Abstract
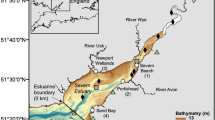
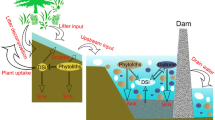
The Scheldt estuary (Belgium/The Netherlands) was sampled along the entire salinity gradient from 2003 to 2005 for silicic acid (DSi), biogenic silica (BSi), suspended particulate matter (SPM) and pigments. Net DSi consumption and/or release within the estuary were investigated by comparing measured DSi concentrations with (fully-transient) model simulations of the concentrations that would have been obtained in case of conservative transport. The DSi consumption was at maximum in May due to diatoms of presumably marine origin blooming in the lower estuary. DSi consumption decreased rapidly in July, probably because of the grazing pressure of copepods also of marine origin, and DSi was released from late summer onwards. Multiple regression analyses showed that most of the BSi did not follow the dynamics of the living diatoms but rather that of the SPM. They also suggested that diatoms were more silicified in the upper estuary than in the lower estuary. Phytoliths were not expected to contribute significantly to the BSi pool. As BSi dynamics strongly differed from those of diatoms and DSi, this study highlighted the importance of taking BSi into account when investigating estuarine silica dynamics. This study also revealed the fundamental role of the coupling between the biogeochemical and ecological functioning of the lower estuary and that of the adjacent coastal zone. This contrasts with the classical consideration that estuaries act as one-way filters for dissolved and particulate material of riverine origin.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSi:
-
(Particulate amorphous) biogenic silica
- BSidet :
-
BSi not associated with living diatoms
- BSiliv :
-
BSi associated with living diatoms
- Chla :
-
Chlorophyll a
- DiatChla :
-
Chla ascribed to diatoms
- DSi:
-
Silicic acid
- POC:
-
Particulate organic carbon
- SPM:
-
Suspended particulate matter
- SPMnbld :
-
SPM not associated with BSi nor with living diatoms
References
Abril G, Nogueira M, Etcheber H, Cabeçadas G, Lemaire E, Brogueira MJ (2002) Behaviour of organic carbon in nine contrasting European estuaries. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 54:241–262
Admiraal W, Breugem P, Jacobs DMLHA, de Ruyter van Steveninck ED (1990) Fixation of dissolved silicate and sedimentation of biogenic silicate in the lower river Rhine during diatom blooms. Biogeochemistry 9:175–185
Anderson GF (1986) Silica, diatoms and a freshwater productivity maximum in Atlantic coastal plain estuaries, Chesapeake Bay. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 22:183–197
Antajan E, Chrétiennot-Dinet M-J, Leblanc C, Daro M-H, Lancelot C (2004) 19′-hexanoyloxyfucoxanthin may not be the appropriate pigment to trace occurrence and fate of Phaeocystis: the case of P. globosa in Belgian coastal waters. J Sea Res 52:165–177
Appeltans W, Hannouti A, Van Damme S, Soetaert K, Vanthomme D, Tackx M (2003) Zooplankton in the Schelde estuary (Belgium/The Netherlands). The distribution of Eurytemora affinis: effect of oxygen? J Plankton Res 25(11):1441–1445
Arndt S (2008) Physical controls on the biogeochemical structure and functioning of a land–ocean transition system. In: Arndt S (ed) Biogeochemical transformations and fluxes in redox-stratified environments: from the shallow coastal ocean to the deep subsurface, chap 6. PhD Thesis, University of Utrecht, Utrecht, pp 147–179
Arndt S, Vanderborght J-P, Regnier P (2007) Diatom growth response to physical forcing in a macrotidal estuary: coupling hydrodynamics, sediment transport, and biogeochemistry. J Geophys Res 112:C05045. doi:10.1029/2006JC003581
Arndt S, Regnier P, Vanderborght J-P (2009) Seasonally-resolved nutrient export fluxes and filtering capacities in a macrotidal estuary. J Mar Syst 78:42–58
Arndt S, Lacroix G, Gypens N, Regnier P, Lancelot C (2011) Nutrient dynamics and phytoplankton development along an estuary–coastal zone continuum: a model study. J Mar Syst 84:49–66
Baeyens W, Van Eck B, Lambert C, Wollast R, Goeyens L (1998) General description of the Scheldt estuary. Hydrobiologia 366:1–14
Beckers O, Wollast R (1976) Comportement de la silice dissoute dans l’estuaire de l’Escaut. In: Nihoul JCJ, Wollast R (eds) Projet Mer, Rapport Final. Volume 10: L’Estuaire de l’Escaut. Services du Premier Ministre, programmation de la Politique Scientifique, Bruxelles, pp 153–170 (in French)
