Abstract
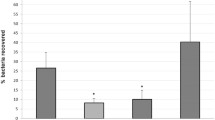
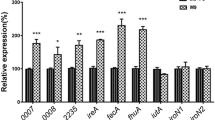
In this work we demonstrate the existence in Vibrio anguillarum 775 (pJM1) of two chromosomal genes encoding outer membrane proteins that operate in the transport of ferric enterobactin. One of them is a novel receptor that we named FetA and the other is the already characterized FvtA that functions in the uptake of iron complexes of both enterobactin and vanchrobactin. Ferric enterobactin transport proficiency was resumed in double mutants for these two genes when they were complemented with either fetA or fvtA, whereas only the cloned fvtA could complement for ferric vanchrobactin transport. Quantitative RT-PCR assays demonstrated that transcription of the fetA gene is regulated by FetR, that is encoded upstream and in reverse orientation from fetA. This gene as well as fetA, are up-regulated in iron limiting condition in a Fur-dependent manner. The two divergent promoters are located in the intergenic region between fetR and fetA that has a putative Fur binding site and an IrgB binding site in the overlapping promoters of fetR and fetA. FetA and FetR show high homology to V. cholerae IrgA and IrgB respectively and the intergenic regions fetA–fetR and irgA–irgB are also highly related suggesting a vertical transmission of the fetA–fetR cluster from V. cholerae to V. anguillarum.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Actis LA, Tolmasky ME, Crosa JH (2011) Vibriosis. In: Woo PTK, Bruno DW (eds) Fish diseases and disorders, vol 3: viral, bacterial, and fungal infections, 2nd edn. CABI International, Oxfordshire, pp 570–605
Alice AF, López CS, Crosa JH (2005) Plasmid- and chromosome-encoded redundant and specific functions are involved in biosynthesis of the siderophore anguibactin in Vibrio anguillarum 775: a case of chance and necessity? J Bacteriol 187:2209–2214
Andrus C, Payne SM (1983) Siderophores and iron regulated proteins in Vibrio and Aeromonas species. Abstr Annu Meet Am Soc Microbiol D 13:61
Balado M, Osorio CR, Lemos ML (2009) FvtA is the receptor for the siderophore vanchrobactin in Vibrio anguillarum: utility as a route of entry for vanchrobactin analogues. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:2775–2783
Crosa JH (1980) A plasmid associated with virulence in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum specifies an iron-sequestering system. Nature 284:566–568
Crosa JH, Hodges LL (1981) Outer membrane proteins induced under conditions of iron limitation in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum 775. Infect Immun 31:223–227
Crosa JH, Walsh CT (2002) Genetics and assembly line enzymology of siderophore biosynthesis in bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:223–249
Di Lorenzo M, Stork M, Tolmasky ME, Actis LA, Farrell D, Welch TJ, Crosa LM, Wertheimer AM, Chen Q, Salinas P, Waldbeser L, Crosa JH (2003) Complete sequence of virulence plasmid pJM1 from the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum strain 775. J Bacteriol 185:5822–5830
Goldberg MB, Boyko SA, Calderwood SB (1990a) Transcriptional regulation by iron of a Vibrio cholerae virulence gene and homology of the gene to the Escherichia coli fur system. J Bacteriol 172:6863–6870
Goldberg MB, DiRita VJ, Calderwood SB (1990b) Identification of an iron-regulated virulence determinant in Vibrio cholerae, using TnphoA mutagenesis. Infect Immun 58:55–60
Goldberg MB, Boyko SA, Calderwood SB (1991) Positive transcriptional regulation of an iron-regulated virulence gene in Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:1125–1129
Lemos ML, Salinas P, Toranzo AE, Barja JL, Crosa JH (1988) Chromosome-mediated iron uptake system in pathogenic strains of Vibrio anguillarum. J Bacteriol 170:1920–1925
Massad G, Arceneaux JE, Byers BR (1991) Acquisition of iron from host sources by mesophilic Aeromonas species. J Gen Microbiol 137:237–241
Morales VM, Backman A, Bagdasarian M (1991) A series of wide-host-range low-copy-number vectors that allow direct screening for recombinants. Gene 97:39–47
Naka H, Crosa JH (2011) Genetic determinants of virulence in the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. Fish Pathol 46:1–10
Naka H, López CS, Crosa JH (2008) Reactivation of the vanchrobactin siderophore system of Vibrio anguillarum by removal of a chromosomal insertion sequence originated in plasmid pJM1 encoding the anguibactin siderophore system. Environ Microbiol 10:265–277
Naka H, López CS, Crosa JH (2010) Role of the pJM1 plasmid-encoded transport proteins FatB, C and D in ferric anguibactin uptake in the fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum. Environ Microbiol Rep 2:104–111
Naka H, Dias GM, Thompson CC, Dubay C, Thompson FL, Crosa JH (2011) Complete genome sequence of the marine fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum harboring the pJM1 virulence plasmid and genomic comparison with other virulent strains of V. anguillarum and V. ordalii. Infect Immun 79:2889–2900
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Sandy M, Han A, Blunt J, Munro M, Haygood M, Butler A (2010) Vanchrobactin and anguibactin siderophores produced by Vibrio sp. DS40M4. J Nat Prod 73:1038–1043
Senanayake SD, Brian DA (1995) Precise large deletions by the PCR-based overlap extension method. Mol Biotechnol 4:13–15
Simon R, Priefer U, Pühler A (1983) A broad host range mobilization system in vivo genetic engineering transposon mutagenesis in gram negative bacteria. Biotechnology 1:787–796
Tolmasky ME, Actis LA, Crosa JH (1988) Genetic analysis of the iron uptake region of the Vibrio anguillarum plasmid pJM1: molecular cloning of genetic determinants encoding a novel trans activator of siderophore biosynthesis. J Bacteriol 170:1913–1919
Tolmasky ME, Wertheimer AM, Actis LA, Crosa JH (1994) Characterization of the Vibrio anguillarum fur gene: role in regulation of expression of the FatA outer membrane protein and catechols. J Bacteriol 176:213–220
Walter MA, Potter SA, Crosa JH (1983) Iron uptake system medicated by Vibrio anguillarum plasmid pJM1. J Bacteriol 156:880–887
Watnick PI, Butterton JR, Calderwood SB (1998) The interaction of the Vibrio cholerae transcription factors, Fur and IrgB, with the overlapping promoters of two virulence genes, irgA and irgB. Gene 209:65–70
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by a Public Health Service grant (AI19018) from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases to J.H.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naka, H., Crosa, J.H. Identification and characterization of a novel outer membrane protein receptor FetA for ferric enterobactin transport in Vibrio anguillarum 775 (pJM1). Biometals 25, 125–133 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-011-9488-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-011-9488-4