Abstract
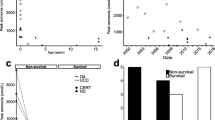
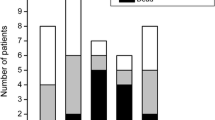
Neonatal onset hyperammonemia in patients with urea cycle disorders (UCDs) is still associated with high morbidity and mortality. Current protocols consistently recommend emergency medical and dietary management. In case of increasing or persistent hyperammonemia, with continuous or progressive neurological signs, dialysis is performed, mostly as ultima ratio. It is presently unknown whether the currently defined ammonia threshold (e.g., at 500 μmol/L) to start dialysis is useful to improve clinical outcome. A systematic review of clinical and biochemical data from published neonatal onset UCD patients was performed to identify factors determining clinical outcome and to investigate in which clinical and biochemical setting dialysis was most effective. A total of 202 patients (118 proximal and 84 distal UCDs) described in 90 case reports or case series were included according to predefined inclusion/exclusion criteria. Median age at onset was three days and mean ammonia that triggered start of dialysis was 1199 μmol/L. Seventy-one percent of all patients received any form of dialysis. Total mortality was 25% and only 20% of all patients had a “normal” outcome. In general, patients with higher ammonia levels were more likely to receive dialysis, but this had for most patients no influence on outcome. In conclusion, in severe neonatal onset hyperammonemia, the current practice of dialysis, which effectively clears ammonia, had no impact on outcome. It may be essential for improving outcome to initiate all available treatment options, including dialysis, as early as possible.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ah Mew N, Krivitzky L, McCarter R, Batshaw M, Tuchman M, Urea Cycle Disorders Consortium of the Rare Diseases Clinical Research N (2013) Clinical outcomes of neonatal onset proximal versus distal urea cycle disorders do not differ. J Pediatr 162: 324–329.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.06.065
Ah Mew N, Simpson KL, Gropman AL, Lanpher BC, Chapman KA, Summar ML (1993) Urea cycle disorders overview. In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, Bean LJH, Bird TD, Ledbetter N, Mefford HC, Smith RJH, Stephens K (eds) (2017) GeneReviews(R), 2017/22/06. University of Washington, Seattle
Alfadhel M, Mutairi FA, Makhseed N, Jasmi FA, Al-Thihli K, Al-Jishi E, AlSayed M, Al-Hassnan ZN, Al-Murshedi F, Häberle J, Ben-Omran T (2016) Guidelines for acute management of hyperammonemia in the Middle East region. Ther Clin Risk Manag 12:479–487. https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S93144
Bachmann C (2003) Outcome and survival of 88 patients with urea cycle disorders: a retrospective evaluation. Eur J Pediatr 162:410–416
Batshaw ML (1983) Sodium benzoate and arginine: alternative pathway therapy in inborn errors of urea synthesis. Prog Clin Biol Res 127:69–83
Batshaw ML, MacArthur RB, Tuchman M (2001) Alternative pathway therapy for urea cycle disorders: twenty years later. J Pediatr 138:S46–S54 discussion S54-5
Batshaw ML, Tuchman M, Summar M, Seminara J, Members of the Urea Cycle Disorders C (2014) A longitudinal study of urea cycle disorders. Mol Genet Metab 113:127–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.08.001
Berry SA, Lichter-Konecki U, Diaz GA, McCandless SE, Rhead W, Smith W, Lemons C, Nagamani SC, Coakley DF, Mokhtarani M, Scharschmidt BF, Lee B (2014) Glycerol phenylbutyrate treatment in children with urea cycle disorders: pooled analysis of short and long-term ammonia control and outcomes. Mol Genet Metab 112:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.02.007
