (2011) Role of obesity-associated dysfunctional adipose tissue in cancer: a molecular nutrition approach. Biochim Biophys Acta 807:664–678
Goodwin PJ, Ennis M, Pritchard KI, Trudeau ME, Koo J, Taylor SK, Hood N (2012) Insulin- and obesity-related variables in early-stage breast cancer: correlations and time course of prognostic associations. J Clin Oncol 30:164–171
Fabian CJ, Kimler BF, Mayo MS, Khan SA (2005) Breast tissue sampling for risk assessment and prevention. Endocr Relat Cancer 12:185–213
Hartmann LC, Sellers TA, Frost MH, Lingle WL, Degnim AC, Ghosh K, Vierkant RA, Maloney SD, Pankratz VS, Hillman DW, Suman VJ, Johnson J, Blake C, Tlsty T, Vachon CM, Melton LJ 3rd, Visscher DW (2005) Benign breast disease and the risk of breast cancer. N Engl J Med 353:229–237
Shaaban AM, Sloane JP, West CR, Foster CS (2002) Breast cancer risk in usual ductal hyperplasia is defined by estrogen receptor alpha and Ki-67 expression. Am J Pathol 160:597–604
Santisteban M, Reynolds C, Barr Fritcher EG, Frost MH, Vierkant RA, Anderson SS, Degnim AC, Visscher DW, Pankratz VS, Hartmann LC (2010) Ki67: a time-varying biomarker of risk of breast cancer in atypical hyperplasia. Breast Cancer Res Treat 121:431–437
Ibarra-Drendall C, Wilke LG, Zalles C, Scott V, Archer LE, Lem S, Yee LD, Lester J, Kulkarni S, Murekeyisoni C, Wood M, Wilson K, Garber J, Gentry C, Stouder A, Broadwater G, Baker JC Jr, Vasilatos SN, Owens E, Rabiner S, Barron AC, Seewaldt VL (2009) Reproducibility of random periareolar fine needle aspiration in a multi-institutional Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB) cross-sectional study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 18:1379–1385
Hofseth LJ, Raafat AM, Osuch JR, Pathak DR, Slomski CA, Haslam SZ (1999) Hormone replacement therapy with estrogen or estrogen plus medroxyprogesterone acetate is associated with increased epithelial proliferation in the normal postmenopausal breast. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:4559–4565
Befort CA, Austin H, Klemp JR (2011) Weight control needs and experiences among rural breast cancer survivors. Psychooncology 20:1069–1075
Befort CA, Klemp JR, Austin HL, Perri MG, Schmitz KH, Sullivan DK, Fabian CJ (2012) Outcomes of a weight loss intervention among rural breast cancer survivors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 132:631–639
Ogden J (2000) The correlates of long-term weight loss: a group comparison study of obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24:1018–1025
Wing RR, Phelan S (2005) Long-term weight loss maintenance. Am J Clin Nutr 82(1 Suppl):222S–225S
Milsom VA, Middleton KM, Perri M (2011) Successful long-term weight loss maintenance in a rural population. Clin Interv Aging 6:303–309
Middleton KM, Patidar SM, Perri MG (2012) The impact of extended care on the long-term maintenance of weight loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev 13:509–517
Acknowledgments
Supported by grants 5R21CA121106 from NIH, and the Breast Cancer Research Foundation (KUMC); 5R01CA129409 from NIH (UT Austin); and CA16672 from NIH (MD Anderson Cancer Center). The University of Virginia Center for Research in Reproduction Ligand Assay and Analysis Core is supported by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver NICHD/NIH (SCCPIR) Grant U54-HD28934. Health Management Resources provided discounted packaged meals and shakes.
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fabian, C.J., Kimler, B.F., Donnelly, J.E. et al. Favorable modulation of benign breast tissue and serum risk biomarkers is associated with >10 % weight loss in postmenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat 142, 119–132 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2730-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2730-8