Abstract
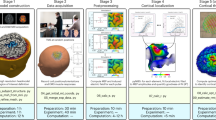
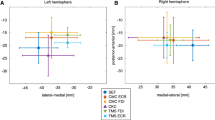
Navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation (nTMS) can be applied to locate and outline cortical motor representations. This may be important, e.g., when planning neurosurgery or focused nTMS therapy, or when assessing plastic changes during neurorehabilitation. Conventionally, a cortical location is considered to belong to the motor cortex if the maximum electric field (E-field) targeted there evokes a motor-evoked potential in a muscle. However, the cortex is affected by a broad E-field distribution, which tends to broaden estimates of representation areas by stimulating also the neighboring areas in addition to the maximum E-field location. Our aim was to improve the estimation of nTMS-based motor maps by taking into account the E-field distribution of the stimulation pulse. The effect of the E-field distribution was considered by calculating the minimum-norm estimate (MNE) of the motor representation area. We tested the method on simulated data and then applied it to recordings from six healthy volunteers and one stroke patient. We compared the motor representation areas obtained with the MNE method and a previously introduced interpolation method. The MNE hotspots and centers of gravity were close to those obtained with the interpolation method. The areas of the maps, however, depend on the thresholds used for outlining the areas. The MNE method may improve the definition of cortical motor areas, but its accuracy should be validated by comparing the results with maps obtained with direct cortical stimulation of the cortex where the E-field distribution can be better focused.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
06 September 2017
An erratum to this article has been published.
References
Awiszus F (2003) TMS and threshold hunting. Suppl to Clin Neurophysioly 56:13–23
Awiszus F, Borckardt JJ (2012) TMS Motor Threshold Assessment Tool 2.0 http://clinicalresearcher.org/software.htm. Accessed 2 June 2014
Bohning DE, He L, George MS, Epstein CM (2001) Deconvolution of transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) maps. J Neural Transm 108:35–52
Borghetti D, Sartucci F, Petacchi E, Guzzetta A, Piras MF, Murri L, Cioni G (2008) Transcranial magnetic stimulation mapping: a model based on spline interpolation. Brain Res Bull 77:143–148
Bungert A, Antunes A, Espenhahn S, Thielscher A (2016) Where does TMS stimulate the motor cortex? Combining electrophysiological measurements and realistic field estimates to reveal the affected cortex position. Cereb Cortex 1–12
Danner N, Julkunen P, Könönen M, Säisänen L, Nurkkala J, Karhu J (2008) Navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation and computed electric field strength reduce stimulator-dependent differences in the motor threshold. J Neurosci Methods 174:116–122
Devanne H, Lavoie BA, Capaday C (1997) Input-output properties and gain changes in the human corticospinal pathway. Exp Brain Res 114:329–338
Fox PT, Narayana S, Tandon N, Sandoval H, Fox SP, Kochunov P, Lancaster JL (2004) Column-based model of electric field excitation of cerebral cortex. Hum Brain Mapp 22:1–14
Goetz SM, Luber B, Lisanby SH, Peterchev AV (2014) A novel model incorporating two variability sources for describing motor evoked potentials. Brain Stimul 7:541–552
Hämäläinen MS, Ilmoniemi RJ (1994) Interpreting magnetic fields of the brain: minimum norm estimates. Med Biol Eng Comput 32:35–42
Heald A, Bates D, Cartlidge NEF, French JM, Miller S (1993) Longitudinal study of central motor conduction time following stroke: 2. Central motor conduction measured within 72 h after stroke as a predictor of functional outcome at 12 months. Brain 116:1371–1385
Ilmoniemi RJ (2009) The triangle phantom in magnetoencephalography. J Jpn Biomagn Bioelectromagn Soc 22:44–45
Ilmoniemi RJ, Ruohonen J, Karhu J (1999) Transcranial magnetic stimulation—a new tool for functional imaging of the brain. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 27:241–284
Jang SH, Ahn SH, Sakong J, Byun WM, Choi BY, Chang CH, Bai D, Son SM (2010) Comparison of TMS and DTT for predicting motor outcome in intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neurol Sci 290:107–111
