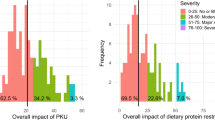
Summary
Phenylketonuria (PKU; OMIM 261600) is an autosomal recessive disorder of phenylalanine metabolism caused by a deficiency of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH; EC 1.14.16.1). Cognitive problems, neuropsychological abnormalities and psychosocial problems have been reported frequently in children and adolescents with PKU, even in those who are treated early and continuously. However, the developmental consequences in adulthood of growing up with PKU are not well known. The aim of this study was to assess the course of life, sociodemographic outcomes and health-related quality of life in young adult patients with PKU identified on neonatal screening who were continuously on treatment. A total of 32 PKU patients 18 to 30 years old completed the Course of Life questionnaire, the RAND-36 Health Survey, and the cognitive scale of the TNO-AZL Adult Quality of Life (TAAQoL) questionnaire. The results of the Course of Life and Health-Related Quality of Life questionnaires were comparable to controls, except that a higher percentage received special education in primary school. Their educational attainment, however, was comparable to that of their peers. The results of this study demonstrate that although PKU is a chronic disease with the burden of strict dietary control, early and continuously treated patients with PKU can have a normal health-related quality of life and course of life.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AMC:
-
Emma Children’s Hospital/Amsterdam Medical Centre
- CoL:
-
course of life
- LUMC:
-
Leiden University Medical Centre
- PKU:
-
phenylketonuria
- PAH:
-
phenylalanine hydroxylase
- QoL:
-
quality of life
- TAAQoL:
-
TNO-AZL Adult Quality of Life
- UMCG:
-
University Medical Center Groningen
- UMCU:
-
University Medical Center Utrecht
References
Bosch AM, Grootenhuis MA, Bakker HD, Heijmans HSA, Wijburg FA, Last BF (2004) Living with classical galactosemia, health related quality of life consequences. Pediatrics 113(5): e423–428.
Fekkes M, Kamphuis RP, Ottenkamp PJ, etal (2001) Health-related quality of life in young adults with minor congenital heart disease. Psychol Health 16:239–250.
Garber J (1984) Classification of childhood psychopathology: a developmental perspective. Child Dev 55: 30–48.
Gassio R, Artuch R, Vilaseca MA, etal (2005) Cognitive functions in classic phenylketonuria and mild hyperphenylalaninaemia: experience in a pediatric population. Dev Med Child Neurol 47: 443–448.
Grootenhuis MA, Stam H, Destrée-Vonk A, Heijmans HSA, Last BF (2003) Levensloop Vragenlijst voor Jong-Volwassenen. [Course of life questionnaire for young adults] Gedrag Gezondheid 31: 336–350.
Hays RD, Sherbourne CS, Mazel RM (1993) The RAND 36-item Health Survey 1.0. Health Econ 2: 217–227.
Hendrikx MMT, Van der Schot LWA, Slijper FME, Huisman J, Kalverboer AF (1994) Phenylketonuria and some aspects of emotional development. Eur J Pediatr 153: 832–835.
Koch R, Burton B, Hoganson G, etal (2002) Phenylketonuria in adulthood: a collaborative study. J Inherit Metab Dis 25: 333–346.
Landolt MA, Nuoffer JM, Steinmann B, Superti-Furga A (2002) Quality of life and psychologic adjustment in children and adolescents with early treated phenylketonuria can be normal. J Pediatr 140: 516–521.
Last BF, Grootenhuis MA, Destrée-Vonk A, Heymans HSA (2000) De ontwikkeling van een levensloopvragenlijst voor jong-volwassenen (LVJV) [The development of a course of life questionnaire for young adults]. Gedrag Gezondheid 8: 22–30.
Lewis M, Miller SM (1990) Handbook of Developmental Psychopathology. New York: Plenum Press.
Lundstedt G, Johansson A, Melin L, Alm J (2001) Adjustment and intelligence among children with phenylketonuria in Sweden. Acta Paediatr 90: 1147–1152.
Ris MD, Weber AM, Hunt MM (1997) Adult psychosocial outcome in early-treated phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 20: 499–508.
Stam H, Grootenhuis MA, Last BF (2005) The course of life of survivors of childhood cancer. Psychooncology 14: 227–238.
Stam H, Hartman EE, Deurloo JA, Groothoff J, Grootenhuis MA (2006) Young adult patients with a history of pediatric disease: impact on course of life and transition into adulthood. J Adolesc Health 39(1): 4–13.
Stemerdink BA, Kalverboer AF, Van der Meere JJ, etal (2000) Behavior and school achievement in patients with early and continuously treated phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 23: 548–562.
Van der Zee KI, Sanderman R (2003) Het meten van de algemene gezondheidstoestand met de RAND-36. Een handleiding. [Measuring general health status with the RAND-36. A guide.] Groningen, The Netherlands: NCG, RijksuniversiteitGroningen.
Verkerk PH (1995) Twenty years of national screening for phenylketonuria in The Netherlands. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 139(45): 2302–2305.
Weglage J, Funders B, Wilken B, etal (1992) Psychosocial and social findings in adolescents with phenylketonuria. Eur J Pediatr 151: 522–525.
Weglage J, Funders B, Ullrich K, Rupp A, Schmidt E (1996) Psychosocial aspects in phenylketonuria. Eur J Pediatr 155[Supplement 1]:s 101–s104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicating editor: John Walter
Competing interests: None declared
References to electronic databases: Phenylketonuria (PKU) OMIM 261600 Phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) EC 1.14.16.1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bosch, A.M., Tybout, W., Spronsen, F.J.v. et al. The course of life and quality of life of early and continuously treated Dutch patients with phenylketonuria. J Inherit Metab Dis 30, 29–34 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-006-0433-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-006-0433-6