Abstract
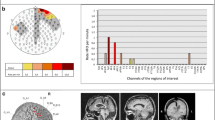
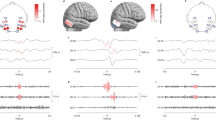
To evaluate the possibility of detecting fast ripples (FRs) on the surface EEG of patients with focal pharmacoresistant epilepsy, and to investigate the relationship between scalp FRs and localization of the seizure onset zone (SOZ). We included 10 patients undergoing combined surface–intracranial EEG with ≥10 spikes in the surface EEG during the first 30 consecutive minutes of N3 sleep. FRs (≥4 consecutive oscillations above 250 Hz with an amplitude clearly exceeding that of the background) on the surface EEG (F3-C3, C3-P3, Fz-Cz, Cz-Pz, F4-C4, C4-P4) were visually marked, and verified by two EEG experts. FRs were categorized as related to the SOZ, if localized in the brain lobe of the SOZ. Low-amplitude FRs with a rate of 0.09/min were found in 6/10 patients: two exhibited events related to the SOZ, three showed no relationship with the SOZ, and in one patient the SOZ was not identified. It may be possible to detect FRs with surface EEG using subdermal electrodes in patients with focal epilepsy. The relationship between surface FRs and the SOZ remains unclear. Future studies aiming at a higher spatial EEG coverage are needed to elucidate their significance.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama T, McCoy B, Go CY, Ochi A, Elliott IM, Akiyama M et al (2011) Focal resection of fast ripples on extraoperative intracranial EEG improves seizure outcome in pediatric epilepsy. Epilepsia 52(10):1802–1811
Alkawadri R, Gaspard N, Goncharova II, Spencer DD, Gerrard JL, Zaveri H et al (2014) The spatial and signal characteristics of physiologic high frequency oscillations. Epilepsia 55(12):1986–1995. doi:10.1111/epi.12851
Andrade-Valenca LP, Dubeau F, Mari F, Zelmann R, Gotman J (2011) Interictal scalp fast oscillations as a marker of the seizure onset zone. Neurology 77(6):524–531
Bagshaw AP, Jacobs J, Levan P, Dubeau F, Gotman J (2009) Effect of sleep stage on interictal high-frequency oscillations recorded from depth macroelectrodes in patients with focal epilepsy. Epilepsia 50(4):617–628
Bénar CG, Chauvière L, Bartolomei F, Wendling F (2010) Pitfalls of high-pass filtering for detecting epileptic oscillations: a technical note on “false” ripples. Clin Neurophysiol 121(3):301–310. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2009.10.019
Berry RB, Brooks R, Gamaldo CE, Harding SM, Marcus CL, Vaughn BV (2012) The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology and technical specifications, version 2.0. American Academy of Sleep Medicine, Darien. http://www.aasmnet.org
Blanco JA, Stead M, Krieger A, Stacey W, Maus D, Marsh E et al (2011) Data mining neocortical high-frequency oscillations in epilepsy and controls. Brain 134(10):2948–2959
Bragin A, Engel J, Wilson CL, Fried I, Buzsáki G (1999a) High-frequency oscillations in human brain. Hippocampus 9(2):137–142
Bragin A, Engel J, Wilson CL, Fried I, Mathern GW (1999b) Hippocampal and entorhinal cortex high-frequency oscillations (100–500 Hz) in human epileptic brain and in kainic acid-treated rats with chronic seizures. Epilepsia 40(2):127–137
Bragin A, Wilson CL, Engel J (2000) Chronic epileptogenesis requires development of a network of pathologically interconnected neuron clusters: a hypothesis. Epilepsia 41(Suppl 6):S144–S152
Crépon B, Navarro V, Hasboun D, Clemenceau S, Martinerie J, Baulac M et al (2010) Mapping interictal oscillations greater than 200 Hz recorded with intracranial macroelectrodes in human epilepsy. Brain 133(1):33–45
Curio G (2000) Linking 600-Hz “spikelike” EEG/MEG wavelets (“σ-bursts”) to cellular substrates. J Clin Neurophysiol 17:377–396
Dümpelmann M, Jacobs J, Schulze-Bonhage A (2015) Temporal and spatial characteristics of high frequency oscillations as a new biomarker in epilepsy. Epilepsia 56(2):197–206. doi:10.1111/epi.12844
Foffani G, Uzcategui YG, Gal B, Menendez de la Prida L (2007) Reduced spike-timing reliability correlates with the emergence of fast ripples in the rat epileptic hippocampus. Neuron 55(6):930–941
Frauscher B, von Ellenrieder N, Ferrari-Marinho T, Avoli M, Dubeau F, Gotman J (2015) Facilitation of epileptic activity during sleep is mediated by high amplitude slow waves. Brain 138:1629–1641. doi:10.1093/brain/awv073
Gobbelé R, Waberski TD, Simon H, Peters E, Klostermann F, Curio G et al (2004) Different origins of low- and high-frequency components (600 Hz) of human somatosensory evoked potentials. Clin Neurophysiol 115(4):927–937
Ibarz JM, Foffani G, Cid E, Inostroza M, Menendez de la Prida L (2010) Emergent dynamics of fast ripples in the epileptic hippocampus. J Neurosci 30(48):16249–16261
Ives JR (2005) New chronic EEG electrode for critical/intensive care unit monitoring. J Clin Neurophysiol 22(2):119–123