Brassier A, Gobin S, Arnoux JB, Valayannopoulos V, Habarou F, Kossorotoff M, Servais A, Barbier V, Dubois S, Touati G, Barouki R, Lesage F, Dupic L, Bonnefont JP, Ottolenghi C, De Lonlay P (2015) Long-term outcomes in ornithine Transcarbamylase deficiency: a series of 90 patients. Orphanet J Rare Dis 10:58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-015-0266-1
Brusilow S, Horwich A (2001) Urea cycle enzymes. In: Scriver C, Beaudet A, Sly W, Valle D (eds) The metabolic & molecular bases of inherited disease, 8th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1909–1963
Brusilow SW (1984) Arginine, an indispensable amino acid for patients with inborn errors of urea synthesis. J Clin Invest 74:2144–2148. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI111640
Brusilow SW, Valle DL, Batshaw M (1979) New pathways of nitrogen excretion in inborn errors of urea synthesis. Lancet 2:452–454
Burgard P, Kölker S, Haege G, Lindner M, Hoffmann GF (2016) Neonatal mortality and outcome at the end of the first year of life in early onset urea cycle disorders-review and meta-analysis of observational studies published over more than 35 years. J Inherit Metab Dis 39:219–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-015-9901-1
Choi JH, Lee BH, Kim JH, Kim GH, Kim YM, Cho J, Cheon CK, Ko JM, Lee JH, Yoo HW (2015) Clinical outcomes and the mutation spectrum of the OTC gene in patients with ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. J Hum Genet 60:501–507. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2015.54
Diaz GA, Krivitzky LS, Mokhtarani M, Rhead W, Bartley J, Feigenbaum A, Longo N, Berquist W, Berry SA, Gallagher R, Lichter-Konecki U, Bartholomew D, Harding CO, Cederbaum S, SE MC, Smith W, Vockley G, Bart SA, Korson MS, Kronn D, Zori R, Merritt JL 2nd, CSN S, Mauney J, Lemons C, Dickinson K, Moors TL, Coakley DF, Scharschmidt BF, Lee B (2013) Ammonia control and neurocognitive outcome among urea cycle disorder patients treated with glycerol phenylbutyrate. Hepatology 57:2171–2179. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26058
Enns GM, Berry SA, Berry GT, Rhead WJ, Brusilow SW, Hamosh A (2007) Survival after treatment with phenylacetate and benzoate for urea-cycle disorders. N Engl J Med 356:2282–2292
Go H, Imamura T, Hashimoto K, Ogasawara K, Sakamoto O, Takubo N, Momoi N, Hosoya M (2012) Successful prospective management of neonatal citrullinemia. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 25:371–373
Häberle J (2013) Clinical and biochemical aspects of primary and secondary hyperammonemic disorders. Arch Biochem Biophys 536:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2013.04.009
Häberle J, Boddaert N, Burlina A, Chakrapani A, Dixon M, Huemer M, Karall D, Martinelli D, Sanjurjo Crespo P, Santer R, Servais A, Valayannopoulos V, Lindner M, Rubio V, Dionisi-Vici C (2012) Suggested guidelines for the diagnosis and management of urea cycle disorders. Orphanet J Rare Dis 7:32
Häberle J, Rubio V (2016) Disorders of the urea cycle and related enzymes. In: Saudubray JM, Baumgartner M, Walter JH (eds) Inborn metabolic diseases, 6th edn. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 295–308
Hanudel M, Avasare S, Tsai E, Yadin O, Zaritsky J (2014) A biphasic dialytic strategy for the treatment of neonatal hyperammonemia. Pediatr Nephrol 29:315–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2638-x
Häussinger D (1990) Nitrogen metabolism in liver: structural and functional organization and physiological relevance. Biochem J 267:281–290
Jalan A, Kudalkar K, Joshi M, Shirke S, Mahamunkar A, Jalan R, Shinde D, Borugale M, Tawde R, Häberle J (2016) Survival and outcome of patients with urea cycle disorders: a single-center experience. Perinatology 17:110–119
