Abstract
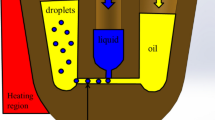
The Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was successfully and rapidly performed in a simple reaction device devoid of channels, pumps, valves, or other control elements used in conventional lab-on-a-chip technology. The basic concept of this device is the transportation of aqueous droplets containing hydrophilic magnetic beads in a flat-bottomed, tray-type reactor filled with silicone oil. The whole droplets sink to the bottom of the reactor because their specific gravity is greater than that of the silicone oil used here. The droplets follow the movement of a magnet located underneath the reactor. The notable advantage of the droplet-based PCR is the ability to switch rapidly the proposed reaction temperature by moving the droplets to the required temperature zones in the temperature gradient. The droplet-based reciprocative thermal cycling was performed by moving the droplets composed of PCR reaction mixture to the designated temperature zones on a linear temperature gradient from 50°C to 94°C generated on the flat bottom plate of the tray reactor. Using human-derived DNA containing the mitochondria genes as the amplification targets, the droplet-based PCR with magnetic reciprocative thermal cycling successfully provided the five PCR products ranging from 126 to 1,219 bp in 11 min with 30 cycles. More remarkably, the human genomic gene amplification targeting glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene was accomplished rapidly in 3.6 min with 40 cycles.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Chabert, K.D. Dorfman, P. Cremoux, J. Roeraade, J.L. Viovy, Anal. Chem. 78, 7722 (2006)
R.B. Fair, A. Khlystov, V. Srinivasan, V. Pamula, K.N. Weaver, in Devices, and Applications, Conf. 5591, SPIE Optics East, Philadelphia, 2004
M. Hashimoto, P. Chen, M.W. Mitchell, D.E. Nikitopoulos, S.A. Soper, M.C. Murphy, Lab Chip 4, 683 (2004)
C.G. Koh, W. Tan, M.Q. Zhao, A.J. Ricco, Z.H. Fan, Anal. Chem. 75, 4591 (2003)
M.U. Kopp, A.J. DeMello, A. Manz, Science 280, 1046 (1998)
Y.J. Liu, C.B. Rauch, R.L. Stevens, R. Lenigk, J.N. Yang, D.B. Rhine, P. Grodzinski, Anal. Chem. 74, 3063 (2002)
K.B. Mullis, F.A. Faloona, Methods Enzymol. 155, 335 (1987)
H. Nagai, Y. Murakami, Y. Morita, K. Yokoyama, E. Tamiya, Anal. Chem. 73, 1043 (2001)
S. Raja, J. Ching, L. Xi, S.J. Hughes, R. Chang, W. Wong, W. McMillan, W.E. Gooding, K.S. McCarty Jr., M. Chestney, J.D. Luketich, T.E. Godfrey, Clin. Chem. 51, 882 (2005)
A. Rida, V. Fernandez, M.A.M. Gijs, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 2396 (2003)
R.K. Saiki, D.H. Gelfand, S. Stoffel, S.J. Scharf, R. Higuchi, G.T. Horn, K.B. Mullis, H.A. Erlich, Science 29, 487 (1988)
J. Sambrook, E.F. Fritsch, T. Maniatis, Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1989)
I. Schneegaß, R. Bräutigam, J.M. Köhler, Lab Chip 1, 42 (2001)
M. Shikida, K. Takayanagi, K. Inouchi, H. Honda, K. Sato, Sens. Actuators, B 113, 563 (2006)
T. Taniguchi, T. Torii, T. Higuchi, Lab Chip 2, 19 (2002)
J. Wang, Z. Chen, P.L.A.M. Corstjens, M.G. Mauk, H.H. Bau, Lab Chip 6, 46 (2006)
E.K. Wheeler, W. Benett, P. Stratton, J. Richards, A. Chen, A. Christian, K.D. Ness, J. Ortega, L.G. Li, T.H. Weisgraber, K. Goodson, F. Milanovich, Anal. Chem. 76, 4011 (2004)
Q. Xiang, B. Xu, R. Fu, D. Li, Biomed. Microdevices 7, 273 (2005)
J. Yang, Y. Liu, C.B. Rauch, R.L. Stevens, R.H. Liu, R. Lenigk, P. Grodzinski, Lab Chip 2, 179 (2002)
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Hiroki Honda, Ryu Konoshita, and Atsushi Inami of this laboratory and Shoichi Konishi of Shimadzu Engineering Inc. for their helping manufacture the prototype for the experiment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohashi, T., Kuyama, H., Hanafusa, N. et al. A simple device using magnetic transportation for droplet-based PCR. Biomed Microdevices 9, 695–702 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-007-9078-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-007-9078-y