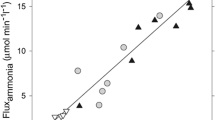
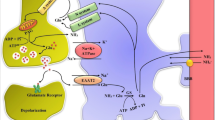
Summary
Acute hyperammonaemia (HA) causes cerebral oedema and severe brain damage in patients with urea cycle disorders (UCDs) or acute liver failure (ALF). Chronic HA is associated with developmental delay and intellectual disability in patients with UCDs and with neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with chronic liver failure. Treatment often cannot prevent severe brain injury and neurological sequelae. The causes of the brain oedema in hyperammonaemic encephalopathy (HAE) have been subject of intense controversy among physicians and scientists working in this field. Currently favoured hypotheses are astrocyte swelling due to increased intracellular glutamine content and neuronal cell death due to excitotoxicity caused by elevated extracellular glutamate levels. While many researchers focus on these mechanisms of cytotoxicity, others emphasize vascular causes of brain oedema. New data gleaned from expression profiling of astrocytes acutely isolated from hyperammonaemic mouse brains point to disturbed water and potassium homeostasis as regulated by astrocytes at the brain microvasculature and in the perisynaptic space as a potential mechanism of brain oedema development in hyperammonaemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht J, Norenberg MD (2006) Glutamine: a Trojan horse in ammonia neurotoxicity. Hepatology 44: 788–794.
Allen NJ, Barres BA (2005) Signaling between glia and neurons: focus on synaptic plasticity. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15: 542–548.
Basile AS (2002) Direct and indirect enhancement of GABAergic neurotransmission by ammonia: implications for the pathogenesis of hyperammonemic syndromes. Neurochem Int 41: 115–122.
Batshaw ML, Roan Y, Jung AL, Rosenberg LA, Brusilow SW (1980) Cerebral dysfunction in asymptomatic carriers of ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. N Engl J Med 302: 482–485.
Batshaw ML, Msall M, Trojak J (1986) The risk of serious illness in carriers of ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. J Pediatr 108: 236–241.
Belanger M, Desjardins P, Chatauret N, Butterworth RF (2006) Selectively increased expression of the astrocytic/endothelial glucose transporter protein GLUT1 in acute liver failure. Glia 53: 557–562.
Bordey A, Hablitz JJ, Sontheimer H (2000) Reactive astrocytes show enhanced inwardly rectifying K+ currents in situ. Neuroreport 11: 3151–3155.
Braissant O, Henry H, Villard AM, et al (2002) Ammonium-induced impairment of axonal growth is prevented through glial creatine. J Neurosci 22: 9810–9820.
Butterworth RF (2007) Neuronal cell death in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 22: 309–320.
Chan H, Butterworth RF (1999) Evidence for an astrocytic glutamate transporter deficit in hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem Res 24: 1397–1401.
Chan H, Hazell AS, Desjardins P, Butterworth RF (2000) Effects of ammonia on glutamate transporter (GLAST) protein and mRNA in cultured rat cortical astrocytes. Neurochem Int 37: 243–248.
DeMars R, LeVan SL, Trend BL, Russell LB (1976) Abnormal ornithine carbamoyltransferase in mice having the sparse-fur mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 73: 1693–1697.
Dermietzel R, Hertberg EL, Kessler JA, Spray DC (1991) Gap junctions between cultured astrocytes: immunocytochemical, molecular, and electrophysiological analysis. J Neurosci 11: 1421–1432.
Desjardins P, Belanger M, Butterworth RF (2001) Alterations in expression of genes coding for key astrocytic proteins in acute liver failure. J Neurosci Res 66: 967–971.
D’Hooge R, Marescau B, Qureshi IA, De Deyn PP (2000) Impaired cognitive performance in ornithine transcarbamylase-deficient mice on arginine-free diet. Brain Res 876: 1–9.
Felipo V, Butterworth RF (2002) Neurobiology of ammonia. Prog Neurobiol 67: 259–279.
Fickbohm DJ, Willard AL (1999) Upregulation of calcium homeostatic mechanisms in chronically depolarized rat myenteric neurons. J Neurophysiol 81: 2683–2695.
Frisch C, Theis M, De Souza Silva MA, et al (2003) Mice with astrocyte-directed inactivation of connexin43 exhibit increased exploratory behaviour, impaired motor capacities, and changes in brain acetylcholine levels. Eur J Neurosci 18: 2313–2318.
Giaume C, Tabernero A, Medina JM (1997) Metabolic trafficking through astrocytic gap junctions. Glia 21: 114–123.
Gropman AL, Summar M, Leonard JV (2007) Neurological implications of urea cycle disorders. J Inherit Metab Dis 30: 865–879.
Gushiken T, Yoshimura N, Saheki T (1985) Transient hyperammonemia during aging in ornithine transcarbamylase-deficient, sparse-fur mice. Biochem Int 11: 637–643.