Jorda A, Rubio V, Portoles M, Vilas J, Garcia-Pino J (1986) A new case of arginase deficiency in a Spanish male. J Inherit Metab Dis 9:393–397
Keskinen P, Siitonen A, Salo M (2008) Hereditary urea cycle diseases in Finland. Acta Paediatr 97:1412–1419
Kido J, Nakamura K, Mitsubuchi H, Ohura T, Takayanagi M, Matsuo M, Yoshino M, Shigematsu Y, Yorifuji T, Kasahara M, Horikawa R, Endo F (2012) Long-term outcome and intervention of urea cycle disorders in Japan. J Inherit Metab Dis 35:777–785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-011-9427-0
Kölker S, Cazorla AG, Valayannopoulos V, Lund AM, Burlina AB, Sykut-Cegielska J, Wijburg FA, Teles EL, Zeman J, Dionisi-Vici C, Baric I, Karall D, Augoustides-Savvopoulou P, Aksglaede L, Arnoux JB, Avram P, Baumgartner MR, Blasco-Alonso J, Chabrol B, Chakrapani A, Chapman K, EC IS, Couce ML, de Meirleir L, Dobbelaere D, Dvorakova V, Furlan F, Gleich F, Gradowska W, Grunewald S, Jalan A, Häberle J, Haege G, Lachmann R, Laemmle A, Langereis E, de Lonlay P, Martinelli D, Matsumoto S, Muhlhausen C, de Baulny HO, Ortez C, Pena-Quintana L, Ramadza DP, Rodrigues E, Scholl-Bürgi S, Sokal E, Staufner C, Summar ML, Thompson N, Vara R, Pinera IV, Walter JH, Williams M, Burgard P (2015) The phenotypic spectrum of organic acidurias and urea cycle disorders. Part 1: the initial presentation. J Inherit Metab Dis 38:1041–1057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-015-9839-3
Leonard JV, Morris AA (2002) Urea cycle disorders. Semin Neonatol 7:27–35
Martin-Hernandez E, Aldamiz-Echevarria L, Castejon-Ponce E, Pedron-Giner C, Couce ML, Serrano-Nieto J, Pintos-Morell G, Belanger-Quintana A, Martinez-Pardo M, Garcia-Silva MT, Quijada-Fraile P, Vitoria-Minana I, Dalmau J, Lama-More RA, Bueno-Delgado MA, Del Toro-Riera M, Garcia-Jimenez I, Sierra-Corcoles C, Ruiz-Pons M, Pena-Quintana LJ, Vives-Pinera I, Morais A, Balmaseda-Serrano E, Meavilla S, Sanjurjo-Crespo P, Perez-Cerda C (2014) Urea cycle disorders in Spain: an observational, cross-sectional and multicentric study of 104 cases. Orphanet J Rare Dis 9:187. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-014-0187-4
McBride KL, Miller G, Carter S, Karpen S, Goss J, Lee B (2004) Developmental outcomes with early orthotopic liver transplantation for infants with neonatal-onset urea cycle defects and a female patient with late-onset ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Pediatrics 114:e523–e526. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2004-0198
Morioka D, Kasahara M, Takada Y, Shirouzu Y, Taira K, Sakamoto S, Uryuhara K, Egawa H, Shimada H, Tanaka K (2005) Current role of liver transplantation for the treatment of urea cycle disorders: a review of the worldwide English literature and 13 cases at Kyoto University. Liver Transpl 11:1332–1342
Msall M, Batshaw ML, Suss R, Brusilow SW, Mellits ED (1984) Neurologic outcome in children with inborn errors of urea synthesis. Outcome of urea-cycle enzymopathies. N Engl J Med 310:1500–1505
Nakamura K, Kido J, Mitsubuchi H, Endo F (2014) Diagnosis and treatment of urea cycle disorder in Japan. Pediatr Int 56:506–509. https://doi.org/10.1111/ped.12439
Nassogne MC, Heron B, Touati G, Rabier D, Saudubray JM (2005) Urea cycle defects: management and outcome. J Inherit Metab Dis 28:407–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-005-0303-7
Palmieri F (2008) Diseases caused by defects of mitochondrial carriers: a review. Biochim Biophys Acta 1777:564–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.03.008
