Abstract
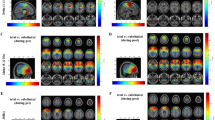
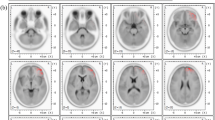
West syndrome is a severe epileptic encephalopathy of infancy with a poor developmental outcome. This syndrome is associated with the pathognomonic EEG feature of hypsarrhythmia. The aim of the study was to describe neuronal networks underlying hypsarrhythmia using the source analysis method (dynamic imaging of coherent sources or DICS) which represents an inverse solution algorithm in the frequency domain. In order to investigate the interaction within the detected network, a renormalized partial directed coherence (RPDC) method was also applied as a measure of the directionality of information flow between the source signals. Both DICS and RPDC were performed for EEG delta activity (1–4 Hz) in eight patients with West syndrome and in eight patients with partial epilepsies (control group). The brain area with the strongest power in the given frequency range was defined as the reference region. The coherence between this reference region and the entire brain was computed using DICS. After that, the RPDC was applied to the source signals estimated by DICS. The results of electrical source imaging were compared to results of a previous EEG-fMRI study which had been carried out using the same cohort of patients. As revealed by DICS, delta activity in hypsarrhythmia was associated with coherent sources in the occipital cortex (main source) as well as the parietal cortex, putamen, caudate nucleus and brainstem. In patients with partial epilepsies, delta activity could be attributed to sources in the occipital, parietal and sensory-motor cortex. In West syndrome, RPDC showed the strongest and most significant direction of ascending information flow from the brainstem towards the putamen and cerebral cortex. The neuronal network underlying hypsarrhythmia in this study resembles the network which was described in previous EEG-fMRI and PET studies with involvement of the brainstem, putamen and cortical regions in the generation of hypsarrhythmia. The RPDC suggests that brainstem could have a key role in the pathogenesis of West syndrome. This study supports the theory that hypsarrhythmia results from ascending brainstem pathways that project widely to basal ganglia and cerebral cortex.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1974) A new look to the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Autom Control 19(6):716–723
Allen PJ, Polizzi G, Krakow K, Fish DR, Lemieux L (1998) Identification of EEG events in the MR scanner: the problem of pulse artifact and a method for its subtraction. Neuroimage 8(3):229–239. doi:10.1006/nimg.1998.0361
Allen PJ, Josephs O, Turner R (2000) A method for removing imaging artifact from continuous EEG recorded during functional MRI. Neuroimage 12(2):230–239. doi:10.1006/nimg.2000.0599
Alva-Moncayo E, Diaz-Leal MC, Olmos-Garcia De Alba G (2002) Electroencephalographic discoveries in children with infantile massive spasms in Mexico. Rev Neurol 34(10):928–932
Astolfi L, Cincotti F, Mattia D, Marciani MG, Baccala LA, de Vico FF, Salinari S, Ursino M, Zavaglia M, Ding L, Edgar JC, Miller GA, He B, Babiloni F (2007) Comparison of different cortical connectivity estimators for high-resolution EEG recordings. Hum Brain Mapp 28(2):143–157. doi:10.1002/hbm.20263
Baccala LA, Sameshima K (2001) Partial directed coherence: a new concept in neural structure determination. Biol Cybern 84(6):463–474
Chiron C, Dulac O, Bulteau C, Nuttin C, Depas G, Raynaud C, Syrota A (1993) Study of regional cerebral blood flow in West syndrome. Epilepsia 34(4):707–715
Chugani HT (2002) Pathophysiology of infantile spasms. Adv Exp Med Biol 497:111–121
Chugani HT, Shields WD, Shewmon DA, Olson DM, Phelps ME, Peacock WJ (1990) Infantile spasms: I. PET identifies focal cortical dysgenesis in cryptogenic cases for surgical treatment. Ann Neurol 27(4):406–413. doi:10.1002/ana.410270408
Chugani HT, Shewmon DA, Sankar R, Chen BC, Phelps ME (1992) Infantile spasms: II. Lenticular nuclei and brain stem activation on positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol 31(2):212–219. doi:10.1002/ana.410310212