Gyato K, Wray J, Huang ZJ, Yudkoff M, Batshaw ML (2004) Metabolic and neuropsychological phenotype in women heterozygous for ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Ann Neurol 55: 80–86.
Hansson E, Muyderman H, Leonova J, et al (2000) Astroglia and glutamate in physiology and pathology: aspects on glutamate transport, glutamate-induced cell swelling and gap-junction communication. Neurochem Int 37: 317–329.
Haydon PG (2001) GLIA: listening and talking to the synapse. Nat Rev Neurosci 2: 185–193.
Hibino H, Fujita A, Iwai K, Yamada M, Kurachi Y (2004) Differential assembly of inwardly rectifying K+ channel subunits, Kir4.1 and Kir5.1, in brain astrocytes. J Biol Chem 279: 44065–44073.
Holm LM, Jahn TP, Moller AL, et al (2005) NH3 and NH4+ permeability in aquaporin-expressing Xenopus oocytes. Pflugers Arch 450: 415–428.
Iacobas DA, Scemes E, Spray DC (2004) Gene expression alterations in connexin null mice extend beyond the gap junction. Neurochem Int 45: 243–250.
Inoue I, Gushiken T, Kobayashi K, Saheki T (1987) Accumulation of large neutral amino acids in the brain of sparse-fur mice at hyperammonemic state. Biochem Med Metab Biol 38: 378–386.
Iyer RK, Yoo PK, Kern RM, et al (2002) Mouse model for human arginase deficiency. Mol Cell Biol 22: 4491–4498.
Jayakumar AR, Rama Rao KV, Schousboe A, Norenberg MD (2004) Glutamine-induced free radical production in cultured astrocytes. Glia 46: 296–301.
Kiening KL, van Landeghem FK, Schreiber S, et al (2002) Decreased hemispheric Aquaporin-4 is linked to evolving brain edema following controlled cortical impact injury in rats. Neurosci Lett 324: 105–108.
Kofuji P, Ceelen P, Zahs KR, Surbeck LW, Lester HA, Newman EA (2000) Genetic inactivation of an inwardly rectifying potassium channel (Kir4.1 subunit) in mice: phenotypic impact in retina. J Neurosci 20: 5733–5740.
Kofuji P, Newman EA (2004) Potassium buffering in the central nervous system. Neuroscience 129: 1045–1056.
Lai JC, Cooper AJ (1986) Brain alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex: kinetic properties, regional distribution, and effects of inhibitors. J Neurochem 47: 1376–1386.
Lichter-Konecki U, Mangin JM, Gordish-Dressman H, Hoffman EP, Gallo V (2008) Gene expression profiling of astrocytes from hyperammonemic mice reveals altered pathways for water and potassium homeostasis in vivo. Glia 56: 365–377.
Lin JH, Weigel H, Cotrina ML, et al (1998) Gap-junction-mediated propagation and amplification of cell injury. Nat Neurosci 1: 494–500.
Maestri NE, Clissold D, Brusilow SW (1999) Neonatal onset ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency: a retrospective analysis. J Pediatr 134: 268–272.
Marcaggi P, Coles JA (2001) Ammonium in nervous tissue: transport across cell membranes, fluxes from neurons to glial cells, and role in signalling. Prog Neurobiol 64: 157–183.
Msall M, Batshaw ML, Suss R, Brusilow SW, Mellits ED (1984) Neurologic outcome in children with inborn errors of urea synthesis. N Engl J Med 310: 1500–1505.
Msall M, Monahan PS, Chapanis N, Batshaw ML (1988) Cognitive development in children with inborn errors of urea synthesis. Acta Paediatr Jpn 30: 435–441.
Murthy CR, Bender AS, Dombro RS, Bai G, Norenberg MD (2000) Elevation of glutathione levels by ammonium ions in primary cultures of rat astrocytes. Neurochem Int 37: 255–268.
Nagelhus EA, Mathiisen TM, Ottersen OP (2004) Aquaporin-4 in the central nervous system: cellular and subcellular distribution and coexpression with KIR4.1. Neuroscience 129: 905–913.
Nakase T, Fushiki S, Naus CC (2003) Astrocytic gap junctions composed of connexin 43 reduce apoptotic neuronal damage in cerebral ischemia. Stroke 34: 1987–1993.
Neusch C, Rozengurt N, Jacobs RE, Lester HA, Kofuji P (2001) Kir4.1 potassium channel subunit is crucial for oligodendrocyte development and in vivo myelination. J Neurosci 21: 5429–5438.
Nolte C, Matyash M, Pivneva T, et al (2001) GFAP promoter-controlled EGFP-expressing transgenic mice: a tool to visualize astrocytes and astrogliosis in living brain tissue. Glia 33: 72–86.
