Abstract
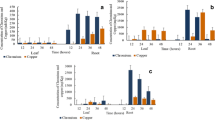
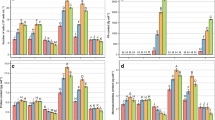
Phytochelatins (PCs), the heavy metal-binding peptides of plants, play a main function in heavy metal detoxification. In this study, Enhalus acoroides samples collected at six distinct seagrass beds from the coast of Khanh Hoa province, Viet Nam, were evaluated for their PCs. The contents of different PCs in each organ including leaf, rhizome, and root were determined by using HPLC analysis. Significant differences of PC2 contents among specific organs and their relation were tested by ANOVA, Tukey test, and Pearson’s correlation. The results showed that higher PC2, appearance of PC3 and a strong correlation between PC2 and Pb concentration were found in the root organ collected from a Pb contaminated area. We conclude that high Pb in the sediment induce high PC2 and PC3 production in the root. This first report on in situ detection of PCs of seagrass encourages future investigation on the ability to use seagrass for phytoremediation and as a bioindicator of heavy metals based on PC contents.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Legorreta T, Mendoza-Cozatl D, Moreno-Sanchez R, Gold-Bouchot G (2008) Thiol peptides induction in the seagrass Thalassia testudinum (Banks ex König) in response to cadmium exposure. Aquat Toxicol 86:12–19. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.09.001
Bankaji I, Caçador I, Sleimi N (2015) Physiological and biochemical responses of Suaeda fruticosa to cadmium and copper stresses: growth, nutrient uptake, antioxidant enzymes, phytochelatin, and glutathione levels. Environ Sci Pollut R 22:13058–13069. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4414-x
Caetano M, Vale C, Cesario R, Fonseca N (2008) Evidence for preferential depths of metal retention in roots of salt marsh plants. Sci Total Environ 390:466–474. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.10.015
Clemens S (2006) Evolution and function of phytochelatin synthases. Plant Physiol 163:319–332. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2005.11.010
Cobbett CS, Goldsbrough P (2002) Phytochelatins and metallothionines: roles in heavy metals detoxification and homeostasis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:159–182. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.100301.135154
Cong M, Zhao J, Lü J, Ren Z, Wu H (2016) Homologous cloning, characterization and expression of a new halophyte phytochelatin synthase gene in Suaeda salsa. Chinese J Oceanol Limnol 34:1034–1043. doi:10.1007/s00343-016-4382-0
Dai NH, Tri PH, Hoa NX, Linh NT (1998) Seagrass beds in the south of Vietnam. Proc. 4th Nat. Conf Mar Sci Tech 2:967–972 (in Vietnamese)
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2011) ProtTest 3: fast selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 27:1164–1165. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btr088
De Vos CHR, Vonk MJ, Vooijs R, Schat H (1992) Glutathione depletion due to copper-induced phytochelatin synthesis causes oxidative stress in Silene cucubalus. Plant Physiol 98:853–858. doi:10.1104/pp.98.3.853
Estrella-Gomez N, Mendoza-Cozatl D, Moreno-Sanchez R, Gonzalez-Mendoza D, Zapata-Perez O, Martinez-Hernandez A, Santamaria JM (2009) The Pb-hyperaccumulator aquatic fern Salvinia minima Baker, responds to Pb2+ by increasing phytochelatins via changes in SmPCS expression and in phytochelatin synthase activity. Aquat Toxicol 91:320–328. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.11.002
Felsenstein J (1992) Phylogenies from restriction sites: a maximum-likelihood approach. Evolution 46:159–175. doi:10.2307/2409811
Fischer S, Kühnlenz T, Thieme M, Schmidt H, Clemens S (2014) Analysis of plant Pb tolerance at realistic submicromolar concentrations demonstrates the role of phytochelatin synthesis for Pb detoxification. Environ Sci Technol 48:7552–7559. doi:10.1021/es405234p
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specified tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416. doi:10.1093/sysbio/20.4.406
Gekeler W, Grill E, Winnacker EL, Zenk Meinhart H (1989) Survey of the plant kingdom for the ability to bind heavy metals through phytochelatins. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C 44:361–369. doi:10.1515/znc-1989-5-605
