Abstract
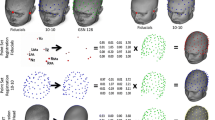
We investigated the variability of electrode positions for a multi-channel, custom electrode cap placed onto participants’ heads without taking scalp measurements. The electrode positions were digitized in a three-dimensional space for 10 young adult participants on three separate occasions. Positional variability was determined for 15 selected electrodes within the three-dimensional preauricular-nasion (PAN) coordinate system and from this system, angular coordinate variability was also determined. The standard deviations of the 15 selected electrodes ranged from 3.0 to 12.7 mm in the PAN system. These data resulted in a variability of 2.0° to 10.4° among the angular coordinates. The measurements indicated slightly greater variability of electrode positions compared to studies when electrodes were placed using scalp measurements. The implication of this study is that the use of electrode caps may not be appropriate when electroencephalographic (EEG) or evoked potential (EP) techniques depend on accurate electrode placement. Additionally, if a longitudinal study is performed, electrode locations should be checked to ensure that they conform with previous sessions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kavanagh KT, Clark ST. Comparison of the mastoid to vertex and mastoid to high forehead electrode arrays in recording auditory evoked potentials. Ear Hear 1989;10(4):259–61
van Olphen AF, Rodenburg M, Verwey C. Distribution of brain stem responses to acoustic stimuli over the human scalp. Audiology 1978;17(6):511–8
Vaughan HG Jr., Ritter W. The sources of auditory evoked responses recorded from the human scalp. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1970;28(4):360–7
Wood CC, Allison T. Interpretation of evoked potentials: a neurophysiological perspective. Can J Psychol 1981;35(2):113–35
Jasper HH. The ten twenty electrode system of the international federation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1958;10:371–5
Towle VL, Bolanos J, Suarez D, Tan K, Grzeszczuk R, Levin DN, et al. The spatial location of EEG electrodes: locating the best-fitting sphere relative to cortical anatomy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1993;86(1):1–6
Epstein CM, Bej MD, Foldvary-Schaefer N, Lagerlund TD, Helmers SL, Husain AM. Guideline 5: guidelines for standard electrode position nomenclature (American Clinical Neurophysiology Society). J Clin Neurophysiol 2006;23(2):107–10
Lagerlund TD, Sharbrough FW, Jack CR Jr., Erickson BJ, Strelow DC, Cicora KM, et al. Determination of 10-20 system electrode locations using magnetic resonance image scanning with markers. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1993;86(1): 7–14
Khosla D, Don M, Kwong B. Spatial mislocalization of EEG electrodes - Effects on accuracy of dipole estimation. Clin Neurophysiol 1999;110(2):261–71
Source Signal Imaging. LOCATOR [computer program]. 4.1. San Diego, CA: Source Signal Imaging, Inc., 1998
Bland JM, Altmann DG. Statistics notes: measurement error. BMJ 1996;312:1654
Acknowledgements
This study was carried out at The University of Memphis, School of Audiology and Speech Language Pathology. Support for the study was from the Center for Research Initiatives and Strategies for the Communicatively Impaired (CRISCI), a State of Tennessee Center of Excellence Grant, and the Assisi Foundation of Memphis. Portions of the paper were presented at the American Academy of Audiology convention, April 2003, San Antonio, TX. The authors are grateful to Rachel Lintvedt for data entry and reliability checks.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atcherson, S.R., Gould, H.J., Pousson, M.A. et al. Variability of Electrode Positions Using Electrode Caps. Brain Topogr 20, 105–111 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-007-0036-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-007-0036-z