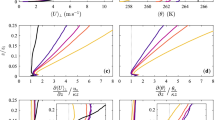
Abstract
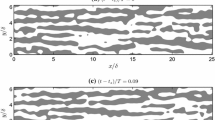
The near-surface flow of a well-resolved large-eddy simulation of the neutrally-stratified planetary boundary layer is used to explore the relationships between coherent structures and the vertical momentum flux. The near-surface flow is characterized by transient streaks, which are alternating bands of relatively higher and lower speed flow that form parallel to the mean shear direction in the lower part of the boundary layer. Although individual streaks are transient, the overall flow is in a quasi-equilibrium state in which the streaks form, grow, decay and regenerate over lifetimes on the order of tens of minutes. Coupled with the streaky flow is an overturning circulation with alternating bands of updrafts and downdrafts approximately centered on the streaks. The surface stress is dominated by upward ejections of slower moving near-surface air and downward sweeps of higher speed air from higher in the boundary layer. Conditional sampling of the ejection and sweep events shows that they are compact, coherent structures and are intimately related to the streaks: ejections (sweeps) preferentially form in the updrafts (downdrafts) of the three-dimensional streak flow. Hence, consistent with other recent studies, we propose that the streak motion plays an important role in the maintenance of the surface stress by establishing the preferential conditions for the ejections and sweeps that dominate the surface stress. The velocity fluctuation spectra in the model near the surface have a k −1 spectral slope over an intermediate range of wavenumbers. This behaviour is consistent with recent theoretical predictions that attempt to evaluate the effects of organized flow, such as near-surface streaks, on the variance spectra.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian R.J., Meinhart C.D., and Tomkins C.D. (2000). ‘Vortex Organisation in the Outer Region of the Turbulent Boundary Layer’. J. Fluid Mech. 422:1–54
Antonia R.A., Rajagopalan S., and Chambers A.J. (1983). ‘Conditional Sampling of Turbulence in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’. J. Climate Appl. Meteorol. 22:69–78
Benaïssa A., Liandrat J., and Anselmet F. (1995). ’Spectral Contribution of Coherent Motions in a Turbulent Boundary Layer’. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 14:697–718
Boppe R.S. and Neu W.L. (1995). ‘Quasi-Coherent Structures in the Marine Atmospheric Surface Layer’. J. Geophys. Res. 100:20635–20648
Boppe R.S., Neu W.L., and Shuai H. (1999). ‘Large-Scale Motions in the Marine Atmospheric Surface Layer’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 92:165–183
Carlotti P. (2002). ‘Two Point Properties of Atmospheric Turbulence Very Close to the Ground: Comparison of a High resolution LES with Theoretical Models’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 104:381–410
Carlotti P. and Drobinski P. (2004). ‘Length-Scales in Wall-Bounded High Reynolds Number Turbulence’. J. Fluid Mech. 516:239–264
Cava D., Schipa S. and Giostra U. (2005). ‘Investigation of Low Frequency Perturbations Induced by a Steep Obstacle’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 115:27–45
Chambers A.J. and Antonia R.A. (1981). ‘Wave-Induced Effect on the Reynolds Shear Stress and Heat Flux in the Marine Surface Layer’. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 11:116–121
Cuxart J., Bougeault P., and Redelsperger J.L. (2000). ‘A Multiscale Turbulence Scheme Apt for LES and Mesoscale Modelling’. Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 126:1–30
Deardorff J. W. (1972). ‘Numerical Investigation of Neutral and Unstable Planetary Boundary Layers’. J. Atmos. Sci. 29: 91–115
Drobinski P. and Foster R.C. (2003). ‘On the Origin of Near-Surface Streaks in the Neutrally-Stratified Planetary Boundary Layer’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 108:247–256
Drobinski P., Brown R.A., Flamant P.H., and Pelon J. (1998). ‘Evidence of Organized Large Eddies by Ground-Based Doppler Lidar, Sonic Anemometer and Sodar’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 88:343–361
Drobinski P., Carlotti P., Newsom R.K., Banta R.M., Foster R.C., and Redelsperger J.L. (2004). ‘The Structure of the Near-Neutral Surface Layer’. J. Atmos. Sci. 61:699–714
Etling D. and Brown R.A. (1993). ‘Roll Vortices in the Planetary Boundary Layer: A Review’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 21:215–248
Farge M. (1992). ‘Wavelet Transforms and their Applications to Turbulence’. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 24:395–457
Foster, R. C. and Drobinski, P.: 2000, ‘Near-Surface Streaks: Comparison of LES with Theory’, Proceedings 14th Symp. on Boundary Layer and Turbulence, Aspen, CO, USA, A.M.S., pp. 499–502.