Boschker HTS, Kromkamp JC, Middelburg JJ (2005) Biomarker and carbon isotopic constraints on bacterial and algal community structure and functioning in a turbid, tidal estuary. Limnol Oceanogr 50(1):70–80
Brochard CJE, Koeman RPT, de Keijzer-de Haan AL, Verweij GL, Fockens K, Esselink P (2005) Biomonitoring van fytoplankton in de Nederlandse zoute wateren 2004, kite-diagrammen. Koeman en bijkerk bv, ecologisch onderzoek en advies, Haren (in Dutch)
Carbonnel V (2009) Silica dynamics and retention in the Scheldt tidal river and estuary (Belgium/The Netherlands). PhD Thesis, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgium. http://theses.ulb.ac.be/ETD-db/collection/available/ULBetd-06132009-201603/ (in English, summary in French)
Carbonnel V, Lionard M, Muylaert K, Chou L (2009) Dynamics of dissolved and biogenic silica in the freshwater reaches of a macrotidal estuary (The Scheldt, Belgium). Biogeochemistry 96(1–3):49–72
Cary L, Alexandre A, Meunier J-D, Boeglin J-L, Braun J-J (2005) Contribution of phytoliths to the suspended load of biogenic silica in the Nyong basin rivers (Cameroon). Biogeochemistry 74:101–104
Chen MS, Wartel S, Van Eck B, Van Maldegem D (2005) Suspended matter in the Scheldt estuary. Hydrobiologia 540(1–3):79–104
Chou L, Wollast R (2006) Estuarine silicon dynamics. In: Ittekot V, Unger D, Humborg C, TacAn N (eds) The silicon cycle. Human perturbations and impacts on aquatic systems. SCOPE 66. Island Press, Washington, pp 93–120
Conley DJ (1997) Riverine contribution of biogenic silica to the oceanic silica budget. Limnol Oceanogr 42(4):774–777
Conley DJ, Kilham SS (1989) Differences in silica content between marine and freshwater diatoms. Limnol Oceanogr 34(1):205–213
Conley DJ, Schelske CL, Stoermer EF (1993) Modification of the biogeochemical cycle of silica with eutrophication. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 101:179–192
Dagnelie P (2006) Statistique théorique et appliquée, vol 2, inférence statistique à une et à deux dimensions, 2e édition. Editions De Boeck Université, Bruxelles (in French)
Delstanche S (2004) Contribution à l’étude du cycle biogéochimique de la silice dans le continuum aquatique de l’Escaut. MSc Thesis, Université Catholique de Louvain, Louvain (in French)
DeMaster DJ (1981) The supply and accumulation of silica in the marine environment. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 45:1715–1732
Derry LA, Kurtz AC, Ziegler K, Chadwick OA (2005) Biological control of terrestrial silica cycling and export fluxes to watersheds. Nature 433:728–731
Dijkman NA, Kromkamp JC (2006a) Phospholipid-derived fatty acids as chemotaxonomic markers for phytoplankton: application for inferring phytoplankton composition. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 324:113–125
Dijkman NA, Kromkamp JC (2006b) Photosynthetic characteristics of the phytoplankton in the Scheldt estuary: community and single-cell fluorescence measurements. Eur J Phycol 41(4):425–434
Dixit S, Van Cappellen P, van Bennekom AJ (2001) Processes controlling solubility of biogenic silica and pore water build-up of silicic acid in marine sediments. Mar Chem 73(3–4):333–352
Ehrenhauss S, Witte U, Janssen F, Huettel M (2004) Decomposition of diatoms and nutrient dynamics in permeable North Sea sediments. Cont Shelf Res 24(6):721–737
Elliot M, McLusky DS (2002) The need for definitions in understanding estuaries. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 55:815–827
Fettweis M, Sas M, Monbaliu J (1998) Seasonal, neap–spring and tidal variation of cohesive sediment concentration in the Scheldt estuary, Belgium. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 47:21–36
Gallinari M, Ragueneau O, Corrin L, DeMaster DJ, Treguer P (2002) The importance of water column processes on the dissolution properties of biogenic silica in deep-sea sediments I. Solubility. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66(15):2701–2717
Gazeau F, Gattuso J-P, Middelburg JJ, Brion N, Schiettecatte L-S, Frankignoulle M, Borges AV (2005) Planktonic and whole system metabolism in a nutrient-rich estuary (the Scheldt estuary). Estuaries 28(6):868–883
