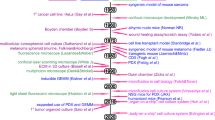
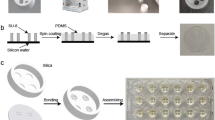
Abstract
Cell migration assays for different chemical environments are important for both scientists and clinicians searching for new therapeutics. In this study, we developed a multi-well-based microfluidic chip that has multiple units for different conditions. In each unit, cells can be patterned and then released to observe their migration. Automatic image analysis and model-based data processing were developed to describe the integrated cell migration assay precisely and quickly. As a demonstration, the migration behaviors of two types of cells in eight chemical conditions were studied. The results showed that supplementation with transforming growth factor-β(TGF-β) significantly promoted the migration of MCF-7 and MCF-10 A cells compared to several growth factors, such as Epidermal Growth Factor(EGF) and basic fibroblast growth factor(bFGF), as well as a control sample. Cells can migrate particularly fast with two or more mixed supplementary factors, such as TGF-β + bFGF + EGF, which indicated a synergy effect. Thus, this chip could be used to quantitatively observe cancer cell migration and demonstrated great potential for use in quantitative migration studies and chemical screening.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. C. Chen, S. G. Allen, P. N. Ingram, R. Buckanovich, S. D. Merajver, E. Yoon, Single-cell migration Chip for chemotaxis-based microfluidic selection of heterogeneous cell populations. Sci. Rep. 5, 13 (2015)
J. H. Chung, E. K. Im, T. Jin, S. M. Lee, S. H. Kim, E. Y. Choi, M. J. Shin, K. H. Lee, Y. Jang, Cathepsin L derived from skeletal muscle cells transfected with bFGF promotes endothelial cell migration. Exp. Mol. Med. 43, 179–188 (2011)
D. Irimia, M. Toner, Spontaneous migration of cancer cells under conditions of mechanical confinement. Integr. Biol. 1, 506–512 (2009)
S. B. Kim, K. I. Koo, H. Bae, M. R. Dokmeci, G. A. Hamilton, A. Bahinski, S. M. Kim, D. E. Ingber, A. Khademhosseini, A mini-microscope for in situ monitoring of cells. Lab Chip 12, 3976–3982 (2012)
Q. J. Kong, R. J. Majeska, M. Vazquez, Migration of connective tissue-derived cells is mediated by ultra-low concentration gradient fields of EGF. Exp. Cell Res. 317, 1491–1502 (2011)
N. Kozlova, A. Samoylenko, L. Drobot, T. Kietzmann, Urokinase modulates EGF-dependent signalling, proliferation and motility of the two breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231. Eur. J. Cancer 50, S123–S123 (2014)
S. Lamouille, E. Connolly, J. W. Smyth, R. J. Akhurst, R. Derynck, TGF-beta-induced activation of mTOR complex 2 drives epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell invasion. J. Cell Sci. 125, 1259–1273 (2012)
D. A. Lauffenburger, A. F. Horwitz, Cell migration: a physically integrated molecular process. Cell 84, 359–369 (1996)
H. Li, C. X. Luo, H. Ji, Q. Ouyang, Y. Chen, Micro-pressure sensor made of conductive PDMS for microfluidic applications. Microelectron. Eng. 87, 1266–1269 (2010)
Y. B. Li, Z. Q. Wang, X. Yan, M. W. Chen, J. L. Bao, G. S. Wu, Z. M. Ge, D. M. Zhou, Y. T. Wang, R. T. Li, IC-4, a new irreversible EGFR inhibitor, exhibits prominent anti-tumor and anti-angiogenesis activities. Cancer Lett. 340, 88–96 (2013)
C. C. Liang, A. Y. Park, J. L. Guan, In vitro scratch assay: a convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2, 329–333 (2007)
C. H. Liao, S. C. Yeh, Y. H. Huang, R. N. Chen, M. M. Tsai, W. J. Chen, H. C. Chi, P. J. Tai, C. J. Liao, S. M. Wu, et al., Positive regulation of spondin 2 by thyroid hormone is associated with cell migration and invasion. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 17, 99–111 (2010)
C. X. Luo, X. J. Zhu, T. Yu, X. J. Luo, Q. Ouyang, H. Ji, Y. Chen, A fast cell loading and high-throughput microfluidic system for long-term cell culture in zero-flow environments. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 101, 190–195 (2008)
J. M. K. Ng, I. Gitlin, A. D. Stroock, G. M. Whitesides, Components for integrated poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic systems. Electrophoresis 23, 3461–3473 (2002)
K. J. Regehr, M. Domenech, J. T. Koepsel, K. C. Carver, S. J. Ellison-Zelski, W. L. Murphy, L. A. Schuler, E. T. Alarid, D. J. Beebe, Biological implications of polydimethylsiloxane-based microfluidic cell culture. Lab Chip 9, 2132–2139 (2009)
K. Saito, T. Oku, N. Ata, H. Miyashiro, M. Hattori, I. Saiki, A modified and convenient method for assessing tumor cell invasion and migration and its application to screening for inhibitors. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 20, 345–348 (1997)
A. Valster, N. L. Tran, M. Nakada, M. E. Berens, A. Y. Chan, M. Symons, Cell migration and invasion assays. Methods 37, 208–215 (2005)
A. D. van der Meer, K. Vermeul, A. A. Poot, J. Feijen, I. Vermes, A microfluidic wound-healing assay for quantifying endothelial cell migration. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 298, H719–H725 (2010)
S. M. Wu, Y. H. Huang, C. T. Yeh, M. M. Tsai, C. H. Liao, W. L. Cheng, W. J. Chen, K. H. Lin, Cathepsin H regulated by the thyroid hormone receptors associate with tumor invasion in human hepatoma cells. Oncogene 30, 2057–2069 (2011)
J. D. Wu, X. Wu, F. Lin, Recent developments in microfluidics-based chemotaxis studies. Lab Chip 13, 2484–2499 (2013)
W. Yang, Z. J. Li, W. L. Zhang, C. X. Luo, Q. Ouyang, G. Yang, Y. G. Wang, A novel density control device for the study of cancer cell autocrine effect. Biomed. Microdevices 15, 683–689 (2013)
J. C. Yarrow, Z. E. Perlman, N. J. Westwood, T. J. Mitchison, A high-throughput cell migration assay using scratch wound healing, a comparison of image-based readout methods. BMC Biotechnol. 4, 9 (2004)
C. H. Zheng, Z. L. Yu, Y. Zhou, L. Tao, Y. H. Pang, T. Chen, X. N. Zhang, H. W. Qiu, H. W. Zhou, Z. T. Chen, et al., Live cell imaging analysis of the epigenetic regulation of the human endothelial cell migration at single-cell resolution. Lab Chip 12, 3063–3072 (2012)
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Feng Liu for helpful discussions. This work was partially supported by the NSF of China (11174012, 11674010, 11434001) and the National Grand Instrument Program of China (2012YQ030142).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 80 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quan, Q., Zhang, S., Wang, X. et al. A parallel and quantitative cell migration assay using a novel multi-well-based device. Biomed Microdevices 18, 99 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-016-0122-7
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-016-0122-7