Abstract
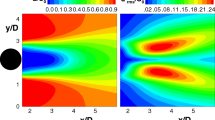
Spectral proper orthogonal decomposition (SPOD) is applied as a post-processing technique to elucidate the relationship between turbulent motion and pollutant removal in a two-dimensional street canyon with an aspect ratio of one and a uniform roof height. A pollutant is continuously emitted from a line source set on the ground of the target canyon. First, the SPOD technique is used to decompose the velocity field obtained from a large-eddy simulation. The external large-scale coherent structures and waves caused by the Kelvin–Helmholtz instabilities are extracted and visualized using the SPOD modes. The SPOD cospectra are defined to further examine the phase relationship between the streamwise and vertical velocity components and concentrations. Based on the SPOD cospectra, the contribution of the turbulent structures at various scales to pollutant removal are quantitatively estimated. The results reveal that both the large-scale coherent structures and Kelvin–Helmholtz instabilities could cause ejection events at the canyon roof level and thus contribute to pollutant removal. Although the former occupy a large proportion of the turbulence kinetic energy, a smaller vertical turbulent mass flux is also observed. Conversely, the latter contribute to stronger ejection and sweep events with stronger vertical components. However, the shapes of the modes indicate that the external large-scale coherent structures also play a role in triggering and transporting the small-scale turbulence at the roof level, which may indirectly contribute to pollutant removal.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araya DB, Colonius T, Dabiri JO (2017) Transition to bluff-body dynamics in the wake of vertical-axis wind turbines. J Fluid Mech 813:346–381. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2016.862
Barbano F, Brattich E, Di Sabatino S (2021) Characteristic scales for turbulent exchange processes in a real urban canopy. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 178:119–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-020-00554-5
Bartlett MS (1948) Smoothing periodograms from time-series with continuous spectra. Nature 161:686–687
Blackman K, Perret L (2016) Non-linear interactions in a boundary layer developing over an array of cubes using stochastic estimation. Phys Fluids 28:095108. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4962938
Blackman K, Perret L, Savory E (2018) Effects of the upstream-flow regime and canyon aspect ratio on non-linear interactions between a street-canyon flow and the overlying noundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 169:537–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-018-0378-y
Cheng WC, Liu CH (2011) Large-eddy simulation of flow and pollutant transports in and above two-dimensional idealized street canyons. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 139:411–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-010-9584-y
Cheng WC, Liu CH, Leung DYC (2008) Computational formulation for the evaluation of street canyon ventilation and pollutant removal performance. Atmos Environ 42:9041–9051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.09.045
Cintolesi C, Pulvirenti B, Di SS (2021) Large-eddy simulations of pollutant removal enhancement from urban canyons. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-021-00610-8
Coceal O, Dobre A, Thomas TG, Belcher SE (2007) Structure of turbulent flow over regular arrays of cubical roughness. J Fluid Mech 589:375–409. https://doi.org/10.1017/S002211200700794X
Cui Z, Cai X, Baker CJ (2004) Large-eddy simulation of turbulent flow in a street canyon. Q J R Meteorol Soc 130:1373–1394. https://doi.org/10.1256/qj.02.150
Di Bernardino A, Monti P, Leuzzi G, Querzoli G (2018) Pollutant fluxes in two-dimensional street canyons. Urban Clim 24:80–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2018.02.002
Germano M, Piomelli U, Moin P, Cabot WH (1991) A dynamic subgrid-scale eddy viscosity model. Phys Fluids A 3:1760–1765. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.857955
Han BS, Baik JJ, Kwak KH, Park SB (2018) Large-eddy simulation of reactive pollutant exchange at the top of a street canyon. Atmos Environ 187:381–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.06.012
Inagaki A, Kanda M (2010) Organized structure of active turbulence over an array of cubes within the logarithmic layer of atmospheric flow. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 135:209–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-010-9477-0