Geider RJ (1987) Light and temperature dependence of the carbon to chlorophyll a ratio in microalgae and cyanobacteria: implications for physiology and growth of phytoplankton. New Phytol 106:1–34
Humborg C, Pastuszak M, Aigars J, Siegmund H, Mörth C-M, Ittekot V (2006) Decreased silica land–sea fluxes through damming in the Baltic Sea catchment—significance of particle trapping and hydrological alterations. Biogeochemistry 77:265–281
Institut Royal Météorologique de Belgique (IRMB) (2003–2004) Bulletins mensuels, Observations climatologiques, parties I et II. Institut Royal Météorologique de Belgique, Bruxelles (in French/Dutch)
Kamatani A, Oku O (2000) Measuring biogenic silica in marine sediments. Mar Chem 68(3):219–229
Koroleff F (1983) Determination of silicon. In: Grasshoff K, Ehrhardt M, Kremling K (eds) Methods of seawater analysis, 2nd, revised and extended edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 174–187
Kromkamp JC, Peene J (2005) Changes in phytoplankton biomass and primary production between 1991 and 2001in the Westerschelde estuary (Belgium/The Netherlands). Hydrobiologia 540(1–3):117–126
Lacroix G, Ruddick K, Ozer J, Lancelot C (2004) Modelling the impact of the Scheldt and Rhine/Meuse plumes on the salinity distribution in Belgian waters (southern North Sea). J Sea Res 52:149–163
Lancelot C (1995) The mucilage phenomenon in the continental coastal waters of the North Sea. Sci Total Environ 165(1–3):83–102
Lionard M (2006) Spatio-temporal phytoplankton dynamics along the Scheldt-North Sea continuum based on HPLC/CHEMTAX pigment analysis. PhD Thesis, University of Ghent, Ghent
Lionard M, Muylaert K, Van Gansbeke D, Vyverman W (2005) Influence of changes in salinity and light intensity on growth of phytoplankton communities from the Schelde river and estuary (Belgium/The Netherlands). Hydrobiologia 540(1–3):105–115
Lionard M, Muylaert K, Tackx M, Vyverman W (2008a) Evaluation of the performance of HPLC–CHEMTAX analysis for determining phytoplankton biomass and composition in a turbid estuary (Schelde, Belgium). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 76(4):809–817
Lionard M, Muylaert K, Hanouti A, Maris T, Tackx M, Vyverman W (2008b) Inter-annual variability in phytoplankton summer blooms in the freshwater tidal reaches of the Schelde estuary (Belgium). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 79(4):694–700
Llewellyn CA, Fishwick RJ, Blackford JC (2005) Phytoplankton community assemblage in the English Channel: a comparison using chlorophyll a derived from HPLC–CHEMTAX and carbon derived from microscopy cell counts. J Plankton Res 27(1):103–119
Loucaides S, Van Cappellen P, Behrends T (2008) Dissolution of biogenic silica from land to ocean: role of salinity and pH. Limnol Oceanogr 53(4):1614–1621
Mackey MD, Mackey DJ, Higgins HW, Wright SW (1996) CHEMTAX—a program for estimating class abundances from chemical markers: application to HPLC measurements of phytoplankton. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 144:265–283
Maris T, Cox T, Van Damme S, Meire P (2007) Onderzoek naar de gevolgen van het Sigmaplan, baggeractiviteiten en havenuitbreiding in de zeeschelde op het milieu. Geïntegreerd eindverslag van het onderzoek verricht in 2006–2007. Universiteit Antwerpen, Antwerpen (in Dutch/English)
Martin-Jézéquel V, Hildebrand M, Brzezinski MA (2000) Silicon metabolism in diatoms: implications for growth. J Phycol 36:821–840
McLusky DS (1993) Marine and estuarine gradients—an overview. Neth J Aquat Ecol 27(2–4):489–493
Meire P, Ysebaert T, Van Damme S, Van den Bergh E, Maris T, Struyf E (2005) The Scheldt estuary: a description of a changing ecosystem. Hydrobiologia 540(1–3):1–11
Michalopoulos P, Aller RC (2004) Early diagenesis of biogenic silica in the Amazon delta: alteration, authigenic clay formation, and storage. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68(5):1061–1085
Muylaert K, Sabbe K, Vyverman W (2000) Spatial and temporal dynamics of phytoplankton communities in a freshwater tidal estuary (Schelde, Belgium). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 50(5):673–687
Muylaert K, Tackx M, Vyverman W (2005) Phytoplankton growth rates in the freshwater tidal reaches of the Schelde estuary (Belgium) estimated using a simple light-limited primary production model. Hydrobiologia 540(1–3):127–140
