Abstract
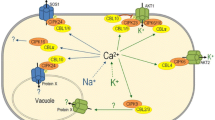
Finger millet (Eleusine coracana) is one of important crops, and its grains contain an exceptionally high content of calcium. In order to investigate the molecular mechanism by which it orchestrate the accumulation of Ca2+ during grain filling, some candidate genes encoding calcium transporters [calcium exchangers (CAX1, CAX3)] and sensors [calcineurin-B like (CBL4 and 10)], a CBL-interacting protein kinase (CIPK24), and calmodulin (CaM) were identified using transcriptomics and differential expression analysis in two genotypes of finger millet differing in grain calcium content. These transporters and sensors are highly expressed in leaves and developing spikes of the genotype with a high grain Ca2+ indicating their potential role in Ca2+ accumulation. Calcium transporters, mainly CAXs, pump Ca2+ inside the cell through plasmalemma and tonoplast, and their activities are regulated by CaM dependent and independent Ca2+ sensor proteins of CaM and CBL-CIPK networks. Abundance of CaM in a high grain Ca2+ genotype is suggestive that CaM might also contribute for grain calcium accumulation by interaction with Ca2+ATPase. The upregulation of CAX1 in vegetative tissues and developing spikes and CAX3 only in developing spikes provides the most plausible clue for calcium transport and accumulation regulated by tripartite interaction in finger millet.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CaM:
-
calmodulin
- CAX:
-
calcium exchanger
- CBL:
-
calcineurin B-like protein
- CIPK-CBL:
-
calcineurin B-like interacting protein kinase
References
Amtmann, A., Blatt, M.R.: Regulation of macronutrient transport. — New Phytol. 181: 35–52, 2009.
Batelli, G., Verslues, P.E., Agius, F., Qiu, Q., Fujii, H., Pan, S., Schumaker, K.S., Grillo, S., Zhu, J.K.: SOS2 promotes salt tolerance in part by interacting with the vacuolar H+-ATPase and upregulating its transport activity. — Mol. cell. Biol. 27: 7781–7790, 2007.
Bodade, R.G., Beedkar, S.D., Manwar, A.V., Khobragade, C.N.: Homology modeling and docking study of xanthine oxidase of Arthrobacter sp. XL26. — Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 47: 298–303, 2010.
Carter, C., Pan, S., Zouhar, J., Avila, E.L., Girke, T., Raikhel, N.V.: The vegetative vacuole?? proteome of Arabidopsis thaliana reveals predicted and unexpected proteins. — Plant Cell 16: 3285–3303, 2004.
Cheng, N.H., Pittman, J.K., Zhu, J.K., Hirschi, K.D.: The protein kinase SOS2 activates the Arabidopsis H+/Ca2+ antiporter CAX1 to integrate calcium transport and salt tolerance. — J. biol. Chem. 279: 2922–2926, 2004.
Cheng, N.H., Pittman, J.K., Shigaki, T., Lachmansingh, J., LeClere, S., Lahner, B., Salt, D.E., Hirschi, K.D.: Functional association of Arabidopsis CAX1 and CAX3 is required for normal growth and ion homeostasis. — Plant Physiol. 138: 2048–2060, 2005.
Cheong, Y.H., Pandey, G.K., Grant, J.J., Batistic, O., Li, L., Kim, B.G., Lee, S.C., Kudla, J., Luan, S.: Two calcineurin B-like calcium sensors, interacting with protein kinase CIPK23, regulate leaf transpiration and root potassium uptake in Arabidopsis. — Plant J. 52: 223–239, 2007.
Chinchole, M., Pathak, R.K., Singh, U.M., Kumar, A.: Molecular characterization of EcCIPK24 gene of finger millet (Eleusine coracana) for investigating its regulatory role in calcium transport. — Biotech 7: 267, 2017.
Conn, S.J., Gilliham, M., Athman, A., Schreiber, A.W., Baumann, U., Moller, I., Cheng, N.H., Stancombe, M.A., Hirschi, K.D., Webb, A.A., Burton, R.: Cell-specific vacuolar calcium storage mediated by CAX1 regulates apoplastic calcium concentration, gas exchange, and plant productivity in Arabidopsis. — Plant Cell. 23: 240–257, 2011.