Issa RI (1986) Solution of the implicitly discretised fluid flow equations by operator-splitting. J Comput Phys 62:40–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9991(86)90099-9
Jaroslawski T, Savory E, Perret L (2020) Roof-level large- and small-scale coherent structures in a street canyon flow. Environ Fluid Mech 20:739–763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10652-019-09721-w
Kanda M (2006) Large-eddy simulations on the effects of surface geometry of building arrays on turbulent organized structures. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 118:151–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-005-5294-2
Kanda M, Moriwaki R, Kasamatsu F (2004) Large-eddy simulation of turbulent organized structures within and above explicitly resolved cube arrays. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 112:343–368. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BOUN.0000027909.40439.7c
Kastner-Klein P, Berkowicz R, Britter R (2004) The influence of street architecture on flow and dispersion in street canyons. Meteorol Atmos Phys 87:121–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-003-0065-4
Kikumoto H, Ooka R (2012) A numerical study of air pollutant dispersion with bimolecular chemical reactions in an urban street canyon using large-eddy simulation. Atmos Environ 54:456–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.02.039
Klein PM, Galvez JM (2015) Flow and turbulence characteristics in a suburban street canyon. Environ Fluid Mech 15:419–438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10652-014-9352-5
Lee JH, Sung HJ, Krogstad PÅ (2011) Direct numerical simulation of the turbulent boundary layer over a cube-roughened wall. J Fluid Mech 669:397–431. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112010005082
Letzel MO, Krane M, Raasch S (2008) High resolution urban large-eddy simulation studies from street canyon to neighbourhood scale. Atmos Environ 42:8770–8784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.08.001
Liu CH, Wong CCC (2014) On the pollutant removal, dispersion, and entrainment over two-dimensional idealized street canyons. Atmos Res 135–136:128–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2013.08.006
Louka P, Belcher SE, Harrison RG (2000) Coupling between air flow in streets and the well-developed boundary layer aloft. Atmos Environ 34:2613–2621. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(99)00477-X
Lumley JL (1970) Stochastic tools in turbulence. Academic Press, Cambridge
Lumley JL (1967) The structure of inhomogeneous turbulent flows. Atmos Turbul wave Propag, 166–178
Meyers J, Sagaut P (2006) On the model coefficients for the standard and the variational multi-scale Smagorinsky model. J Fluid Mech 569:287–319. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112006002850
Michioka T, Sato A (2012) Effect of incoming turbulent structure on pollutant removal from two-dimensional street canyon. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 145:469–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-012-9733-6
Michioka T, Sato A, Takimoto H, Kanda M (2011) Large-eddy simulation for the mechanism of pollutant removal from a two-dimensional street canyon. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 138:195–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-010-9556-2
Oke TR (2002) Boundary Layer Climates, 2nd edn. Routledge, London
Park SJ, Kim JJ, Kim MJ, Park RJ, Cheong HB (2015) Characteristics of flow and reactive pollutant dispersion in urban street canyons. Atmos Environ 108:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.02.065
Pavageau M, Schatzmann M (1999) Wind tunnel measurements of concentration fluctuations in an urban street canyon. In: Atmospheric Environment. Pergamon, pp. 3961–3971
Perret L, Rivet C (2013) Dynamics of a turbulent boundary layer over cubical roughness elements: Insight from PIV measurements and POD analysis. In: Proceedings of Eighth International Symposium on Turbulence and Shear Flow Phenomena. Poitiers, France
Roe PL (1986) Characteristic-based schemes for the Euler equations. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 18:337–365. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.fl.18.010186.002005
Rowley CW, Colonius T, Murray RM (2004) Model reduction for compressible flows using POD and Galerkin projection. Phys D Nonlinear Phenom 189:115–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHYSD.2003.03.001
