Abstract
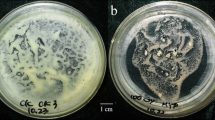
Cell lines able to grow on media containing 50, 100, 150 or 200 mM NaCl were established from potato callus cultures by direct recurrent selection or gradual selection. In callus subjected to direct selection only small clusters of cells survived on medium with 150 or 200 mM NaCl, whereas on 100 mM small cell portions appear necrotic. When cell lines were obtained by successive subcultures on media with increased concentrations of NaCl, salt-tolerant calli were more compact and developed a greenish colour free from necrotic areas. The response of calli lines grown on media with NaCl was compared to control line. The NaCl-tolerant calli showed a decrease in relative growth rate and water content, with higher reductions in the 150 mM tolerant callus. Lipid peroxidation was increased in 50 mM and 100 mM NaCl-tolerant calli, while in 150 mM tolerant callus remained similar to 100 mM values. There was a significant increase in ascorbic acid content in 100 mM and 150 mM NaCl-tolerant calli as compared to the 50 mM, that was two-fold the value found in the control. Also, the contents of soluble and insoluble proteins increased in salt-tolerant lines. SDS-PAGE of soluble proteins showed the synthesis of specific polypeptides in the presence of NaCl in culture medium and the synthesis of a new polypeptide.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AsA:
-
ascorbic acid
- BA:
-
benzylaminopurine
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- SDS-PAGE:
-
sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- TCA:
-
trichloroacetic acid
References
Apel, K., Hirt, H.: Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction.-Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 55: 373–399, 2004.
Benavídes, M.P., Marconi, P.L., Gallego, S.M., Comba, M.E., Tomaro, M.L.: Relationship between antioxidant defence systems and salt tolerance in Solanum tuberosum.-Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 27: 273–278, 2000.
Binzel, M.L., Hasegawa, P.M., Handa, A.K., Bressan, R.A.: Adaptation of tobacco cells to NaCl.-Plant Physiol. 79: 118–125, 1985.
Borsani, O., Valpuesta, V., Botella, M.A.: Developing salt tolerant plants in a new century: a molecular biology approach.-Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 73: 101–115, 2003.
Davenport, S.B., Gallego, S.M., Benavides, M.P., Tomaro, M.L.: Behaviour of antioxidant defense system in the adaptive response to salt stress in Helianthus annuus L. cells.-Plant Growth Regul. 40: 81–88, 2003.
Dracup, M.: Increasing salt tolerance of plants through cell culture requires greater understanding of tolerance mechanisms.-Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 18: 1–15, 1991.
Dunbar, B.S. (ed.): Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis and Immunological Techniques.-Plenum Press, New York-London 1988.
Fidalgo, F., Santos, A., Santos, I., Salema, R.: Effects of long-term salt stress on antioxidant defence systems, leaf water relations and chloroplast ultrastructure of potato plants.-Ann. appl. Biol. 145: 185–192, 2004.
Gossett, D.R., Millhollon, E.P., Lucas, M.C.: Antioxidant response to NaCl stress in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive cultivars of cotton.-Crop Sci. 34: 706–714, 1994.
Gossett, D.R., Banks, S.W., Millhollon, E.P., Lucas, M.C.: Antioxidant response to NaCl stress in a control and an NaCl-tolerant cotton cell line grown in the presence of paraquat, buthionine sulfoximine, and exogenous glutathione.-Plant Physiol. 112: 803–809, 1996.
Gu, R., Liu, Q., Pei, D., Jiang, X.: Understanding saline and osmotic tolerance of Populus euphratica suspended cells.-Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 78: 261–265, 2004.
Hasegawa, P.M., Bressan, R.A., Zhu, J.-K., Bohnert, H.J.: Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity.-Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant mol. Biol. 51: 463–499, 2000.
Hawkins, H.-J., Lips, S.H.: Cell suspension cultures of Solanum tuberosum L. as a model system for N and salinity response. Effect of salinity on NO3 − uptake and PM-ATPase activity.-J. Plant Physiol. 150: 103–109, 1997.
Hernández, J.A., Olmos, E., Corpas, F.J., Sevilla, F., Del Río, L.A.: Salt-induced oxidative stress in chloroplasts of pea plants.-Plant Sci. 105: 151–167, 1995.
Hernández, J.A., Jiménez, A., Mullineaux, P., Sevilla, F.: Tolerance of pea (Pisum sativum L.) to long-term salt stress is associated with induction of antioxidant defences.-Plant Cell Environ. 23: 853–862, 2000.
Khan, M.H., Panda, S.K.: Induction of oxidative stress in roots of Oryza sativa L. in response to salt stress.-Biol. Plant. 45: 625–627, 2002.
Laemmli, U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.-Nature 227: 680–685, 1970.
Lam, S.-L.: Plantlet formation from potato tuber discs in vitro.-Amer. Potato J. 54: 465–468, 1977.