Gonzalez-Mendoza D, Moreno AQ, Zapata-Perez O (2007) Coordinated responses of phytochelatin synthase and metallothionein genes in black mangrove, Avicennia germinans, exposed to cadmium and copper. Aquat Toxicol 83:306–314. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.05.005
Gupta M, Chandra P (1998) Bioaccumulation and toxicity of mercury in rooted-submerged macrophyte Vallisneria spiralis. Environ Pollut 103:327–332. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(98)00102-x
Gupta M, Rai UN, Tripathi RD, Chandra P (1995) Lead induced changes in glutathione and phytochelatin in Hydrilla verticillata (l.f.) Royle. Chemosphere 30:2011–2020. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(95)00075-J
Han RM, Lefèvre I, Ruan CJ, Qin P, Lutts S (2012) NaCl differently interferes with Cd and Zn toxicities in the wetland halophyte species Kosteletzkya virginica (L.) Presl. Plant Growth Regul 68:97–109. doi:10.1007/s10725-012-9697-z
Hirata K, Tsujimoto Y, Namba T, Ohta T, Hirayanagi N, Miyasaka H, Zenk MH, Miyamoto K (2001) Strong induction of phytochelatin synthesis by zinc in marine green alga, Dunaliella tertiolecta. J Biosci Bioeng 92:24–29. doi:10.1016/S1389-1723(01)80193-6
Inouhe M (2005) Phytochelatins. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:65–78. doi:10.1590/S1677-04202005000100006
Kumar GP, Prasad VMN (2004) Cadmium-inducible proteins in Ceratophyllum demersum L. (a fresh water macrophyte): toxicity bioassays and relevance to cadmium detoxification. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 73:174–181. doi:10.1007/s00128-004-0410-4
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol. doi:10.1093/molbev/msw054
Lafabrie C, Pergent G, Kantin R, Pergent-Martini C, Gonzalez JL (2007) Trace metals assessment in water, sediment, mussel and seagrass species—validation of the use of Posidonia oceanica as a metal biomonitor. Chemosphere 68:2033–2039. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.02.039
Li W, Liu B, Yu L, Feng D, Wang H, Wang J (2009) Phylogenetic analysis, structural evolution and functional divergence of the 12-oxo-phytodienoate acid reductase gene family in plants. BMC Evol Biol 9:90. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-9-90
Lutts S, Lefèvre I (2015) How can we take advantage of halophyte properties to cope with heavy metal toxicity in salt-affected areas? Ann Bot 115:509–528. doi:10.1093/aob/mcu264
MacFarlane GR, Burchett MD (2000) Cellular distribution of copper, lead and zinc in the grey mangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. Aquat Bot 68:45–59. doi:10.1016/S0304-3770(00)00105-4
Mellado M, Contreras RA, Gonzalez A, Dennett G, Moenne A (2012) Copper-induced synthesis of ascorbate, glutathione and phytochelatins in the marine alga Ulva compressa (Chlorophyta). Plant Physiol Biochem 51:102–108. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2011.10.007
Minocha R, Thangavel P, Dhankher OP, Long S (2008) Separation and quantification of monothiols and phytochelatins from a wide variety of cell cultures and tissues of trees and other plants using high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1207:72–83. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2008.08.023
Mishra SA, Dubey RS (2006) Heavy metal up take and detoxification mechanisms in plants. Int J Agric Res 1:122–141. doi:10.3923/ijar.2006.122.141
Nguyen XV, Klein M, Riemenschneider A, Papenbrock J (2014) Distinctive features and role of sulfur-containing compounds in marine plants, seaweeds, seagrasses and halophytes, from an evolutionary point of view. In: Khan MA, Böer B, Öztürk M, Al Abdessalaam TZ, Clüsener-Godt M, Gul B(eds) Sabkha ecosystems: cash crop halophyte and biodiversity conservation, volume IV. Springer, Netherlands, pp 299–312. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-7411-7_21
Olsen JL, Rouzé P, Verhelst B et al (2016) The genome of the seagrass Zostera marina reveals angiosperm adaptation to the sea. Nature 530:331–335. doi:10.1038/nature16548
Papenbrock J (2012) Highlights in seagrasses’ phylogeny, physiology and metabolism: what makes them special? ISRN Botany. doi:10.5402/2012/103892