Curio G, Oppel F (1988) Intraparenchymatous ponto-mesencephalic field distribution of brain-stem auditory evoked potentials in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 69(3):259–265
Curio G, Oppel F, Scherg M (1987) Peripheral origin of BAEP wave II in a case with unilateral pontine pathology: a comparison of intracranial and scalp records. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 66(1):29–33
Ding M, Bressler SL, Yang W, Liang H (2000) Short-window spectral analysis of cortical event-related potentials by adaptive multivariate autoregressive modeling: data preprocessing, model validation, and variability assessment. Biol Cybern 83(1):35–45
Drongelen W, Yuchtman M, VanVeen BD, van Huffelen AC (1996) A spatial filtering technique to detect and localize multiple sources in the brain. Brain Topogr 9(1):39–49
Dulac O (2001) What is West syndrome? Brain Dev 23(7):447–452. doi:10.1016/S0387-7604(01)00268-6
Fuchs M, Kastner J, Wagner M, Hawes S, Ebersole JS (2002) A standardized boundary element method volume conductor model. Clin Neurophysiol 113(5):702–712
Fusco L, Vigevano F (1993) Ictal clinical electroencephalographic findings of spasms in West syndrome. Epilepsia 34(4):671–678
Glass RB, Fernbach SK, Norton KI, Choi PS, Naidich TP (2004) The infant skull: a vault of information. Radiographics 24(2):507–522. doi:10.1148/rg.24203510524/2/507
Groening K, Brodbeck V, Moeller F, Wolff S, van Baalen A, Michel CM, Jansen O, Boor R, Wiegand G, Stephani U, Siniatchkin M (2009) Combination of EEG-fMRI and EEG source analysis improves interpretation of spike-associated activation networks in paediatric pharmacoresistant focal epilepsies. Neuroimage 46(3):827–833. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.02.026
Gross J, Kujala J, Hamalainen M, Timmermann L, Schnitzler A, Salmelin R (2001) Dynamic imaging of coherent sources: studying neural interactions in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(2):694–699. doi:10.1073/pnas.98.2.69498/2/694
Gross J, Timmermann L, Kujala J, Dirks M, Schmitz F, Salmelin R, Schnitzler A (2002) The neural basis of intermittent motor control in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(4):2299–2302. doi:10.1073/pnas.03268209999/4/2299
Guzzetta F, Frisone MF, Ricci D, Rando T, Guzzetta A (2002) Development of visual attention in West syndrome. Epilepsia 43(7):757–763. doi:10.1046/j.1528-1157.2002.34601.x
Haginoya K, Kon K, Yokoyama H, Tanaka S, Kato R, Munakata M, Yagi T, Takayanagi M, Yoshihara Y, Nagai M, Yamazaki T, Maruoka S, Iinuma K (2000) The perfusion defect seen with SPECT in West syndrome is not correlated with seizure prognosis or developmental outcome. Brain Dev 22(1):16–23. doi:10.1016/S0387-7604(99)00081-9
Hellwig B, Haussler S, Lauk M, Guschlbauer B, Koster B, Kristeva-Feige R, Timmer J, Lucking CH (2000) Tremor-correlated cortical activity detected by electroencephalography. Clin Neurophysiol 111(5):806–809. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(00)00248-0
Hellwig B, Haussler S, Schelter B, Lauk M, Guschlbauer B, Timmer J, Lucking CH (2001) Tremor-correlated cortical activity in essential tremor. Lancet 357(9255):519–523. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04044-7
Hellwig B, Schelter B, Guschlbauer B, Timmer J, Lucking CH (2003) Dynamic synchronisation of central oscillators in essential tremor. Clin Neurophysiol 114(8):1462–1467. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(03)00116-0
Holmes MD (2008) Dense array EEG: methodology and new hypothesis on epilepsy syndromes. Epilepsia 49:3–14. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01505.x
Holmes MD, Brown M, Tucker DM (2004) Are “generalized” seizures truly generalized? Evidence of localized mesial frontal and frontopolar discharges in absence. Epilepsia 45(12):1568–1579. doi:10.1111/j.0013-9580.2004.23204.x
Holmes MD, Quiring J, Tucker DM (2010) Evidence that juvenile myoclonic epilepsy is a disorder of frontotemporal corticothalamic networks. Neuroimage 49(1):80–93. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.08.004
Hrachovy RA, Frost JD Jr (1989) Infantile spasms. Pediatr Clin N Am 36(2):311–329
