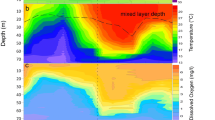
Abstract
Trophodynamics of meso-zooplankton in the North Sea (NS) were assessed at a site in the southern NS, and at a shallow and a deep site in the central NS. Offshore and neritic species from different ecological niches, including Calanus spp., Temora spp. and Sagitta spp., were collected during seven cruises over 14 months from 2007 to 2008. Bulk stable isotope (SI) analysis, phospholipid-derived fatty acid (PLFA) compositions, and δ 13CPLFA data of meso-zooplankton and particulate organic matter (POM) were used to describe changes in zooplankton relative trophic positions (RTPs) and trophodynamics. The aim of the study was to test the hypothesis that the RTPs of zooplankton in the North Sea vary spatially and seasonally, in response to hydrographic variability, with the microbial food web playing an important role at times. Zooplankton RTPs tended to be higher during winter and lower during the phytoplankton bloom in spring. RTPs were highest for predators such as Sagitta sp. and Calanus helgolandicus and lowest for small copepods such as Pseudocalanus elongatus and zoea larvae (Brachyura). δ 15NPOM-based RTPs were only moderate surrogates for animals’ ecological niches, because of the plasticity in source materials from the herbivorous and the microbial loop food web. Common (16:0) and essential (eicosapentaenoic acid, EPA and docosahexaenoic acid, DHA) structural lipids showed relatively constant abundances. This could be explained by incorporation of PLFAs with δ 13C signatures which followed seasonal changes in bulk δ 13CPOM and PLFA δ 13CPOM signatures. This study highlighted the complementarity of three biogeochemical approaches for trophodynamic studies and substantiated conceptual views of size-based food web analysis, in which small individuals of large species may be functionally equivalent to large individuals of small species. Seasonal and spatial variability was also important in altering the relative importance of the herbivorous and microbial food webs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham WR, Hesse C, Pelz O (1998) Ratios of carbon isotopes in microbial lipids as an indicator of substrate usage. Appl Environ Microb 64(11):4202–4209
Azam F, Fenchel T, Field JG, Gray JS, Meyer-Reil L-A, Thingstad F (1983) The ecological role of water-column microbes in the sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 10:257–263
Backhaus JO, Harms IH, Krause M, Heath MR (1994) An hypothesis concerning the space-time succession of Calanus finmarchicus in the northern North Sea. ICES J Mar Sci 51:169–180
Baines SB, Pace ML (1991) The production of dissolved organic matter by phytoplankton and its importance to bacteria: patterns across marine and freshwater systems. Limnol Oceanogr 36(6):1078–1090
Beaugrand G, Brander KM, Lindley JA, Souissi S, Reid PC (2003) Plankton effect on cod recruitment in the North Sea. Nature 426:661–664
Bequevort S, Rousseau V, Lancelot C (1998) Major and comparable roles of free-living and attached bacteria in the degradation of Phaeocystis-derived organic matter in Belgian Coastal waters of the North Sea. Aquat Microb Ecol 14:39–48
Bergé J-P, Barnathan G (2005) Fatty acids from lipids of marine organisms: molecular biodiversity, roles as biomarkers of biologically active compounds, and economical aspects. Adv Biochem Eng Biot 96:49–125
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Phys 37(8):911–917
Bonnet D, Richardson A, Harris RP, Hirst A, Beaugrand G, Edwards M, Ceballos S, Diekman R, López-Urrutia A, Valdes L, Carlotti F, Molinero JC, Weikert H, Greve W, Lucic D, Albaina A, Yahia ND, Umani SF, Miranda A, dos Santos A, Cook K, Robinson S, Fernandes de Puelles ML (2005) An overview of Calanus helgolandicus ecology in European waters. Prog Oceanogr 65:1–53
Boschker HTS, Middelburg JJ (2002) Stable isotopes and biomarkers in microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 40:85–95
Boschker HTS, de Brouwer JFC, Cappenberg TE (1999) The contribution of macrophyte-derived organic matter to microbial biomass in salt-marsh sediments: stable isotope analysis of microbial biomarkers. Limnol Oceanogr 44(2):309–319