Pawlik-Skowrońska B, Pirszel J, Brown MT (2007) Concentrations of phytochelatins and glutathione found in natural assemblages of seaweeds depend on species and metal concentrations of the habitat. Aquat Toxicol 83:190–199. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.04.003
Rai UN, Tripathi RD, Gupta M, Chandra P (1995) Induction of phytochelatins under cadmium stress in water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes). Environ Sci Health 30:2007–2026. doi:10.1080/10934529509376318
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Scarano G, Morelli E (2002) Characterization of cadmium- and lead-phytochelatin complexes formed in a marine microalga in response to metal exposure. Biometals 15:145–151. doi:10.1023/A:1015288000218
Sneller FE, van Heerwaarden LM, Koevoets PL, Vooijs R, Schat H, Verkleij JA (2000) Derivatization of phytochelatins from Silene vulgaris, induced upon exposure to arsenate and cadmium: comparison of derivatization with Ellman’s reagent and monobromobimane. J Agric Food Chem 48:4014–4019. doi:10.1021/jf9903105
Song WY, Mendoza-Cózatl DG, Lee Y, Schroeder JI, Ahn SN, Lee HS, Wicker T, Martinoia E (2014) Phytochelatin–metal(loid) transport into vacuoles shows different substrate preferences in barley and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 37:1192–1201. doi:10.1111/pce.12227
Sousa AI, Caçador I, Lillebø AI, Pardal MA (2008) Heavy metal accumulation in Halimione portulacoides: intra- and extra-cellular metal binding sites. Chemosphere 70:850–857. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.07.012
Srivastava S, Mishra S, Tripathi RD, Dwivedi S, Trivedi PK, Tandon PK (2007) Phytochelatins and antioxidant systems respond differentially during arsenite and arsenate stress in Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle. Environ Sci Technol 41:2930–2936. doi:10.1021/es062167j
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML Version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30:1312–1313. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033
Sun Q, Liu WB, Wang C (2011) Different response of phytochelatins in two aquatic macrophytes exposed to cadmium at environmentally relevant concentrations. Afr J Biotechnol 10:6292–6299. doi:10.5897/AJB10.1785
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metals toxicity and the environment. In: Luch A (ed) Molecular, clinical and environmental toxicology. Springer, Basel, pp 133–164
Tripathi RD, Rai UN, Gupta M, Chandra P (1996) Induction of phytochelatins in Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle under cadmium stress. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 56:505–512. doi:10.1007/s001289900073
Tsuji N, Hirayanagi N, Iwabe O, Namba T, Tagawa M, Miyamoto S, Miyasaka H, Takagi M, Hirata K, Miyamoto K (2003) Regulation of phytochelatin synthesis by zinc and cadmium in marine green alga, Dunaliella tertiolecta. Phytochemistry 62:453–459. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(02)00559-9
Tupan CI, Herawati EY, Arfiati D (2014) Detection of phytochelatin and glutathione in seagrass Thalassia hemprichii as a detoxification mechanism due to lead heavy metal exposure. Aquat Sci Technol 2:67–78. doi:10.5296/ast.v2i2.5853
Yadav SK (2010) Heavy metals toxicity in plants: an overview on the role of glutathione and phytochelatins in heavy metal stress tolerance of plants. S Afr J Bot 76:167–179. doi:10.1016/j.sajb.2009.10.007
Yamasaki H, Pilon M, Shikanai T (2008) How do plants respond to copper deficiency? Plant Signal Behav 3:231–232. doi:10.4161/psb.3.4.5094
Acknowledgement
We best gratitude to staff of Department of Marine Botany, Department of Marine Biochemistry, Institute of Oceanography, Viet Nam Academy of Science and Technology for providing the necessary facilities to carry out this work. This study was funded by NAFOSTED (106-NN.02-2014.04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, XV., Le-Ho, KH. & Papenbrock, J. Phytochelatin 2 accumulates in roots of the seagrass Enhalus acoroides collected from sediment highly contaminated with lead. Biometals 30, 249–260 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-017-9998-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-017-9998-9