Hrachovy RA, Frost JD Jr (2003) Infantile epileptic encephalopathy with hypsarrhythmia (infantile spasms/West syndrome). J Clin Neurophysiol 20(6):408–425
Hrachovy RA, Frost JD Jr, Kellaway P (1981) Sleep characteristics in infantile spasms. Neurology 31(6):688–693
Jambaque I, Chiron C, Dulac O, Raynaud C, Syrota P (1993) Visual inattention in West syndrome: a neuropsychological and neurofunctional imaging study. Epilepsia 34(4):692–700
Juhasz C, Chugani HT, Muzik O, Chugani DC (2001) Neuroradiological assessment of brain structure and function and its implication in the pathogenesis of West syndrome. Brain Dev 23(7):488–495. doi:10.1016/S0387-7604(01)00295-9
Kaminski MDM, Truccolo WA, Bressler SL (2001) Evaluating causal relations in neural systems: Granger causality, directed transfer function and statistical assessment of significance. Biol Cybern 85(2):145–157
Kobayashi K, Oka M, Inoue T, Ogino T, Yoshinaga H, Ohtsuka Y (2005) Characteristics of slow waves on EEG associated with epileptic spasms. Epilepsia 46(7):1098–1105. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2005.63004.x
Kramer U, Sue WC, Mikati MA (1997) Hypsarrhythmia: frequency of variant patterns and correlation with etiology and outcome. Neurology 48(1):197–203
Kujala J, Gross J, Salmelin R (2008) Localization of correlated network activity at the cortical level with MEG. Neuroimage 39(4):1706–1720. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.10.042
Kwan P, Arzimanoglou A, Berg AT, Brodie MJ, Allen Hauser W, Mathern G, Moshe SL, Perucca E, Wiebe S, French J (2010) Definition of drug resistant epilepsy: consensus proposal by the ad hoc Task Force of the ILAE Commission on Therapeutic Strategies. Epilepsia 51(6):1069–1077. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02397.x
Lado FA, Moshe SL (2002) Role of subcortical structures in the pathogenesis of infantile spasms: what are possible subcortical mediators? Int Rev Neurobiol 49:115–140
Langlais PJ, Wardlow ML, Yamamoto H (1991) Changes in CSF neurotransmitters in infantile spasms. Pediatr Neurol 7(6):440–445
Legatt AD (2002) Mechanisms of intraoperative brainstem auditory evoked potential changes. J Clin Neurophysiol 19(5):396–408
Legatt AD, Arezzo JC, Vaughan HG Jr (1986) Short-latency auditory evoked potentials in the monkey. II. Intracranial generators. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 64(1):53–73
Maris E, Oostenveld R (2007) Nonparametric statistical testing of EEG- and MEG-data. J Neurosci Methods 164(1):177–190. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.03.024
Maris E, Schoffelen JM, Fries P (2007) Nonparametric statistical testing of coherence differences. J Neurosci Methods 163(1):161–175. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.02.011
Metsahonkala L, Gaily E, Rantala H, Salmi E, Valanne L, Aarimaa T, Liukkonen E, Holopainen I, Granstrom ML, Erkinjuntti M, Gronroos T, Sillanpaa M (2002) Focal and global cortical hypometabolism in patients with newly diagnosed infantile spasms. Neurology 58(11):1646–1651
Michel CM, Murray MM, Lantz G, Gonzalez S, Spinelli L, Grave de Peralta R (2004) EEG source imaging. Clin Neurophysiol 115(10):2195–2222. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2004.06.001
Moeller F, Muthuraman M, Stephani U, Deuschl G, Raethjen J, Siniatchkin M (2012) Representation and propagation of epileptic activity in absences and generalized photoparoxysmal responses. Hum Brain Mapp. doi:10.1002/hbm.22026
Moller AR, Burgess J (1986) Neural generators of the brain-stem auditory evoked potentials (BAEPs) in the rhesus monkey. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 65(5):361–372
Moller AR, Jho HD, Yokota M, Jannetta PJ (1995) Contribution from crossed and uncrossed brainstem structures to the brainstem auditory evoked potentials: a study in humans. Laryngoscope 105(6):596–605. doi:10.1288/00005537-199506000-00007
Morimatsu Y, Murofushi K, Handa T, Shinoara T, Shiraki H (1972) Pathology in severe physical and mental disabilities in children–with special reference to 4 cases of nodding spasm. Shinkei Kenkyu No Shimpo 16(3):465–470
