Abstract
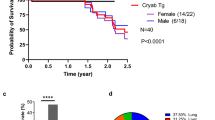
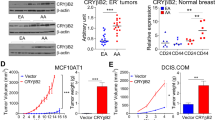
Recent studies indicate that the small heat shock protein αB-crystallin is expressed in poor prognosis basal-like breast tumors and likely contributes to their aggressive phenotype. However, the mechanisms underlying the deregulated expression of αB-crystallin in basal-like tumors are poorly understood. Using a bioinformatics approach, we identified a putative DNA binding motif in the human αB-crystallin promoter for the proto-oncogene Ets1, a member of the ETS transcription factor family that bind to DNA at palindromic ETS-binding sites (EBS). Here we demonstrate that ectopic expression of Ets1 activates the αB-crystallin promoter by an EBS-dependent mechanism and increases αB-crystallin protein levels, while silencing Ets1 reduces αB-crystallin promoter activity and protein levels. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analyses showed that endogenous Ets1 binds to the αB-crystallin promoter in basal-like breast cancer cells in vivo. Interrogation of publically available gene expression data revealed that Ets1 is expressed in human basal-like breast tumors and is associated with poor survival. Collectively, our results point to a previously unrecognized link between the oncogenic transcription factor Ets1 and αB-crystallin in basal-like breast cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horwitz J (1992) α-Crystallin can function as a molecular chaperone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10449–10453. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.21.10449
Mehlen P, Kretz-Remy C, Preville X, Arrigo AP (1996) Human hsp27, Drosophila hsp27 and human αB-crystallin expression-mediated increase in glutathione is essential for the protective activity of these proteins against TNFα-induced cell death. EMBO J 15:2695–2706
Clark JI, Muchowski PJ (2000) Small heat-shock proteins and their potential role in human disease. Curr Opin Struct Biol 10:52–59. doi:10.1016/S0959-440X(99)00048-2
Kamradt MC, Chen F, Cryns VL (2001) The small heat shock protein αB-crystallin negatively regulates cytochrome c- and caspase-8-dependent activation of caspase-3 by inhibiting its autoproteolytic maturation. J Biol Chem 276:16059–16063. doi:10.1074/jbc.C100107200
Kamradt MC, Lu M, Werner ME et al (2005) The small heat shock protein αB-crystallin is a novel inhibitor of TRAIL-induced apoptosis that suppresses the activation of caspase-3. J Biol Chem 280:11059–11066. doi:10.1074/jbc.M413382200
Mao YW, Liu JP, Xiang H, Li DW (2004) Human αA- and αB-crystallins bind to Bax and Bcl-XS to sequester their translocation during staurosporine-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 11:512–526. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4401384
Chelouche-Lev D, Kluger HM, Berger AJ, Rimm DL, Price JE (2004) αB-crystallin as a marker of lymph node involvement in breast carcinoma. Cancer 100:2543–2548. doi:10.1002/cncr.20304
Chin D, Boyle GM, Williams RM et al (2005) αB-crystallin, a new independent marker for poor prognosis in head and neck cancer. Laryngoscope 115:1239–1242. doi:10.1097/01.MLG.0000164715.86240.55
Moyano JV, Evans JR, Chen F et al (2006) αB-crystallin is a novel oncoprotein that predicts poor clinical outcome in breast cancer. J Clin Invest 116:261–270. doi:10.1172/JCI25888
Ivanov O, Chen F, Wiley EL et al (2008) αB-crystallin is a novel predictor of resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 111:411–417. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9796-0
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB et al (2000) Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 406:747–752. doi:10.1038/35021093
Swamynathan SK, Piatigorsky J (2002) Orientation-dependent influence of an intergenic enhancer on the promoter activity of the divergently transcribed mouse Shsp/αB-crystallin and Mkbp/HspB2 genes. J Biol Chem 277:49700–49706. doi:10.1074/jbc.M209700200
Doerwald L, van Rheede T, Dirks RP et al (2004) Sequence and functional conservation of the intergenic region between the head-to-head genes encoding the small heat shock proteins αB-crystallin and HspB2 in the mammalian lineage. J Mol Evol 59:674–686. doi:10.1007/s00239-004-2659-y
Gopal-Srivastava R, Piatigorsky J (1993) The murine αB-crystallin/small heat shock protein enhancer: identification of αBE-1, αBE-2, αBE-3, and MRF control elements. Mol Cell Biol 13:7144–7152
Gopal-Srivastava R, Cvekl A, Piatigorsky J (1996) Pax-6 and αB-crystallin/small heat shock protein gene regulation in the murine lens. Interaction with the lens-specific regions, LSR1 and LSR2. J Biol Chem 271:23029–23036. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.38.23029
Somasundaram T, Bhat SP (2000) Canonical heat shock element in the αB-crystallin gene shows tissue-specific and developmentally controlled interactions with heat shock factor. J Biol Chem 275:17154–17159. doi:10.1074/jbc.M000304200