Leone, A., Costa, A., Tucci, M., Grillo, S.: Comparative analysis of short-and long-term changes in gene expression caused by low water potential in potato (Solanum tuberosum) cell-suspension cultures.-Plant Physiol. 106: 703–712, 1994a.
Leone, A., Costa, A., Tucci, M., Grillo, S.: Adaptation versus shock response to polyethylene glycol-induced low water potential in cultured potato cells.-Physiol. Plant. 92: 21–30, 1994b.
Lutts, S., Almansouri, M., Kinet, J.-M.: Salinity and water stress have contrasting effects on the relationship between growth and cell viability during and after stress exposure in durum wheat callus.-Plant Sci. 167: 9–18, 2004.
Miki, Y., Hashiba, M., Hisajima, S.: Establishment of salt stress tolerant rice plants through step up NaCl treatment in vitro.-Biol. Plant. 44: 391–395, 2001.
Munns, R.: Comparative physiology of salt and water stress.-Plant Cell Environ. 25: 239–250, 2002.
Niknam, V., Razavi, N., Ebrahimzadeh, H., Sharifizadeh, B.: Effect of NaCl on biomass, protein and proline contents, and antiioxidant enzyles in seedling and calli of two Trigonella species.-Biol. Plant. 50: 591–596, 2006.
Ochatt, S.J., Marconi, P.L., Radice, S., Arnozis, P.A., Caso, O.H.: In vitro recurrent selection of potato: production and characterization of salt tolerant cell lines and plants.-Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 55: 1–8, 1999.
Olmos, E., Hellín, E.: Mechanisms of salt tolerance in a cell line of Pisum sativum: biochemical and physiological aspects.-Plant Sci. 120: 37–45, 1996.
Özdemir, F., Bor, M., Demiral, T., Türkan, İ.: Effects of 24-epibrassinolide on seed germination, seedling growth, lipid peroxidation, proline content and antioxidative system of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under salinity stress.-Plant Growth Regul. 42: 203–211, 2004.
Peterson, G.L.: A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable.-Anal. Biochem. 83: 346–356, 1977.
Pruvot, G., Cuiné, S., Peltier, G., Rey, P.: Characterization of a novel drought-induced 34-kDa protein located in the thylakoids of Solanum tuberosum L. plants.-Planta 198: 471–479, 1996a.
Pruvot, G., Massimino, J., Peltier, G., Rey, P.: Effects of low temperature, high salinity and exogenous ABA on the synthesis of two chloroplastic drought-induced proteins in Solanum tuberosum.-Physiol. Plant. 97: 123–131, 1996b.
Rodríguez-Rosales, M.P., Kerkeb, L., Bueno, P., Donaire, J.P.: Changes induced by NaCl in lipid content and composition, lipoxygenase, plasma membrane H+-ATPase and antioxidant enzyme activities of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum. Mill) calli.-Plant Sci. 143: 143–150, 1999.
Rus, A.M., Panoff, M., Perez-Alfocea, F., Bolarin, M.C.: NaCl responses in tomato calli and whole plants.-J. Plant Physiol. 155: 727–733, 1999.
Shankhdhar, D., Shankhdhar, S.C., Mani, S.C., Pant, R.C.: In vitro selection for salt tolerance in rice.-Biol. Plant. 43: 477–480, 2000.
Shigeoka, S., Ishikawa, T., Tamoi, M., Miyagawa, Y., Takeda, T., Yabuta, Y., Yoshimura, K.: Regulation and function of ascorbate peroxidase isoenzymes.-J. exp. Bot. 53: 1305–1319, 2002.
Shukla, V.K.S., Kokate, C.K., Srivastava, K.C.: Spectrophotometric determination of ascorbic acid.-Microchem. J. 24: 124–126, 1979.
Singh, N.K., Bracker, C.A., Hasegawa, P.M., Handa, A.K., Buckel, S., Hermodson, M.A., Pfankoch, E., Regnier, F.E., Bressan, R.A.: Characterization of osmotin. A thaumatin-like protein associated with osmotic adaptation in plant cells.-Plant Physiol. 85: 529–536, 1987.
Smirnoff, N., Wheeler, G.L.: Ascorbic acid in plants: biosynthesis and function.-Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 19: 267–290, 2000.
Sotiropoulos, T.E., Dimassi, K.N., Tsirakoglou, V., Therios, I.N.: Response of two Prunus rootstocks to KCl induced salinity in vitro.-Biol. Plant. 50: 477–480, 2006.
Wang, J., Zhang, H., Allen, R.D.: Overexpression of an Arabidopsis peroxisomal ascorbate peroxidase gene in tobacco increases protection against oxidative stress.-Plant Cell Physiol. 40: 725–732, 1999.
Zhu, J.-K.: Plant salt tolerance.-Trends Plant Sci. 6: 66–71, 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Queirós, F., Fidalgo, F., Santos, I. et al. In vitro selection of salt tolerant cell lines in Solanum tuberosum L.. Biol Plant 51, 728–734 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-007-0149-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-007-0149-y