Julkunen P (2014) Methods for estimating cortical motor representation size and location in navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation. J Neurosci Methods 232:125–133
Julkunen P, Säisänen L, Danner N, Awiszus F, Könönen M (2012) Within-subject effect of coil-to-cortex distance on cortical electric field threshold and motor evoked potentials in transcranial magnetic stimulation. J Neurosci Methods 206:158–164
Jussen D, Zdunczyk A, Schmidt S, Rösler J, Buchert R, Julkunen P, Karhu J, Brandt S, Picht T, Vajkoczy P (2016) Motor plasticity after extra-intracranial bypass surgery in occlusive cerebrovascular disease. Neurology 87:27–35
Kallioniemi E, Julkunen P (2016) Alternative stimulation intensities for mapping cortical motor area with navigated TMS. Brain Topogr 29:395–404
Kallioniemi E, Pitkänen M, Säisänen L, Julkunen P (2015) Onset latency of motor evoked potentials in motor cortical mapping with neuronavigated transcranial magnetic stimulation. Open Neurol J 9:62–69
Liepert J, Bauder H, Miltner WHR, Taub E, Weiller C (2000) Treatment-induced cortical reorganization after stroke in humans. Stroke 31:1210–1216
Malcolm MP, Triggs WJ, Light KE, Shechtman O, Khandekar G, Gonzalez Rothi LJ (2006) Reliability of motor cortex transcranial magnetic stimulation in four muscle representations. Clin Neurophysiol 117:1037–1046
Matthäus L, Trillenberg P, Fadini T, Finke M, Schweikard A (2008) Brain mapping with transcranial magnetic stimulation using a refined correlation ratio and Kendall’s τ. Stat Med 27:5252–5270
Nieminen JO, Koponen LM, Ilmoniemi RJ (2015) Experimental characterization of the electric field distribution induced by TMS devices. Brain Stimul 8:582–589
Nummenmaa A, Stenroos M, Ilmoniemi RJ, Okada YC, Hämäläinen MS, Raij T (2013) Comparison of spherical and realistically shaped boundary element head models for transcranial magnetic stimulation navigation. Clin Neurophysiol 124:1995–2007
Numminen J, Ahlfors S, Ilmoniemi R, Montonen J, Nenonen J (1995) Transformation of multichannel magnetocardiographic signals to standard grid form. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 42:72–78
Opitz A, Legon W, Rowlands A, Bickel WK, Paulus W, Tyler WJ (2013) Physiological observations validate finite element models for estimating subject-specific electric field distributions induced by transcranial magnetic stimulation of the human motor cortex. NeuroImage 81:253–264
Opitz A, Zafar N, Bockermann V, Rohde V, Paulus W (2014) Validating computationally predicted TMS stimulation areas using direct electrical stimulation in patients with brain tumors near precentral regions. NeuroImage 4:500–507
Paiva WS, Fonoff ET, Marcolin MA, Cabrera HN, Teixeira MJ (2012) Cortical mapping with navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation in low-grade glioma surgery. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 8:197–201
Parker RL (1977) Understanding inverse theory. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 5:35–64
Picht T, Schmidt S, Brandt S, Frey D, Hannula H, Neuvonen T, Karhu J, Vajkoczy P, Suess O (2011) Preoperative functional mapping for rolandic brain tumor surgery: comparison of navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation to direct cortical stimulation. Neurosurgery 69:581–589
Picht T, Krieg SM, Sollmann N, Rösler J, Niraula B, Neuvonen T, Savolainen P, Lioumis P, Mäkelä JP, Deletis V, Meyer B, Vajkoczy P, Ringel F (2013) A comparison of language mapping by preoperative navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation and direct cortical stimulation during awake surgery. Neurosurgery 72:808–819
Pitkänen M, Kallioniemi E, Julkunen P (2015) Extent and location of the excitatory and inhibitory cortical hand representation maps: a navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Brain Topogr 28:657–665
Raffin E, Pellegrino G, Di Lazzaro V, Thielscher A, Siebner HR (2015) Bringing transcranial mapping into shape: sulcus-aligned mapping captures motor somatotopy in human primary motor hand area. NeuroImage 120:164–175