Muylaert K, Gonzales R, Franck M, Lionard M, van der Zee C, Cattrijsse A, Sabbe K, Chou L, Vyverman W (2006) Spatial variation in phytoplankton dynamics in the Belgian coastal zone of the North Sea studied by microscopy, HPLC–CHEMTAX and underway fluorescence recordings. J Sea Res 55:253–265
Muylaert K, Sabbe K, Vyverman W (2009) Changes in phytoplankton diversity and community composition along the salinity gradient of the Schelde estuary (Belgium/The Netherlands). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 82:335–340
Ragueneau O, Tréguer P, Leynaert A, Anderson RF, Brzezinski MA, DeMaster DJ, Dugdale RC, Dymond J, Fischer G, Francois R, Heinze C, Maier-Reimer E, Martin-Jézéquel V, Nelson DM, Quéguiner B (2000) A review of the Si cycle in the modern ocean: recent progress and missing gaps in the application of biogenic opal as a paleoproductivity proxy. Glob Planet Chang 26(4):317–365
Ragueneau O, Conley DJ, Leynaert A, Ni Longphuirt S, Slomp CP (2006) Role of diatoms in silicon cycling and coastal marine food webs. In: Ittekot V, Unger D, Humborg C, TacAn N (eds) The silicon cycle. Human perturbations and impacts on aquatic systems. SCOPE 66. Island Press, Washington, pp 163–195
Regnier P, Mouchet A, Wollast R, Ronday R (1998) A discussion of methods for estimating residual fluxes in strong tidal estuaries. Cont Shelf Res 18:1543–1571
Rijstenbil JW, Bakker C, Jackson RH, Merks AGA, de Visscher PRM (1993) Spatial and temporal variation in community composition and photosynthetic characteristics of phytoplankton in the upper Westerschelde estuary (Belgium, SW Netherlands). Hydrobiologia 269(270):263–273
Roubeix V (2007) Transformations biogéochimiques et transfert du silicium dans la zone de transition fleuve-mer : le rôle des diatomées planctoniques. PhD Thesis, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Bruxelles (in French and English)
Roubeix V, Lancelot C (2008) Effect of salinity on growth, cell size and silicification of an euryhaline freshwater diatom: Cyclotella meneghiniana Kütz. Transit Water Bull 1:31–38
Roubeix V, Becquevort S, Lancelot C (2008) Influence of bacteria and salinity on diatom biogenic silica dissolution in estuarine systems. Biogeochemistry 88(1):47–62
Rousseau V, Leynaert A, Daoud N, Lancelot C (2002) Diatom succession, silicification and silicic acid availability in Belgian coastal waters (Southern North Sea). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 236:61–73
Sicko-Goad LM, Schelske CL, Stoermer EF (1984) Estimation of intracellular carbon and silica content of diatoms from natural assemblages using morphometric techniques. Limnol Oceanogr 29(6):1170–1178
Soetaert K, Herman PMJ (1995) Estimating estuarine residence times in the Westerschelde (The Netherlands) using a box model with fixed dispersion coefficients. Hydrobiologia 311:215–224
Soetaert K, Van Rijswijk P (1993) Spatial and temporal patterns of the zooplankton in the Westerschelde estuary. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 97:47–59
Soetaert K, Herman PMJ, Kromkamp JC (1994) Living in the twilight: estimating net phytoplankton growth in the Westerschelde estuary (The Netherlands) by means of an ecosystem model (MOSES). J Plankton Res 16:1277–1301
Soetaert K, Hoffmann M, Meire P, Starink M, van Oevelen D, Van Regenmortel S, Cox T (2004) Modeling growth and carbon allocation in two reed beds (Phragmites australis) in the Scheldt estuary. Aquat Bot 79:211–234
Soetaert K, Middelburg JJ, Heip C, Meire P, Van Damme S, Maris T (2006) Long-term change in dissolved inorganic nutrients in the heterotrophic Scheldt estuary (Belgium, The Netherlands). Limnol Oceanogr 51(1, part 2):409–423
Struyf E, Van Damme S, Gribsholt B, Middelburg JJ, Meire P (2005) Biogenic silica in tidal freshwater marsh sediments and vegetation (Schelde estuary, Belgium). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 303:51–60
Tackx M, Azémar F, Boulêtreau S, De Pauw N, Bakker K, Sautour B, Gasparini S, Soetaert K, Van Damme S, Meire P (2005) Zooplankton in the Schelde estuary, Belgium and The Netherlands: long-term trends in spring populations. Hydrobiologia 540:275–278
Temmerman S, Govers G, Wartel S, Meire P (2003) Spatial and temporal factors controlling short-term sedimentation in a salt and freshwater tidal marsh, Scheldt estuary, Belgium, SW Netherlands. Earth Surf Process Landf 28:739–755