Muthuraman M, Raethjen J, Hellriegel H, Deuschl G, Heute U (2008) Imaging coherent sources of tremor related EEG activity in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2008:4716–4719. doi:10.1109/IEMBS.2008.4650266
Muthuraman M, Heute U, Deuschl G, Raethjen J (2010) The central oscillatory network of essential tremor. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2010:154–157. doi:10.1109/IEMBS.2010.5627211
Muthuraman M, Tamas G, Hellriegel H, Deuschl G, Raethjen J (2012a) Source analysis of Beta-synchronisation and cortico-muscular coherence after movement termination based on high resolution electroencephalography. PLoSOne 7(3):e33928
Muthuraman M, Heute U, Arning K, Anwar AR, Elble R, Deuschl G, Raethjen J (2012b) Oscillating central motor networks in pathological tremors and voluntary movements. What makes the difference?. NeuroImage. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.01.088
Neumaier A, Schneider T (2001) Estimation of parameters and eigenmodes of multivariate autoregressive models. ACM Trans Math Softw 27(1):27–57
Neville BG (1972) The origin of infantile spasms: evidence from a case of hydranencephaly. Dev Med Child Neurol 14(5):644–647
Oostenveld RFP, Maris E, Schoffelen JM (2011) FieldTrip: open source soft ware for advanced analysis of MEG, EEG, and invasive electrophysiological data. Comput Intell Neurosci. doi:10.1155/2011/156869
Panayiotopoulos CP (2005) Epileptic encephalopathies in infancy and early childhood in which the epileptiform abnormalities may contribute to progressive dysfunction. In: Panayiotopoulos CP (ed) The epilepsies. Seizures, syndromes and management, 2010/09/08 edn. Bladon Medical Publishing, Oxfordshire. doi:NBK2606 [bookaccession]
Paquereau J, Meurice JC, Neau JP, Ingrand P, Patte F (1994) Auditory brain-stem responses (ABRs) in sleep respiratory disorders. Eur J Clin Invest 24(3):156–160
Plourde G, Garcia-Asensi A, Backman S, Deschamps A, Chartrand D, Fiset P, Picton TW (2008) Attenuation of the 40-hertz auditory steady state response by propofol involves the cortical and subcortical generators. Anesthesiology 108(2):233–242. doi:10.1097/01.anes.0000299839.33721.6d
Rando T, Baranello G, Ricci D, Guzzetta A, Tinelli F, Biagioni E, La Torre G, Epifanio R, Signorini S, Fazzi E, Mercuri E, Cioni G, Guzzetta F (2005) Cognitive competence at the onset of West syndrome: correlation with EEG patterns and visual function. Dev Med Child Neurol 47(11):760–765. doi:10.1017/S0012162205001593
Riedel H, Kollmeier B (2002) Auditory brain stem responses evoked by lateralized clicks: is lateralization extracted in the human brain stem? Hear Res 163(1–2):12–26. doi:S0378595501003628
Sameshima K, Baccala LA (1999) Using partial directed coherence to describe neuronal ensemble interactions. J Neurosci Methods 94(1):93–103
Satoh J, Mizutani T, Morimatsu Y (1986) Neuropathology of the brainstem in age-dependent epileptic encephalopathy: especially of cases with infantile spasms. Brain Dev 8(4):443–449
Schack B, Hesse W, Moller E, Arnold M (2003) The use of time-variant EEG Granger causality for inspecting directed interdependencies of neural assemblies. J Neurosci Methods 124(1):27–44. doi:10.1016/S0165-0270(02)00366-7
Schelter B, Timmer J, Eichler M (2009) Assessing the strength of directed influences among neural signals using renormalized partial directed coherence. J Neurosci Methods 179(1):121–130. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2009.01.006
Scherg M, von Cramon D (1985) A new interpretation of the generators of BAEP waves I–V: results of a spatio-temporal dipole model. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 62(4):290–299
Schneider T, Neumaier A (2001) Algorithm 808: ARfit: a Matlab package for the estimation of parameters and eigenmodes of multivariate autoregressive models. ACM Trans Math Softw 27(1):58–65
Schnitzler A, Timmermann L, Gross J (2006) Physiological and pathological oscillatory networks in the human motor system. J Physiol Paris 99(1):3–7. doi:10.1016/j.jphysparis.2005.06.010
Schnitzler A, Münks C, Butz M, Timmermann L, Gross J (2009) Synchronized brain network associated with essential tremor as revealed by magnetoencephalography. Mov Disord 24(11):1629–1635
