Abstract
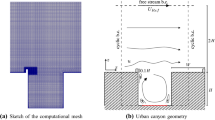
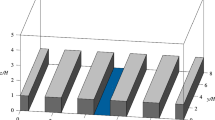
Large-eddy simulations are conducted to investigate the effects of the incoming turbulent structure of the flow on pollutant removal from an ideal canyon. The target canyon is a two-dimensional street canyon with an aspect ratio of 1.0 (building height to street width). Three turbulent flows upwind of the street canyon are generated by using different block configurations, and a tracer gas is released as a ground-level line source at the centre of the canyon floor. Mean velocity profiles for the three flows are similar, except near the roof. However, the root-mean-square values of the velocity fluctuations and the Reynolds shear stress increase with the friction velocity of the incoming turbulent flow. The spatially-averaged concentration within the canyon decreases with increasing friction velocity. Coherent structures of low-momentum fluid, generated above the upwind block configurations, contribute to pollutant removal, and the amount of pollutant removal is directly related to the size of the coherent structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boris JP, Book D (1976) Flux-corrected transport. III: minimal-error FCT algorithms. J Comput Phys 20: 397–431
Cai X-M, Barlow JF, Belcher SE. (2008) Dispersion and transfer of passive scalars in and above street canyons—large-eddy simulations. Atmos Environ 42: 5885–5895
Cheng WC, Liu C-H (2011) Large-eddy simulation of flow and pollutant transports in and above two-dimensional idealized street canyon. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 139: 1–27
Coceal O, Dobre A, Thomas TG, Belcher SE (2007) Structure of turbulent flow over regular arrays of cubical roughness. J Fluid Mech 589: 375–409
Cui Z, Cai X, Baker CJ (2004) Large-eddy simulation of turbulent flow in a street canyon. Q J R Meteorol Soc 130: 1373–1394
Garbero V, Salizzoni P, Soulhac L (2010) Experimental study of pollutant dispersion within a network of street. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 136: 457–487
Germano M, Piomelli U, Moin P, Cabot WH (1991) A dynamic subgrid-scale eddy viscosity model. Phys Fluids A 3: 1760–1766
Inagaki A, Kanda M (2010) Organized structure of active turbulence over an array of cubes within the logarithmic layer of atmospheric flow. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 135: 209–228
Kanda M (2006) Large-eddy simulations on the effects of surface geometry of building arrays on turbulent organized structures. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 118: 151–168
Kanda M, Moriwaki R, Kasamatsu F (2004) Large-eddy simulation of turbulent organized structures within and above explicitly resolved cube arrays. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 112: 343–368
Kim J, Moin P (1985) Application of a fractional-step method to incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. J Comput Phys 59: 308–323
Lee JH, Sung HJ, Krogstad P (2011) Direct numerical simulation of the turbulent boundary layer over a cube-roughed wall. J Fluid Mech 669: 397–431
Leonardi S, Orlandi P, Djenidi L, Antonia RA (2004) Structure of turbulent channel flow with square bars on one wall. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 25: 384–392
Letzel M, Krane M, Raasch S (2008) High resolution urban large-eddy simulation studies from street canyon to neighborhood scale. Atmos Environ 42: 8770–8784
Li X-X, Liu C-H, Leung DYC (2008) Large-eddy simulations of flow and pollutant dispersion in high-aspect-ration urban street canyons with wall model. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 129: 249–268
Lilly DK (1992) A proposed modification of the Germano subgrid-scale closure method. Phys Fluids A 4: 633–636
Liu C-H, Barth MC (2002) Large-eddy simulation of flow and scalar transport in a modeled street canyon. J Appl Meteorol 41: 660–673
Liu C-H, Barth MC, Leung DYC (2004) Large-eddy simulation of flow and pollutant transport in street canyons of different building-height-to-street-width ratios. J Appl Meteorol 43: 1410–1424
Liu C-H, Leung DYC, Barth MC (2005) On the prediction of air and pollutant exchange rates in street canyons of different aspect ratios using large-eddy simulation. Atmos Environ 39: 1567–1574
Meroney R, Pavageau M, Rafailidis S, Schatzmann M (1996) Study of line source characteristics for 2-D physical modeling of pollutant dispersion in street canyons. J Wind Eng Ind Aerodyn 62: 37–56
Michioka T, Kuorse R, Sada K, Makino H (2005) Direct numerical simulation of a particle-laden mixing layer with a chemical reaction. Int J Multiph Flow 31: 843–866
Michioka T, Sato A, Takimoto H, Kanda M (2011) Large-eddy simulation for the mechanism of pollutant removal from a two-dimensional street canyon. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 138: 195–213
Pavageau M, Schatzmann M (1999) Wind tunnel measurements of concentration fluctuations in an urban street canyon. Atmos Environ 33: 3961–3971
Sagaut P (2002) Large eddy simulation for incompressible flows: an introduction, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, p 426
Salizzoni P, Soulhac L, Mejean P, Perkins RJ (2008) Influence of a two-scale surface roughness on a neutral turbulent boundary layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 127: 97–110
Salizzoni P, Soulhac L, Mejean P (2009) Street canyon ventilation and atmospheric turbulence. Atmos Environ 44: 5056–5067
Takimoto H, Sato A, Barlow JF, Moriwaki R, Inagaki A, Onomura S, Kanda M (2011) Particle image velocimetry measurements of turbulent flow within outdoor and indoor urban scale models and flushing motions in urban canopy layers. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 140: 295–314
Walton A, Cheng AYS (2002) Large-eddy simulation of pollution dispersion in an urban street canyon—Part II: idealized canyon simulation. Atmos Environ 36: 3615–3627
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michioka, T., Sato, A. Effect of Incoming Turbulent Structure on Pollutant Removal from Two-Dimensional Street Canyon. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 145, 469–484 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-012-9733-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-012-9733-6