Salizzoni P, Soulhac L, Mejean P (2009) Street canyon ventilation and atmospheric turbulence. Atmos Environ 43:5056–5067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.06.045
Schmidt OT, Colonius T (2020) Guide to spectral proper orthogonal decomposition. AIAA J 58:1023–1033. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J058809
Schmidt OT, Towne A, Rigas G, Colonius T, Brès GA (2018) Spectral analysis of jet turbulence. J Fluid Mech 855:953–982. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2018.675
Siddiqui MS, Latif STM, Saeed M, Rahman M, Badar AW, Hasan SM (2020) Reduced order model of offshore wind turbine wake by proper orthogonal decomposition. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 82:108554. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJHEATFLUIDFLOW.2020.108554
Sirovich L (1987) Turbulence and the dynamics of coherent structures. I Coherent Structures Q Appl Math 45:561–571
Smagorinsky J (1963) General circulation experiments with the primitive equations. Mon Weather Rev 91:99–164. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1963)091%3c0099:gcewtp%3e2.3.co;2
Solazzo E, Britter RE (2007) Transfer processes in a simulated urban street canyon. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 124:43–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-007-9176-7
Spalding DB (1962) A new analytical expression for the drag of a flat plate valid for both the turbulent and laminar regimes. Int J Heat Mass Transf 5:1133–1138. https://doi.org/10.1016/0017-9310(62)90189-8
Taira K, Brunton SL, Dawson STM, Rowley CW, Colonius T, McKeon BJ, Schmidt OT, Gordeyev S, Theofilis V, Ukeiley LS (2017) Modal analysis of fluid flows: an overview. AIAA J 55:4013–4041. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J056060
Takimoto H, Inagaki A, Kanda M, Sato A, Michioka T (2013) Length-scale similarity of turbulent organized structures over surfaces with different roughness types. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 147:217–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-012-9790-x
The OpenFOAM Foundation Ltd (2020) OpenFOAM | Free CFD Software | The OpenFOAM Foundation. https://openfoam.org/. Accessed 16 Jan 2021
Tominaga Y, Stathopoulos T (2011) CFD modeling of pollution dispersion in a street canyon: comparison between LES and RANS. J Wind Eng Ind Aerodyn 99:340–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2010.12.005
Towne A, Schmidt OT, Colonius T (2018) Spectral proper orthogonal decomposition and its relationship to dynamic mode decomposition and resolvent analysis. J Fluid Mech 847:821–867. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2018.283
Van Driest ER (1956) On turbulent flow near a wall. J Aeronaut Sci 23:1007–1011. https://doi.org/10.2514/8.3713
Walton A, Cheng AYS (2002) Large-eddy simulation of pollution dispersion in an urban street canyon—Part II: Idealised canyon simulation. Atmos Environ 36:3615–3627. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00260-1
Welch PD (1967) The use of fast Fourier transform for the estimation of power spectra: a method based on time averaging over short, modified periodograms. IEEE Trans Audio Electroacoust 15:70–73. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAU.1967.1161901
Zhang J, Zhao X (2020) Machine-learning-based surrogate modeling of aerodynamic flow around distributed structures. AIAA J 59:868–879. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J059877
Zhang YW, Gu ZL, Cheng Y, Lee SC (2011) Effect of real-time boundary wind conditions on the air flow and pollutant dispersion in an urban street canyon-Large eddy simulations. Atmos Environ 45:3352–3359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.03.055
Zhang B, Ooka R, Kikumoto H (2021) Identification of three-dimensional flow features around a square-section building model via spectral proper orthogonal decomposition. Phys Fluids 33:35151. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0041395
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 7626 kb)
Supplementary file2 (MP4 7573 kb)
Supplementary file3 (MP4 7802 kb)
Supplementary file4 (MP4 7650 kb)
Supplementary file5 (MP4 7605 kb)
Supplementary file6 (MP4 7456 kb)
Supplementary file7 (MP4 7735 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Ooka, R. & Kikumoto, H. Spectral Proper Orthogonal Decomposition Analysis of Turbulent Flow in a Two-Dimensional Street Canyon and Its Role in Pollutant Removal. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 183, 97–123 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-021-00676-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-021-00676-4