Tréguer P, Pondaven P (2000) Silica control of carbon dioxide. Nature 406:358–359
Tréguer P, Nelson DM, Van Bennekom AJ, DeMaster DJ, Leynaert A, Quéguiner B (1995) The silica balance in the world ocean: a reestimate. Science 268:375–379
Uncles RJ, Stephens JA, Smith RE (2002) The dependence of estuarine turbidity on tidal intrusion length, tidal range and residence time. Cont Shelf Res 22(11–13):1835–1856
Van Damme S, Struyf E, Maris T, Ysebaert T, Dehairs F, Tackx M, Heip C, Meire P (2005) Spatial and temporal patterns of water quality along the estuarine salinity gradient of the Scheldt estuary (Belgium and The Netherlands): results of an integrated monitoring approach. Hydrobiologia 540(1–3):29–45
Van der Zee C, Chou L (2005) Seasonal cycling of phosphorus in the Southern Bight of the North Sea. Biogeosciences 2:27–42
Van der Zee C, Roevros N, Chou L (2007) Phosphorus speciation, transformation and retention in the Scheldt estuary (Belgium/The Netherlands) from the freshwater tidal limits to the North Sea. Mar Chem 106(1–2):76–91
Van Maldegem DC, Mulder HPJ, Langerak A (1993) A cohesive sediment balance for the Scheldt Estuary. Neth J Aquat Ecol 27(2–4):247–256
Vanderborght J-P, Wollast R, Loijens M, Regnier P (2002) Application of a transport-reaction model to the estimation of biogas fluxes in the Scheldt estuary. Biogeochemistry 59:207–237
Verlaan PAJ, Donze M, Kuik P (1998) Marine vs fluvial suspended matter in the Scheldt estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 46:873–883
Wollast R (1978) Modelling of biological and chemical processes in the Scheldt estuary. In: Nihoul JCJ (ed) Hydrodynamics of Estuaries and Fjords. Elsevier Oceanography Series, vol 23. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 63–77
Wollast R, De Broeu F (1971) Study of the behavior of dissolved silica in the estuary of the Scheldt. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 35:613–620
Wright SW, Jeffrey SW (1997) High-resolution HPLC system for chlorophylls and carotenoids of marine phytoplankton. In: Jeffrey SW, Mantoura RFC, Wright SW (eds) Phytoplankton pigments in oceanography: guidelines to modern methods. UNESCO Publishing, Paris, pp 327–341
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Michaël Tsagaris, Laura Rebreanu and Nathalie Roevros for their assistance in field sampling. Laure-Sophie Schiettecatte (Unité d’Océanographie Chimique, Université de Liège) is acknowledged for sampling of the “Ste Anna” station. POC concentrations were measured by Nathalie Roevros, and BSi concentrations in June–July 2003 by Séverine Delstanche. Pierre Regnier, Damien Cardinal and Koenraad Muylaert commented on a previous version of the manuscript. We are grateful to the officers and crewmembers of the RV Belgica for their assistance during the various sampling campaigns in the Scheldt estuary. Water discharge data were provided by the Flanders Hydraulics Research, Hydrological Information Centre. DSi concentrations from various databases were used in this work: OMES data from the “Onderzoek naar de Milieu-Effecten van het Sigmaplan” project that were produced either by Universiteit Antwerpen (UA) or by Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB), and SISCO data from the SISCO project that were published elsewhere (Carbonnel et al. 2009). This study was financed in the framework of the SISCO project by the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office (BELSPO) under contract number EV/11/17A. Additional funding was provided by the Belgian French Community (convention number FRFC 2.4579.04) and by the TIMOTHY project financed by BELSPO (Interuniversity Attraction Pole, IAP 6/13). This is also a contribution to the FP7 GEOCARBON project (Contract No. 283080) funded by the European Union. Leila J. Hamdan (Associated Editor) and two anonymous reviewers are acknowledged for their constructive comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carbonnel, V., Vanderborght, JP., Lionard, M. et al. Diatoms, silicic acid and biogenic silica dynamics along the salinity gradient of the Scheldt estuary (Belgium/The Netherlands). Biogeochemistry 113, 657–682 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-012-9796-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-012-9796-y