Abstract
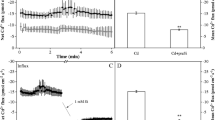
Silicon (Si) could enhance plant tolerance to heavy metals; however, the mechanism of Si-mediated alleviation of cadmium (Cd) toxicity in Poa annua was not clear. In this study, we found that 100 μM Cd significantly inhibited the growth of Poa annua seedlings. Furthermore, Cd enhanced the H2O2 and malondialdehyde content. The activities of superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase were enhanced, but the catalase and peroxidase activities were reduced by Cd treatment. Cd also altered the activity and expression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) in Poa annua roots. Application of Na3PO4, an inhibitor of G6PDH, decreased the activity of G6PDH, the expression of G6PDH, and increased the Cd toxicity, suggesting that G6PDH is involved in the regulation of oxidative stress induced by Cd. Application of 1 mM Si alleviated the inhibition of Cd on the growth of Poa annua seedlings. Si application not only led to reduced oxidative injuries but also decreased the accumulation of Cd in Poa annua seedlings under Cd stress. Furthermore, Si decreased the activity of G6PDH and the expression of G6PDH under Cd stress, which demonstrated that Si attenuates the Cd toxicity in Poa annua probably through decreasing the expression of G6PDH under Cd stress. When G6PDH was inhibited, the alleviation impact of Si on Cd stress was abolished. Taken together, these results demonstrated that the Cd tolerance in Poa annua enhanced by Si is mainly due to the decrease of Cd uptake in roots and lowering the oxidative stress induced by Cd.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APX:
-
ascorbate peroxidase
- CAT:
-
catalase
- EDTA:
-
ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid
- G6PDH:
-
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- GR:
-
glutathione reductase
- GSH:
-
glutathione
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- NADPH:
-
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- OPPP:
-
oxidative pentose phosphate pathway
- PAGE:
-
polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- PEPC:
-
phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
- 6PGDH:
-
6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase
- PMSF:
-
phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride
- POD:
-
peroxidase
- PVDF:
-
polyvinylidene fluoride
- PVP:
-
polyvinyl pyrrolidone
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- TBA:
-
thiobarbituric acid
- TCA:
-
trichloroacetic acid
References
Ádám, A.L., Bestwick, C.S., Barna, B., Mansfield, J.W.: Enzymes regulating the accumulation of active oxygen species during the hypersensitive reaction of bean to Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola. — Planta 197: 240–249, 1995.
Aebi, H.: Catalase in vitro. — Methods Enzymol. 105: 121–126, 1984.
Balakhnina, T.I., Matichenkov, V.V., Wlodarczyk, T., Borkowska, A., Nosalewicz, M. Fomina, I.R.: Effects of silicon on growth processes and adaptive potential of barley plants under optimal soil watering and flooding. — Plant Growth Regul. 67: 35–43, 2012.
Bradford, M.M.: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. — Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254, 1976.
Dal Corso, G., Farinati, S., Furini, A.: Regulatory networks of cadmium stress in plants. — Plant Signal Behav. 5: 663–667, 2010.
Dal Santo, S., Stampfl, H., Krasensky, J., Kempa, S., Gibon, Y., Petutschnig, E., Rozhon, W., Heuck, A., Clausen, T., Jonak, C.: Stress-induced GSK3 regulates the redox stress response by phosphorylating glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in Arabidopsis. — Plant Cell 24: 3380–3392, 2012.
Esposito, S., Carfagna, S., Massaro, G., Vona, V., Di, M.R.V.: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in barley roots: kinetic properties and localization of the isoforms. — Planta 212: 627–634, 2001.
Exley, C.: Silicon in life: a bioinorganic solution to bioorganic essentiality. — J. Inorg. Biochem. 69: 139–144, 1998.
Feng, J.G., Shi, Q.H., Wang, X.F., Wei, M., Yang, F.J., Xu, H.N.: Silicon supplementation ameliorated the inhibition of photosynthesis and nitrate metabolism by cadmium (Cd) toxicity in Cucumis sativus L. — Sci. Hort. 123: 521–530, 2010.
Gallego, S.M., Pena, L.B., Barcia, R.A., Azpilicueta, C.E., Iannone, M.F., Rosales, E.P., Zawoznik, M.S., Groppa, M.D., Benavides, M.P.: Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insights into regulatory mechanisms. — Environ. exp. Bot. 83: 33–46, 2012.
Graeve, K., Von Schaewen, A., Scheibe, R.: Purification, characterization, and cDNA sequence of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). — Plant J. 5: 353–361, 1994.
Hodges, D.M., Delong, J.M., Forney, C.F., Prange, R.K.: Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. — Planta 207: 604–711, 1999.
Janda, T., Szalai, G., Tari, I., Páldi, E.: Hydroponic treatment with salicylic acid decreases the effects of chilling in maize (Zea mays L) plants. — Planta 208: 175–180, 1999.