Seth A, Watson DK (2005) ETS transcription factors and their emerging roles in human cancer. Eur J Cancer 41:2462–2478. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2005.08.013
Lincoln DWII, Bove K (2005) The transcription factor Ets-1 in breast cancer. Front Biosci 10:506–511. doi:10.2741/1546
Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno V et al (2007) Oncomine 3.0: genes, pathways, and networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression profiles. Neoplasia N Y 9:166–180. doi:10.1593/neo.07112
Watabe T, Yoshida K, Shindoh M et al (1998) The Ets-1 and Ets-2 transcription factors activate the promoters for invasion-associated urokinase and collagenase genes in response to epidermal growth factor. Int J Cancer 77:128–137. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19980703)77:1<128::AID-IJC20>3.0.CO;2-9
Behrens P, Rothe M, Wellmann A, Krischler J, Wernert N (2001) The Ets-1 transcription factor is up-regulated together with MMP 1 and MMP 9 in the stroma of pre-invasive breast cancer. J Pathol 194:43–50. doi:10.1002/path.844
Span PN, Manders P, Heuvel JJ et al (2002) Expression of the transcription factor Ets-1 is an independent prognostic marker for relapse-free survival in breast cancer. Oncogene 21:8506–8509. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206040
Buggy Y, Maguire TM, McGreal G et al (2004) Overexpression of the Ets-1 transcription factor in human breast cancer. Br J Cancer 91:1308–1315. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602128
Charafe-Jauffret E, Ginestier C, Monville F et al (2006) Gene expression profiling of breast cell lines identifies potential new basal markers. Oncogene 25:2273–2284. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209254
Myers E, Hill AD, Kelly G et al (2005) Associations and interactions between Ets-1 and Ets-2 and coregulatory proteins, SRC-1, AIB1, and NCoR in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:2111–2122. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1192
Woods DB, Ghysdael J, Owen MJ (1992) Identification of nucleotide preferences in DNA sequences recognised specifically by c-Ets-1 protein. Nucleic Acids Res 20:699–704. doi:10.1093/nar/20.4.699
Li R, Pei H, Watson DK (2000) Regulation of Ets function by protein-protein interactions. Oncogene 19:6514–6523. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204035
Wernert N, Raes MB, Lassalle P et al (1992) c-ets1 proto-oncogene is a transcription factor expressed in endothelial cells during tumor vascularization and other forms of angiogenesis in humans. Am J Pathol 140:119–127
Dimberg A, Rylova S, Dieterich LC et al (2008) αB-crystallin promotes tumor angiogenesis by increasing vascular survival during tube morphogenesis. Blood 111:2015–2023. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-04-087841
Maddala R, Rao VP (2005) α-Crystallin localizes to the leading edges of migrating lens epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res 306:203–215. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.01.026
Yehiely F, Moyano JV, Evans JR, Nielsen TO, Cryns VL (2006) Deconstructing the molecular portrait of basal-like breast cancer. Trends Mol Med 12:537–544. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2006.09.004
Baker KM, Wei G, Schaffner AE, Ostrowski MC (2003) Ets-2 and components of mammalian SWI/SNF form a repressor complex that negatively regulates the BRCA1 promoter. J Biol Chem 278:17876–17884. doi:10.1074/jbc.M209480200
Delannoy-Courdent A, Mattot V, Fafeur V et al (1998) The expression of an Ets1 transcription factor lacking its activation domain decreases uPA proteolytic activity and cell motility, and impairs normal tubulogenesis and cancerous scattering in mammary epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 111:1521–1534
Hahne JC, Okuducu AF, Kaminski A, Florin A, Soncin F, Wernert N (2005) Ets-1 expression promotes epithelial cell transformation by inducing migration, invasion and anchorage-independent growth. Oncogene 24:5384–5388. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208761
van de Vijver MJ, He YD, van’t Veer LJ et al (2002) A gene-expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 347:1999–2009. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa021967
Richardson AL, Wang ZC, De Nicolo A et al (2006) X chromosomal abnormalities in basal-like human breast cancer. Cancer Cell 9:121–132. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.01.013
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. M. Zhou and M. Sharon Stack for plasmids. This work was supported by NIH grants R01CA097198 (VLC), R21CA125181 (VLC) and T32GM08061 (JDB), and by the Breast Cancer Research Foundation (VLC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bosman, J.D., Yehiely, F., Evans, J.R. et al. Regulation of αB-crystallin gene expression by the transcription factor Ets1 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 119, 63–70 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0330-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0330-4