Iwatani Y, Kagitani-Shimono K, Tominaga K, Okinaga T, Kishima H, Kato A et al (2012) Ictal high-frequency oscillations on scalp EEG recordings in symptomatic West syndrome. Epilepsy Res 102(1–2):60–70. doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2012.04.020
Jacobs J, LeVan P, Chander R, Hall J, Dubeau F, Gotman J (2008) Interictal high-frequency oscillations (80–500 Hz) are an indicator of seizure onset areas independent of spikes in the human epileptic brain. Epilepsia 49(11):1893–1907
Jirsch JD, Urrestarazu E, LeVan P, Olivier A, Dubeau F, Gotman J (2006) High-frequency oscillations during human focal seizures. Brain 129(6):1593–1608
Kerber K, Dümpelmann M, Schelter B, Le Van P, Korinthenberg R, Schulze-Bonhage A et al (2014) Differentiation of specific ripple patterns helps to identify epileptogenic areas for surgical procedures. Clin Neurophysiol 125(7):1339–1445. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2013.11.030
Kobayashi K, Watanabe Y, Inoue T, Oka M, Yoshinaga H, Ohtsuka Y (2010) Scalp-recorded high-frequency oscillations in childhood sleep-induced electrical status epilepticus. Epilepsia 51(10):2190–2194
Kobayashi K, Yoshinaga H, Toda Y, Inoue T, Oka M, Ohtsuka Y (2011) High-frequency oscillations in idiopathic partial epilepsy of childhood. Epilepsia 52(10):1812–1819
Kobayashi K, Akiyama T, Oka M, Endoh F, Yoshinaga H (2015) A storm of fast (40–150 Hz) oscillations during hypsarrhythmia in West syndrome. Ann Neurol 77:58–67
Kucewicz MT, Cimbalnik J, Matsumoto JY, Brinkmann BH, Bower MR, Vasoli V et al (2014) High frequency oscillations are associated with cognitive processing in human recognition memory. Brain 137(8):2231–2244
Matsumoto A, Brinkmann BH, Matthew Stead S, Matsumoto J, Kucewicz MT, Marsh WR et al (2013) Pathological and physiological high-frequency oscillations in focal human epilepsy. J Neurophysiol 110(8):1958–1964
Melani F, Zelmann R, Dubeau F, Gotman J (2013) Occurrence of scalp-fast oscillations among patients with different spiking rate and their role as epileptogenicity marker. Epilepsy Res 106(3):345–356
Miao A, Xiang J, Tang L, Ge H, Liu H, Wu T et al (2014) Using ictal high-frequency oscillations (80–500 Hz) to localize seizure onset zones in childhood absence epilepsy: a MEG study. Neurosci Lett 566:21–26. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2014.02.038
Schevon CA, Trevelyan AJ, Schroeder CE, Goodman RR, McKhann G, Emerson RG (2009) Spatial characterization of interictal high frequency oscillations in epileptic neocortex. Brain 132(11):3047–3059
Staba RJ, Wilson CL, Bragin A, Fried I, Engel J (2002) Quantitative analysis of high-frequency oscillations (80–500 Hz) recorded in human epileptic hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. J Neurophysiol 88(4):1743–1752
Staba RJ, Wilson CL, Bragin A, Jhung D, Fried I, Engel J Jr (2004) High-frequency oscillations recorded in human medial temporal lobe during sleep. Ann Neurol 56:108–115
Staley KJ (2007) Neurons skip a beat during fast ripples. Neuron 55(6):828–830
Tao JX, Ray A, Hawes-Ebersole S, Ebersole JS (2005) Intracranial EEG substrates of scalp EEG interictal spikes. Epilepsia 46(5):669–676
Urrestarazu E, Chander R, Dubeau F, Gotman J (2007) Interictal high-frequency oscillations (100–500 Hz) in the intracerebral EEG of epileptic patients. Brain 130(9):2354–2366
Van Klink NEC, van’t Klooster MA, Zelmann R, Leijten FSS, Ferrier CH, Braun KPJ et al (2014) High frequency oscillations in intra-operative electrocorticography before and after epilepsy surgery. Clin Neurophysiol 125(11):2212–2219. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2014.03.004
Von Ellenrieder N, Beltrachini L, Perucca P, Gotman J (2014) Size of cortical generators of epileptic interictal events and visibility on scalp EEG. Neuroimage 94:47–54. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.02.032
Worrell GA, Gardner AB, Stead SM, Hu S, Goerss S, Cascino GJ et al (2008) High-frequency oscillations in human temporal lobe: simultaneous microwire and clinical macroelectrode recordings. Brain 131(4):928–937
Wu JY, Sankar R, Lerner JT, Matsumoto JH, Vinters HV, Mathern GW (2010) Removing interictal fast ripples on electrocorticography linked with seizure freedom in children. Neurology. 75(19):1686–1694
Zelmann R, Lina JM, Schulze-Bonhage A, Gotman J, Jacobs J (2014) Scalp EEG is not a blur: it can see high frequency oscillations although their generators are small. Brain Topogr 27(5):683–704
Acknowledgments
Birgit Frauscher was supported by the Austrian Science Fund (Schrödinger Fellowship Abroad J3485-B24).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pizzo, F., Frauscher, B., Ferrari-Marinho, T. et al. Detectability of Fast Ripples (>250 Hz) on the Scalp EEG: A Proof-of-Principle Study with Subdermal Electrodes. Brain Topogr 29, 358–367 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-016-0481-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-016-0481-7