Khandekar, S., Leisner, S.: Soluble silicon modulates expression of Arabidopsis thaliana genes involved in copper stress. — J Plant Physiol. 168: 699–705, 2011.
Laemmli, U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. — Nature 227: 680–685, 1970.
Li, P., Song, A., Li, Z.J., Fan, F.L., Liang, Y.C.: Silicon ameliorates manganese toxicity by regulating manganese transport and antioxidant reactions in rice (Oryza sativa L.). — Plant Soil 354: 407–419, 2012.
Lin, Y.Z., Lin, S.Z., Guo, H., Zhang, Z.Y., Chen, X.Y.: Functional analysis of PsG6PDH, a cytosolic glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Populus suaveolens, and its contribution to cold tolerance improvement in tobacco plants. — Biotechnol. Lett. 35: 1509–1518, 2013.
Liu, S., Yang, R., Pan, Y., Ma, M., Pan, J., Zhao, Y., Cheng, Q., Wu, M., Wang, M., Zhang, L.: Nitric oxide contributes to minerals absorption, proton pumps and hormone equilibrium under cadmium excess in Trifolium repens L. plants. — Ecotoxicol. environ. Safety 119: 35–46, 2015.
Ma, F.J., Yamaji, N.: Silicon uptake and accumulation in higher plants. — Trends Plant Sci. 11: 392–397, 2006.
Mitani, N., Ma, J.F.: Uptake system of silicon in different plant species. — J. exp. Bot. 56: 1255–1261, 2005.
Mittler, R., Vanderauwera, S., Gollery, M., Breusegem, F.V.: Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. — Trends Plant Sci. 9: 490–498, 2004.
Peng, Y., Huang, B.R., Xu, L.X., Li, Z.: Heat stress effects on osmotic potential, membrane fatty acid composition and lipid peroxidation content of two Kentucky bluegrass cultivars differing in drought tolerance. — Acta horticult. sin. 40: 971–980, 2013.
Porra, R.J., Thompson, W.A., Kriedman, P.A.: Determination of accurate extinction coefficients and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophylls a and b extracted with four different solvents: verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorption spectroscopy. — Biochim. biophys. Acta 975: 384–394, 1989.
Prochazkova, D., Sairam, R.K., Srivastava, G.C., Singh, D.V.: Oxidative stress and antioxidant activity as the basis of senescence in maize leaves. — Plant Sci. 161: 765–771, 2001.
Rizwan, M., Meunier, J.D., Miche, H., Keller, C.: Effect of silicon on reducing cadmium toxicity in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. cv. Claudio W) grown in a soil with aged contamination. — J. Hazard Mater. 209–210: 326–334, 2011.
Rodríguez-Serrano, M., Romero-Puertas, M.C., Pazmiño, D.M., Testillano, P.S., Risueño, M.C., Del Rio, L.A., Sandalio, L.M.: Cellular response of pea plants to cadmium toxicity: cross talk between reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide, and calcium. — Plant Physiol. 150: 229–243, 2009.
Salvemini, F., Franze, A., Iervolino, A., Filosa, S., Salzano, S., Ursini, V.: Enhanced glutathione levels and oxido resistance mediated by increased glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase expression. — J. biol. Chem. 274: 2750–2757, 1999.
Scharte, J., Schön, H., Tiaden, Z., Weis, E., Von Schaewen, A.: Isoenzyme replacement of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in the cytosol improves stress tolerance in plants. — PNAS 106: 8061–8066, 2009.
Sharma, S.S., Dietz, K.J.: The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. — Trends Plant Sci. 14: 43–50, 2009.
Shetty, R., Jensen, B., Shetty, N.P., Hansen, M., Hansen, C.W., Starkey, K.R., Jørgensen, H.J.L.: Silicon induced resistance against powdery mildew of roses caused by Podosphaera pannosa. — Plant Pathol. 61: 120–131, 2012.
Shi, G.R., Cai, Q.S., Liu, C.F., Wu, L.: Silicon alleviates cadmium toxicity in peanut plants in relation to cadmium distribution and stimulation of antioxidative enzymes. — Plant Growth Regul. 61: 45–52, 2010.
Slaski, J.J., Zhang, G.C., Basu, U., Stephens, J.L., Taylor, G.J.: Aluminum resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum) is associated with rapid, Al-induced changes in activities of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase in root apices. — Physiol. Plant. 98: 477–484, 1996.
Song, A., Li, P., Li, Z.J., Fan, F.L., Nikolic, M., Liang, Y.C.: The alleviation of zinc toxicity by silicon is related to zinc transport and antioxidative reactions in rice. — Plant Soil 344: 319–333, 2011.
Sun, Y.B., Zhou, Q.X., Wang, L., Liu, W.T.: The influence of different growth stages and dosage of EDTA on Cd uptake and accumulation in Cd hyperaccumulator (Solanum nigrum L.). — Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 82: 348–353, 2009.