Conn, S., Gilliham, M.: Comparative physiology of elemental distributions in plants. — Ann. Bot. 105: 1081–1102, 2010.
Funahashi, A., Morohashi, M., Kitano, H., Tanimura, N., CellDesigner: a process diagram editor for gene-regulatory and biochemical networks. — Biosilico 1: 159–162, 2003.
Gilliham, M., Dayod, M., Hocking, B.J., Xu, B., Conn, S.J., Kaiser, B.N., Leigh, R.A., Tyerman, S.D.: Calcium delivery and storage in plant leaves: exploring the link with water flow. — J. exp. Bot. 62: 2233–2250, 2011.
Gupta, S.M., Arora, S., Mirza, N., Pande, A., Lata, C., Puranik, S., Kumar, J., Kumar, A.: Finger millet: a “certain” crop for an “uncertain” future and a solution to food insecurity and hidden hunger under stressful environments. — Front. Plant Sci. 8: 643, 2017.
Hashimoto, K., Saito, M., Iida, H., Matsuoka, H.: Evidence for the plasma membrane localization of a putative voltagedependent Ca2+ channel, OsTPC1, in rice. — Plant Biotechnol. 22: 235–239, 2005.
Karley, A.J., White, P.J.: Moving cationic minerals to edible tissues: potassium, magnesium, calcium. — Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 12: 291–298, 2009.
Kitchen, D.B., Decornez, H., Furr, J.R., Bajorath, J.: Docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: methods and applications. — Nat. Rev. Drug Dis. 3: 935–949, 2004.
Kumar, A., Mirza, N., Charan, T., Sharma, N., Gaur, V.S.: Isolation, characterization and immunolocalization of a seed dominant CaM from finger millet (Eleusine coracana L. Gartn.) for studying its functional role in differential accumulation of calcium in developing grains. — Appl. Biol. Biotech. 172: 2955–2973, 2014.
Kumar, A., Pathak, R.K., Gupta, S.M., Gaur, V.S., Pandey, D.: Systems biology for smart crops and agricultural innovation: filling the gaps between genotype and phenotype for complex traits linked with robust agricultural productivity and sustainability. — OMICS 19: 581–601, 2015a.
Kumar, A., Sharma, N., Panwar, P., Gupta, A.K.: Use of SSR, RAPD markers and protein profiles based analysis to differentiate Eleusine coracana genotypes differing in their protein content. — Mol. Biol. Rep. 39: 4949–4960, 2012.
Kumar, A., Singh, U.M., Manohar, M., Gaur, V.S.: Calcium transport from source to sink: understanding the mechanism(s) of acquisition, translocation, and accumulation for crop biofortification. — Acta Physiol. Plant. 37: 1722, 2015b.
Li, R., Zhang, J., Wei, J., Wang, H., Wang, Y., Ma, R.: Functions and mechanisms of the CBL–CIPK signaling system in plant response to abiotic stress. — Progr. natur. Sci. 19: 667–676, 2009.
Livak, K.J., Schmittgen, T.D.: Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. — Methods 25: 402–408, 2001.
Mao, J., Manik, S.M., Shi, S., Chao, J., Jin, Y., Wang, Q., Liu, H.: Mechanisms and physiological roles of the CBL-CIPK networking system in Arabidopsis thaliana. — Genes 7: 62, 2016.
Mirza, N., Taj, G., Arora, S., Kumar, A.: Transcriptional expression analysis of genes involved in regulation of calcium translocation and storage in finger millet (Eleusine coracana L. Gartn.). — Gene 550: 171–179, 2014.
Nath, M., Goel, A., Taj, G., Kumar, A.: Molecular cloning and comparative in silico analysis of calmodulin genes from cereals and millets for understanding the mechanism of differential calcium accumulation. — J. Proteomics Bioinform. 3: 294–301, 2010.
Nath, M., Roy, P., Shukla, A., Kumar, A.: Spatial distribution and accumulation of calcium in different tissues, developing spikes and seeds of finger millet genotypes. — J. Plant Nutr. 36: 539–550, 2013.