Foster R.C. (1997). ‘Structure and Energetics of Optimal Ekman Layer Perturbations’. J. Fluid Mech. 333:97–123
Ganapathisubramani B., Longmire E.K., and Marusic I. (2003). ‘Characteristics of Vortex Packets in Turbulent Boundary Layers’. J. Fluid Mech. 478:35–46
Ganapathisubramani B., Hutchins N., Hambleton W.T., Longmire E.K., and Marusic I. (2005). ‘Investigation of Large-Scale Coherence in a Turbulent Boundary Layer using Two-Point Correlations’. J. Fluid Mech. 524:57–80
Giostra U., Cava D., and Schipa S. (2002). ‘Structure Functions in a Wall-Turbulent Shear Flow’. Boundary-Layer Meterol. 103:337–359
Högström U., Hunt J.C.R., and Smedman A.S. (2002). ‘Theory and Measurements for Turbulence Spectra and Variances in the Atmospheric Neutral Surface Layer’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 103:101–124
Högström U. (1990). ‘Analysis of Turbulence Structure in the Surface Layer with a Modified Similarity Theory Formulations for Neutral Conditions’. J. Atmos. Sci. 47:1949–1972
Hommema S.E. and Adrian R.J. (2003). ‘Packet Structure of Surface Eddies in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 106:35–60
Hunt J.C.R. and Morrison J.F. (2000). ‘Eddy Structure in Turbulent Boundary Layers’. Eur. J. Mech. B – Fluids 19:673–694
Hunt J.C.R. and Carlotti P. (2001). ‘Statistical Structure at the Wall of the High Reynolds Number Turbulent Boundary Layer’. Flow, Turbulence, Combustion 66:453–475
Kader, B. A. and Yaglom, A. M.: 1989, ‘Spectra and Correlation Functions of Surface Layer Atmospheric Turbulence in Unstable Thermal Stratification’, in O. Métais and M. Lesieur (eds.), Turbulence 89: Organized Structures and Turbulence in Fluid Mechanics, 1989 grenoble, France.
Katul G., Chu C.R., Parlange M.B., Albertson J.D., and Ortenburger T.A. (1995). ‘The Low Wave Number Spectral Characteristics of Turbulent Velocity and Temperature in the Unstable Atmospheric Surface Layer’. J. Geophys. Res. 100:14243–14255
Katul, G., Hsieh, C. I., Kuhn, G., Ellsworth, D., and Nie, D.: 1997, ‘Turbulent Eddy Motion at the Forest-Atmosphere Interface’, J. Geophys. Res. 102(D12), 13,409–13,421
Khanna S. and Brasseur J.G. (1998). ‘Three-Dimensional Buoyancy- and Shear-Induced Local Structure of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer’. J. Atmos. Sci. 55:710–743
Kim K.C. and Adrian R.J. (1999). ‘Very Large-Scale Motion in the Outer Layer’. Phys. Fluids 11:417–422
Lafore J.P., Stein J., Asencio N., Bougeault P., Ducrocq V., Duron J., Fischer C., Héreil P., Mascart P., Masson V., Pinty J.P., Redelsperger J.L., Richard E., and Vilà- Guerau de Arellano J. (1998). ‘The Meso-Nh atmospheric simulation system Part I: adiabatic formulation and control simulation’. Ann. Geophys. 16:90–109
Lin C.L., McWilliams J.C., Moeng C.H., and Sullivan P.P. (1996). ‘Coherent Structures in a Neutrally-Stratified Planetary Boundary Layer’. Phys. Fluids 8:2626–2639
Lin C.L., Sullivan P.P., Moeng C.H., and McWilliams J.C. (1997). ‘The Effect of Surface Roughness on Flow Structures in a Neutrally-Stratified Planetary Boundary Layer’. Phys. Fluids 9:3235–3249
Mahrt L. and Gibson W. (1992). ‘Flux Decomposition into Coherent Structures’. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 60:143–168
Moeng C.H. and Sullivan P.P. (1994). ‘A Comparison of Shear- and Buoyancy-Driven Planetary Boundary Layer Flows’. J. Atmos. Sci. 51:999–1022
Mourad P.D. (1996). ‘Inferring the Multiscale Structure of Atmospheric Turbulence using Satellite-Based SAR Imagery’. J. Geophys. Res. 101:18433–18499
Porté-Agel F., Meneveau C., and Parlange M.B. (2000). ‘A Scale-Dependent Dynamic Model for Large-Eddy Simulation: Application to a Neutral Atmospheric Boundary Layer’. J. Fluid Mech. 415:216–284
Savtchenko A. (1999). ‘Effect of Large Eddies on Atmospheric Surface Layer Turbulence and the Underlying Wave Field’. J. Geophys. Res. 104:3149–3157
Toh S. and Itano T. (2005). ‘Interaction Between a Large-Scale Structure and Near-Wall Structures in Channel Flow’. J. Fluid. Mech. 524:249–262
Townsend A.A. (1976). The Structure of Turbulent Shear Flows, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 429 pp.
Weckwerth, T. M., Grund, C. J., and Mayor, S. D.: 1997, ‘Linearly-Organized Coherent Structures in the Surface Layer’, Proceedings 12th Symp. on Boundary Layer and Turbulence, Vancouver, B.C., Canada, A.M.S., pp. 22–23.
Wilczak J.M. and Tillman J.E. (1980). ‘The Three-Dimensional Structure of Convection in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’. J. Atmos. Sci. 37:2424–2443
Wilson D.K. (1996). ‘Empirical Orthogonal Function Analysis of the Weakly Convective Atmospheric Boundary Layer Part I: Eddy Structures’. J. Atmos. Sci. 53:801–823
Young G.S., Kristovich D.S., Hjelmfelt M.R. and Foster R.C. (2002). ‘Rolls, Streets, Waves and More: A Review of Quasi-Two Dimensional Structures in the Atmospheric Boundary Layer’. Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 83:997–1001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foster, R.C., Vianey, F., Drobinski, P. et al. Near-Surface Coherent Structures and The Vertical Momentum Flux in a Large-Eddy Simulation of the Neutrally-Stratified Boundary Layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 120, 229–255 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-006-9054-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-006-9054-8