Tian, W.N., Braunstein, L.D., Pang, J., Stuhlmeier, K.M., Xi, Q.C., Tian, X., Stanton, R.C.: Importance of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity for cell growth. — J. biol. Chem. 273: 10609–10617, 1998.
Vaculík, M., Landberg, T., Greger, M., Luxová, M., Stoláriková, M., Lux, A.: Silicon modifies root anatomy, and uptake and subcellular distribution of cadmium in young maize plants. — Ann. Bot. 110: 433–443, 2012.
Van Assche, F., Cardinaels, C., Clijsters, H.: Induction of enzyme capacity in plants as a result of heavy metal toxicity: dose-response relations in Phaseolus vulgaris L., treated with zinc and cadmium. — Environ. Pollut. 52: 103–115, 1988.
Veljovic-Jovanovic, S.D., Noctor, G., Foyer, C.H.: Are leaf hydrogen peroxide concentrations commonly overestimated? The potential influence of artefactual interference by tissue phenolics and ascorbate. — Plant Physiol. Biochem. 40: 501–507, 2002.
Wang, H.H., Yang, L.D., Li, Y., Hou, J.J., Huang, J.J., Liang, W.H.: Involvement of ABA- and H2O2-dependent cytosolic glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in maintaining redox homeostasis in soybean roots under drought stress. — Plant Physiol. Biochem. 107: 126–136, 2016.
Wang, M., Zou, J.H., Duan, X.C., Jiang, W.S., Liu, D.H.: Cadmium accumulation and its effects on metal uptake in maize (Zea mays L.). — Bioresour. Technol. 98: 82–88, 2007.
Wang, X.M., Ma, Y.Y., Huang, C.H., Wan, Q., Li, N., Bi, Y.R.: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase plays a central role in modulating reduced glutathione levels in reed callus under salt stress. — Planta 227: 611–623, 2008a.
Wang, Z., Zhang, Y.X., Huang, Z.B., Huang, L.: Antioxidative response of metal accumulator and non-accumulator plants under cadmium stress. — Plant Soil 310: 137–149, 2008b.
Weber, M., Trampczynska, A., Clemens, S.: Comparative transcriptome analysis of toxic metal responses in Arabidopsis thaliana and the Cd2+-hypertolerant facultative metallophyte Arabidopsis halleri. — Plant Cell Environ. 29: 950–963, 2006.
Yan, H., Filardo, F., Hu, X., Zhao, X., Fu, D.: Cadmium stress alters the redox reaction and hormone balance in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) leaves. — Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 23: 3758–69, 2016.
Yang, Y.T., Fu, Z.W., Su, Y.C., Zhang, X., Li, G.Y., Guo, J.L., Que, Y.X., Xu, L.P.: A cytosolic glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene, ScG6PDH, plays a positive role in response to various abiotic stresses in sugarcane. — Sci. Rep. 4: 7090, 2014.
Zhang, C.C., Wang, L.J., Nie, Q., Zhang, W.X., Zhang, F.S.: Long-term effects of exogenous silicon on cadmium translocation and toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). — Environ. exp. Bot. 62: 300–307, 2008.
Zhang, F.Q., Zhang, H.X., Wang, G.P., Xu, L.L., Shen, Z.G.: Cadmium-induced accumulation of hydrogen peroxide in the leaf apoplast of Phaseolus aureus and Vicia sativa and the roles of different antioxidant enzymes. — J. Hazard Mater. 168: 76–84, 2009.
Zhang, L., Liu, J., Wang, X.M., Bi, Y.R.: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase acts as a regulator of cell redox balance in rice suspension cells under salt stress. — Plant Growth Regul. 69: 139–148, 2013.
Zhao, C.Z, Li, P., Wang, X.M., Li, P., Wang, X.Y., Wang, F., Wang, J.F., Chang, N., Bi Y.R.: Nitrogen deprivation induces cross-tolerance of Poa annua callus to salt stress. — Biol. Plant. 60: 543–554, 2016.
Zhao, L.Q., Zhang, F., Guo, J.K., Yang, Y.L., Li, B.B., Zhang, L.X.: Nitric oxide functions as a signal in salt resistance in the calluses from two ecotypes of reed. — Plant Physiol. 134: 849–857, 2004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgements: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31671595; 31670244), the National Program on Key Basic Research Project (2012CB026105), the Foundation of Science and Technology Program of Gansu Province (1506RJZA209), the National High Technology Research and Development Program (2007AA021401), and the Foundation of Science and Technology Program of Lanzhou City (2015-3-53).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Zhao, C.Z., Zhand, Y.Q. et al. Silicon enhances the tolerance of Poa annua to cadmium by inhibiting its absorption and oxidative stress. Biol Plant 61, 741–750 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-017-0731-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-017-0731-x