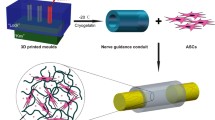
Abstract
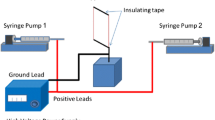
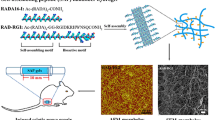
Nerve guidance conduits (NGCs) composed of biocompatible polymers have been attracting attention as an alternative for autograft surgery in peripheral nerve regeneration. However, the nerve tissues repaired by NGCs often tend to be inadequate and lead to functional failure because of the lack of cellular supports. This paper presents a chitosan-collagen hydrogel conduit containing cells to induce peripheral nerve regeneration with cellular support. The conduit composed of two coaxial hydrogel layers of chitosan and collagen is simply made by molding and mechanical anchoring attachment with holes made on the hydrogel tube. A chitosan layer strengthens the conduit mechanically, and a collagen layer provides a scaffold for cells supporting the axonal extension. The conduits of different diameters (outer diameter approximately 2–4 mm) are fabricated. The conduit is bioabsorbable with lysozyme, and biocompatible even under bio absorption. In the neuron culture demonstration, the conduit containing Schwann cells induced the extension of the axon of neurons directed to the conduit. Our easily fabricated conduit could help the high-quality regeneration of peripheral nerves and contribute to the nerve repair surgery.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. J. E. Armstrong, C. N. Svendsen, Cell Transplant., 9 (2000)
M.G. Burnett, E.L. Zager, J. Neurosurg. 16, 5 (2004)
W. Daly, L. Yao, D. Zeugolis, A. Windebank, A. Pandit, J. R. Soc. Interface 9, 67 (2011)
G.R.D. Evans, Anat. Rec. 263, 4 (2001)
G.R.D. Evans, K. Brandt, S. Katz, P. Chauvin, L. Otto, M. Bogle, B. Wang, R.K. Meszlenyi, L.C. Lu, A.G. Mikos, C.W. Patrick, Biomaterials 23, 3 (2002)
A. Faroni, S. A. Mobasseri, P. J. Kingham, A. J. Reid, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 82–83 (2015)
D.S. Forman, R.A. Berenberg, Brain Res. 156, 2 (1978)
S.P. Frostick, Q. Yin, G.J. Kemp, Microsurgery 18, 7 (1998)
S. Itai, H. Tajima, H. Onoe, Biofabrication 11, 1 (2018)
S. Itoh, I. Yamaguchi, M. Suzuki, S. Ichinose, K. Takakuda, H. Kobayashi, K. Shinomiya, J. Tanaka, Brain Res. 993, 1–2 (2003)
S. Li, S.J. Archibald, C. Krarup, R.D. Madison, Clin. Mater. 9, 3–4 (1992)
Y.T. Liu, X.J. Zhou, J. Ma, Y.B. Ge, X. Cao, J. Spinal Cord Med. 38, 4 (2015)
H. Molander, Y. Olsson, O. Engkvist, S. Bowald, I. Eriksson, Muscle Nerve 5, 1 (1982)
T. Nakamura, Y. Inada, S. Fukuda, M. Yoshitani, A. Nakada, S.I. Itoi, S.I. Kanemaru, K. Endo, Y. Shimizu, Brain Res. 1027, 1–2 (2004)
A.R. Nectow, K.G. Marra, D.L. Kaplan, Tissue Eng. B Rev. 18, 1 (2011)
R.J. Nordtveit, K.M. Varum, O. Smidsrod, Carbohydr. Polym. 23, 4 (1994)
L.A. Pfister, M. Papaloizos, H.P. Merkle, B. Gander, J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 12, 2 (2007)
W.Z. Ray, S.E. Mackinnon, Exp. Neurol. 223, 1 (2010)
F. Ridley, Proc. Royal Soc. Med., 21 (1928),
R.L. Rietze, B.A. Reynolds, Methods Enzymol. 419, 1 (2006)
L.R. Robinson, Muscle Nerve 23, 6 (2000)
F.J. Rodriguez, E. Verdu, D. Ceballos, X. Navarro, Exp. Neurol. 161, 2 (2000)
H.J. Seddon, Br. Med. J. 2, 4260 (1942)
D.K. Sen, G.S. Sarin, Br. J. Ophthalmol. 70, 4 (1986)
T. Taguchi, H. Kobayashi, H. Saito, Y. Uchida, M. Aizawa, J Adhesion Soc. Japan 43, 8 (2007)
G. Terenghi, J. Anatomy 194, 1 (1999)
P.A. Wieringa, A.R.G. de Pinho, S. Micera, R.J.A. van Wezel, L. Moroni, Adv. Healthcare Mater. 7, 8 (2018)
Funding
This work was partly supported by Translational Research program; Strategic PRomotion for practical application of INnovative medical Technology (TR-SPRINT) from Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED), Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Ethics approval is not required for this study.
Data availability
The data that supports the findings of this study are available within the article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Itai, S., Suzuki, K., Kurashina, Y. et al. Cell-encapsulated chitosan-collagen hydrogel hybrid nerve guidance conduit for peripheral nerve regeneration. Biomed Microdevices 22, 81 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-020-00536-x
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-020-00536-x