Picca S, Dionisi-Vici C, Abeni D, Pastore A, Rizzo C, Orzalesi M, Sabetta G, Rizzoni G, Bartuli A (2001) Extracorporeal dialysis in neonatal hyperammonemia: modalities and prognostic indicators. Pediatr Nephrol 16:862–867
Picca S, Dionisi-Vici C, Bartuli A, De Palo T, Papadia F, Montini G, Materassi M, Donati MA, Verrina E, Schiaffino MC, Pecoraro C, Iaccarino E, Vidal E, Burlina A, Emma F (2015) Short-term survival of hyperammonemic neonates treated with dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 30:839–847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-2945-x
Picker JD, Puga AC, Levy HL, Marsden D, Shih VE, Degirolami U, Ligon KL, Cederbaum SD, Kern RM, Cox GF (2003) Arginase deficiency with lethal neonatal expression: evidence for the glutamine hypothesis of cerebral edema. J Pediatr 142:349–352. https://doi.org/10.1067/mpd.2003.97
Sancho-Vaello E, Marco-Marin C, Gougeard N, Fernandez-Murga L, Rüfenacht V, Mustedanagic M, Rubio V, Häberle J (2016) Understanding N-acetyl-L-glutamate synthase deficiency: mutational Spectrum, impact of clinical mutations on enzyme functionality, and structural considerations. Hum Mutat 37:679–694. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.22995
Schaefer F, Straube E, Oh J, Mehls O, Mayatepek E (1999) Dialysis in neonates with inborn errors of metabolism. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14:910–918
Summar M, Pietsch J, Deshpande J, Schulman G (1996) Effective hemodialysis and hemofiltration driven by an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation pump in infants with hyperammonemia. J Pediatr 128:379–382
Summar ML, Koelker S, Freedenberg D, Le Mons C, Häberle J, Lee HS, Kirmse B (2013) The incidence of urea cycle disorders. Mol Genet Metab 110:179–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2013.07.008
Takahashi T, Yamada K, Kobayashi H, Hasegawa Y, Taketani T, Fukuda S, Yamaguchi S (2015) Metabolic disease in 10 patients with sudden unexpected death in infancy or acute life-threatening events. Pediatr Int 57:348–353. https://doi.org/10.1111/ped.12660
Uchino T, Endo F, Matsuda I (1998) Neurodevelopmental outcome of long-term therapy of urea cycle disorders in Japan. J Inherit Metab Dis 21(Suppl 1):151–159
van Karnebeek C, Häberle J (2015) Carbonic anhydrase VA deficiency. In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, Bean LJH, Bird TD, Dolan CR, Fong CT, Smith RJH, Stephens K (eds) GeneReviews, 2015/04/04 edn. University of Washington, Seattle
Vandenbroucke JP (2001) In defense of case reports and case series. Ann Intern Med 134:330–334
Woo HI, Ki CS, Lee SY, Kim JW, Song J, Jin DK, Park WS, Lee DH, Lee YW, Park HD (2013) Mutation spectrum of the ASS1 gene in Korean patients with citrullinemia type I. Clin Biochem 46:209–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.10.008
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (grant 310030_153196). The authors are grateful to Jin-Ho Choi & Han-Wook Yoo, MD, PhD, Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, who helped to complete missing data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
None.
Studies with human or animal
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the authors.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Carlo Dionisi-Vici
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 141 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hediger, N., Landolt, M.A., Diez-Fernandez, C. et al. The impact of ammonia levels and dialysis on outcome in 202 patients with neonatal onset urea cycle disorders. J Inherit Metab Dis 41, 689–698 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-018-0157-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-018-0157-4