Schoffelen JM, Oostenveld R, Fries P (2008) Imaging the human motor system’s beta-band synchronization during isometric contraction. Neuroimage 41(2):437–447. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.01.045
Siniatchkin M, van Baalen A, Jacobs J, Moeller F, Moehring J, Boor R, Wolff S, Jansen O, Stephani U (2007) Different neuronal networks are associated with spikes and slow activity in hypsarrhythmia. Epilepsia 48(12):2312–2321. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.01195.x
Siniatchkin M, Groening K, Moehring J, Moeller F, Boor R, Brodbeck V, Michel CM, Rodionov R, Lemieux L, Stephani U (2010) Neuronal networks in children with continuous spikes and waves during slow sleep. Brain 133(9):2798–2813. doi:10.1093/brain/awq183
Sudmeyer M, Saleh A, Wojtecki L, Cohnen M, Gross J, Ploner M, Hefter H, Timmermann L, Schnitzler A (2006) Wilson’s disease tremor is associated with magnetic resonance imaging lesions in basal ganglia structures. Mov Disord 21(12):2134–2139. doi:10.1002/mds.21136
Tass P, Rosenblum MG, Weule J, Kurths J, Pikovsky A, Volkmann J, Schnitzler A, Freund HJ (1998) Detection of n:m phase locking from noisy data: application to magnetoencephalography. Phys Rev Lett 81(15):3291–3294
Timmermann L, Gross J, Butz M, Kircheis G, Haussinger D, Schnitzler A (2003a) Mini-asterixis in hepatic encephalopathy induced by pathologic thalamo-motor-cortical coupling. Neurology 61(5):689–692
Timmermann L, Gross J, Dirks M, Volkmann J, Freund HJ, Schnitzler A (2003b) The cerebral oscillatory network of parkinsonian resting tremor. Brain 126(Pt 1):199–212
Van Veen BD, van Drongelen W, Yuchtman M, Suzuki A (1997) Localization of brain electrical activity via linearly constrained minimum variance spatial filtering. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 44(9):867–880. doi:10.1109/10.623056
Volkmann J, Joliot M, Mogilner A, Ioannides AA, Lado F, Fazzini E, Ribary U, Llinas R (1996) Central motor loop oscillations in parkinsonian resting tremor revealed by magnetoencephalography. Neurology 46(5):1359–1370
Vulliemoz S, Thornton R, Rodionov R, Carmichael DW, Guye M, Lhatoo S, McEvoy AW, Spinelli L, Michel CM, Duncan JS, Lemieux L (2009) The spatio-temporal mapping of epileptic networks: combination of EEG-fMRI and EEG source imaging. Neuroimage 46(3):834–843
Wenzel D (1987) Evoked potentials in infantile spasms. Brain Dev 9(4):365–368
Wilke C, van Drongelen W, Kohrman M, He B (2010) Neocortical seizure foci localization by means of a directed transfer function method. Epilepsia 51(4):564–572. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02329.x
Wilke C, Worrell G, He B (2011) Graph analysis of epileptogenic networks in human partial epilepsy. Epilepsia 52(1):84–93. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2010.02785.x
Wolters CH, Anwander A, Maess B, Macleod RS, Friederici AD (2004) The influence of volume conduction effects on the EEG/MEG reconstruction of the sources of the Early Left Anterior Negativity. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 5:3569–3572. doi:10.1109/IEMBS.2004.1404003
Zhang Z (1995) A fast method to compute surface-potentials generated by dipoles within multilayer anisotropic spheres. Phys Med Biol 40(3):335–349
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful patients, parents and colleagues who contributed to the study. The funding for the study was provided by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG). The study was conducted in the frames of D3 and D2 subproject of Sonderforschungsbereich (SFB) 855.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any conflict of interest to disclose.
Ethical Publication Statement
We confirm that we have read the Journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. Natia and M. Muthuraman have contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Japaridze, N., Muthuraman, M., Moeller, F. et al. Neuronal Networks in West Syndrome as Revealed by Source Analysis and Renormalized Partial Directed Coherence. Brain Topogr 26, 157–170 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-012-0245-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-012-0245-y