Norenberg MD (1977) A light and electron microscopic study of experimental portal-systemic (ammonia) encephalopathy. Progression and reversal of the disorder. Lab Invest 36: 618–627.
Norenberg MD, Jayakumar AR, Rama Rao KV, Panickar KS (2007) New concepts in the mechanism of ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling. Metab Brain Dis 22: 219–234.
Panatier A, Theodosis DT, Mothet JP, et al (2006) Glia-derived D-serine controls NMDA receptor activity and synaptic memory. Cell 125: 775–784.
Patejunas G, Bradley A, Beaudet AL, O’Brien WE (1994) Generation of a mouse model for citrullinemia by targeted disruption of the argininosuccinate synthetase gene. Somat Cell Mol Genet 20: 55–60.
Rama Rao KV, Jayakumar AR, Norenberg MD (2003a) Induction of the mitochondrial permeability transition in cultured astrocytes by glutamine. Neurochem Int 43: 517–523.
Rama Rao KV, Chen M, Simard JM, Norenberg MD (2003b) Increased aquaporin-4 expression in ammonia-treated cultured astrocytes. Neuroreport 14: 2379–2382.
Rao VLR, Audet RM, Butterworth RF (1997) Increased neuronal nitric oxide synthase expression in brain following portacaval anastomosis. Brain Res 765: 169–172.
Ratnakumari L, Qureshi IA, Butterworth RF (1994) Regional amino acid Neurotransmitter changes in brains of spf/Y mice with congenital ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Metab Brain Dis 9: 43–51.
Robinson MB, Hopkins K, Batshaw ML, McLaughlin BA, Heyes MP, Oster-Granite ML (1995) Evidence of excitotoxicity in the brain of the ornithine carbamoyltransferase deficient sparse fur mouse. Dev Brain Res 90: 35–44.
Robitaille R (1998) Modulation of synaptic efficacy and synaptic depression by glial cells at the frog neuromuscular junction. Neuron 21: 847–855.
Rouach N, Glowinski J, Giaume C (2000) Activity-dependent neuronal control of gap-junctional communication in astrocytes. J Cell Biol 149: 1513–1526.
Saadoun S, Papadopoulos MC, Krishna S (2003) Water transport becomes uncoupled from K+ siphoning in brain contusion, bacterial meningitis, and brain tumours: immunohistochemical case review. J Clin Pathol 56: 972–975.
Song G, Dhodda VK, Blei AT, Dempsey RJ, Rao VL (2002) GeneChip analysis shows altered mRNA expression of transcripts of neurotransmitter and signal transduction pathways in the cerebral cortex of portacaval shunted rats. J Neurosci Res 68: 730–737.
Sontheimer H, Minturn JE, Black JA, Waxman SG, Ransom BR (1990) Specificity of cell-cell coupling in rat optic nerve astrocytes in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87: 9833–9837.
Sugimoto H, Koehler RC, Wilson DA, Brusilow SW, Traystman RJ (1997) Methionine sulfoximine, a glutamine synthetase inhibitor, attenuates increased extracellular potassium activity during acute hyperammonemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17: 44–49.
Reed Sutton RV, Pan Y, Davis EC, Craigen WJ (2003) A mouse model of argininosuccinic aciduria: biochemical characterization. Mol Genet Metab 78: 11–16.
Tanigami H, Rebel A, Martin LJ, et al (2005) Effect of glutamine synthetase inhibition on astrocyte swelling and altered astroglial protein expression during hyperammonemia in rats. Neuroscience 131: 437–449.
Tsacopoulos M, Magistretti PJ (1996) Metabolic coupling between glia and neurons. J Neurosci 16: 877–885.
Wallraff A, Kohling R, Heinemann U, Theis M, Willecke K, Steinhauser C (2006) The impact of astrocytic gap junctional coupling on potassium buffering in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 26: 5438–5447.
Wehner T, Bontert M, Eyupoglu I, et al (2003) Bone marrow-derived cells expressing green fluorescent protein under the control of the glial fibrillary acidic protein promoter do not differentiate into astrocytes in vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci 23: 5004–5011.
Westhoff CM, Wylie DE (2006) Transport characteristics of mammalian Rh and Rh glycoproteins expressed in heterologous systems. Transfus Clin Biol 13: 132–138.
Zhou BG, Norenberg MD (1999) Ammonia downregulates GLAST mRNA glutamate transporter in rat astrocyte cultures. Neurosci Lett 276: 145–148.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicating editor: Verena Peters
Competing interests: None declared
References to electronic databases: Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency: OMIM 311250. Ornithine transcarbamylase: EC 2.1.3.3.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lichter-Konecki, U. Profiling of astrocyte properties in the hyperammonaemic brain: Shedding new light on the pathophysiology of the brain damage in hyperammonaemia. J Inherit Metab Dis 31, 492–502 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-008-0834-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-008-0834-9