Panwar, P., Nath, M., Yadav, V. K., Kumar, A.: Comparative evaluation of genetic diversity using RAPD, SSR and cytochrome P450 gene based markers with respect to calcium content in finger millet (Eleusine coracana L. Gaertn.). — J. Genet. 89: 121–133, 2010.
Pathak, R.K., Baunthiyal, M., Pandey, N., Pandey, D., Kumar, A.: Modeling of the jasmonate signaling pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana with respect to pathophysiology of Alternaria blight in Brassica. — Sci. Rep. 7: 16790, 2017.
Pathak, R.K., Baunthiyal, M., Shukla, R., Pandey, D., Taj, G., Kumar, A.: In silico identification of mimicking molecules as defense inducers triggering jasmonic acid mediated immunity against Alternaria blight disease in Brassica species. — Front. Plant Sci. 8: 609, 2017.
Pathak, R.K., Giri, P., Taj, G., Kumar, A.: Molecular modeling and docking approach to predict the potential interacting partners involved in various biological processes of MAPK with downstream WRKY transcription factor family in Arabidopsis thaliana. — Int. J. Comp. Bioinform. in Silico Model. 2: 262–268, 2013a.
Pathak, R.K., Taj, G., Pandey, D., Arora, S., Kumar, A.: Modeling of the MAPK machinery activation in response to various abiotic and biotic stresses in plants by a system biology approach. — Bioinformation 9: 443, 2013b.
Pathak, R.K., Taj, G., Pandey, D., Kasana, V.K., Baunthiyal, M., Kumar, A.: Molecular modeling and docking studies of phytoalexin(s) with pathogenic protein(s) as molecular targets for designing the derivatives with anti-fungal action on Alternaria spp. of Brassica. — Plant Omics 9: 172, 2016.
Pittman, J.K., Shigaki, T., Cheng, N.H., Hirschi, K.D.: Mechanism of N-terminal auto inhibition in the Arabidopsis Ca2+/H+ antiporter CAX1. — J. biol. Chem. 277: 26452–26459, 2002.
Pittman, J.K., Zhu, J.K., Hirschi, K.D.: The protein kinase SOS2 activates the Arabidopsis H+/Ca2+ antiporter CAX1 to integrate calcium transport and salt tolerance. — J. biol. Chem. 279: 2922–2926, 2004.
Punshon, T., Hirschi, K., Yang, J., Lanzirotti, A., Lai, B., Guerinot, M.L.: The role of CAX1 and CAX3 in elemental distribution and abundance in Arabidopsis seed. — Plant Physiol. 158: 352–362, 2012.
Reddy, A.R., Chaitanya, K.V., Vivekanandan, M.: Droughtinduced responses of photosynthesis and antioxidant metabolism in higher plants. — J. Plant Physiol. 161: 1189–1202, 2004.
Singh, U.M., Metwal, M., Singh, M., Taj, G., Kumar, A.: Identification and characterization of calcium transporter gene family in finger millet in relation to grain calcium content. — Gene 566: 37–46, 2015.
White, P.J.: Calcium channels in higher plants. — Biochim. biophys. Acta Biomembranes 1465: 171–189, 2000.
Xu, D., Zhang, Y.: Improving the physical realism and structural accuracy of protein models by a two-step atomiclevel energy minimization. — Biophys. J. 101: 2525–2534, 2011.
Zielinski, R.E.: Calmodulin and calmodulin binding proteins in plants. — Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant mol. Biol. 9: 697–725, 1998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgements: This work was financially supported by the program supporting research and development in Agricultural Biotechnology (grant No. BT/PR7849/AGR/02/374/2006-Part II) and by the HRD-DBT, the Goverment of India. MS acknowledges the DST Young Scientist Fellowship from the SERB, Department of Science & Technology, New Delhi (YSS/2015/001278). Bioinformatics Distributed Information Sub Centre, G.B. Pant University of Agriculture & Technology, Pantnagar is also duly acknowledged for providing computational facilities.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kokane, S.B., Pathak, R.K., Singh, M. et al. The role of tripartite interaction of calcium sensors and transporters in the accumulation of calcium in finger millet grain. Biol Plant 62, 325–334 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-018-0776-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-018-0776-5