Rossini PM, Burke D, Chen R, Cohen LG, Daskalakis Z, Di Iorio R, Di Lazzaro V, Ferreri F, Fitzgerald PB, George MS, Hallett M, Lefaucheur JP, Langguth B, Matsumoto H, Miniussi C, Nitsche MA, Pascual-Leone A, Paulus W, Rossi S et al (2015) Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord, roots and peripheral nerves: basic principles and procedures for routine clinical and research application. An updated report from an I.F.C.N. Committee. Clin Neurophysiol 126:1071–1107
Rothwell JC, Hallett M, Berardelli A, Eisen A, Rossini P, Paulus W (1999) Magnetic stimulation: motor evoked potentials. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 52:97–103
Säisänen L, Julkunen P, Niskanen E, Danner N, Hukkanen T, Lohioja T, Nurkkala J, Mervaala E, Karhu J, Könönen M (2008) Motor potentials evoked by navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation in healthy subjects. J Clin Neurophysiol 25:367–372
Sarvas J (1987) Basic mathematical and electromagnetic concepts of the biomagnetic inverse problem. Phys Med Biol 32:11–22
Thickbroom GW, Sammut R, Mastaglia FL (1998) Magnetic stimulation mapping of motor cortex: factors contributing to map area. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 109:79–84
Thielscher A, Kammer T (2002) Linking physics with physiology in TMS: a sphere field model to determine the cortical stimulation site in TMS. NeuroImage 17:1117–1130
Thielscher A, Wichmann FA (2009) Determining the cortical target of transcranial magnetic stimulation. NeuroImage 47:1319–1330
Traversa R, Cicinelli P, Bassi A, Rossini PM, Bernardi G (1997) Mapping of motor cortical reorganization after stroke: a brain simulation study with focal magnetic pulses. Stroke 28:110–117
Vitikainen A-M, Salli E, Lioumis P, Mäkelä JP, Metsähonkala L (2013) Applicability of nTMS in locating the motor cortical representation areas in patients with epilepsy. Acta Neurochir 155:507–518
Wassermann EM, McShane LM, Hallett M, Cohen LG (1992) Noninvasive mapping of muscle representations in human motor cortex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 85:1–8
Wassermann EM, Pascual-Leone A, Valls-Solé J, Toro C, Cohen LG, Hallett M (1993) Topography of the inhibitory and excitatory responses to transcranial magnetic stimulation in a hand muscle. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 89:424–433
Wilson SA, Thickbroom GW, Mastaglia FL (1993) Topography of excitatory and inhibitory muscle responses evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation in the human motor cortex. Neurosci Lett 154:52–56
Wolf SL, Butler AJ, Campana GI, Parris TA, Struys DM, Weinstein SR, Weiss P (2004) Intra-subject reliability of parameters contributing to maps generated by transcranial magnetic stimulation in able-bodied adults. Clin Neurophysiol 115:1740–1747
Acknowledgements
The study was funded by the State Research Funding (Research Committee of the Kuopio University Hospital Catchment Area, projects 5041730 and 5041747, Kuopio, Finland); Finnish Cultural Foundation, Helsinki, Finland; Cancer Society of Finland, Helsinki, Finland; Päivikki and Sakari Sohlberg Foundation, Helsinki, Finland; Academy of Finland (Decisions Nos. 255347, 265680, and 294625), Helsinki, Finland; Russian Academic Excellence Project ‘5-100’, RFBR Grant (No. 16-04-01883) and Skolkovo personal grant “Umnik”. The funding sources had no involvement in the study design, in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data, in the writing of the report, or in the decision to submit the article for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Petro Julkunen and Jaakko O. Nieminen have received unrelated consulting fees from Nexstim Plc, Elisa Kallioniemi has received unrelated travel support from Nexstim Plc, and Risto J. Ilmoniemi is an advisor and a minority shareholder of the company. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-017-0587-6.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pitkänen, M., Kallioniemi, E., Julkunen, P. et al. Minimum-Norm Estimation of Motor Representations in Navigated TMS Mappings. Brain Topogr 30, 711–722 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-017-0577-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-017-0577-8