Boschker HTS, Kromkamp JC, Middelburg JJ (2005) Biomarker and carbon isotopic constraints on bacterial and algal community structure and functioning in a turbid, tidal estuary. Limnol Oceanogr 50(1):70–80
Brett MT, Müller-Navarra DC (1997) The role of highly unsaturated fatty acids in aquatic foodweb processes. Freshw Biol 38:483–499
Brown J, Hill AE, Fernand L, Horsburgh KJ (1999) Observations of a seasonal jet-like circulation at the central North Sea cold pool margin. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 48:343–355
Bundy MH, Vandeploeg HA, Lavrentyev PJ, Kovalcik PA (2005) The importance of microzooplankton versus phytoplankton to copepod populations during late winter and early spring in Lake Michigan. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 62:2371–2385
Burkhardt S, Riebesell U, Zondervan I (1999a) Effects of growth rate, CO2 concentration, and cell size on the stable carbon isotope fractionation in marine phytoplankton. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63(22):3729–3741
Burkhardt S, Riebesell U, Zondervan I (1999b) Stable carbon isotope fractionation by marine phytoplankton in response to daylength, growth rate, and CO2 availability. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 184:31–41
Cabana G, Rasmussen JB (1996) Comparison of aquatic food chains using nitrogen isotopes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10844–10847
Calbet A (2001) Mesozooplankton grazing effect on primary production: a global comparative analysis in marine ecosystems. Limnol Oceanogr 46(7):1824–1830
Calbet A, Carlotti F, Gaudy R (2007) The feeding ecology of the copepod Centropages typicus (Kröyer). Progr Oceanogr 72:137–150
Canuel EA, Cloern JE, Ringelberg DB, Guckert JB, Rau GH (1995) Molecular and isotopic tracers used to examine sources organic matter and its incorporation into the food webs of San Francisco Bay. Limnol Oceanogr 40(1):67–81
Carlotti F, Bonnet D, Halsband-Lenk C (2007) Development and growth of Centropages typicus. Progr Oceanogr 72:164–195
Cifuentes LA, Salata GG (2001) Significance of carbon isotope discrimination between bulk carbon and extracted phospholipid fatty acids in selected terrestrial and marine environments. Org Geochem 32:613–621
Clarke KR, Gorley RN (2006) PRIMER v6: user manual/tutorial. PRIMER-E Ltd., Plymouth
Cloern JE (1996) Phytoplankton bloom dynamics in coastal ecosystems: a review with some general lessons from sustained investigation of San Francisco Bay, California. Rev Geophys 34(2):127–168
Cushing DH (1989) A difference in structure between ecosystems in strongly stratified waters and in those that are only weakly stratified. J Plankton Res 11(1):1–13
Dalpadado J, Ellertsen B, Melle W, Dommasnes A (2000) Food and feeding conditions of Norwegian spring-spawning herring (Clupea harengus) through its feeding migrations. ICES J Mar Sci 57(4):843–857
Dalsgaard J, St. John M, Kattner G, Müller-Navarra DC, Hagen W (2003) Fatty acid trophic markers in the pelagic marine environment. Adv Mar Biol 6:225–340
Das K, Lepoint G, Leroy Y, Bouquegneau J (2003) Marine mammals from the southern North Sea: feeding ecology data from δ 13C and δ 15N measurements. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 263:287–298
de Laender F, van Oevelen D, Soetaert K, Middelburg JJ (2010) Carbon transfer in a herbivore- and a microbial loop-dominated pelagic food web in the southern Barents Sea during spring and summer. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 398:93–107
Edwards M, Richardson AJ (2004) Impact of climate change on marine pelagic phenology and trophic mismatch. Nature 430:881–884
Edwards M, John AWG, Hunt HG, Lindley JA (1999) Exceptional influx of oceanic species into the North Sea. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 79:737–739
Eisma D, Kalf J (1987) Distribution, organic content and particle size of suspended matter in the North Sea. Neth J Sea Res 21(4):265–285
Elifantz H, Malmstrom RR, Cottrell MT, Kirchman DL (2005) Assimilation of polysaccharides and glucose by major bacterial groups in the Delaware Estuary. Appl Environ Microb 71(12):7799–7805
El-Sabaawi R, Dower JF, Kainz M, Mazumder A (2009) Characterizing dietary variability and trophic positions of coastal calanoid copepods: insight from stable isotopes and fatty acids. Mar Biol 156:225–237
Engel A, Goldthwait S, Passow U, Alldredge A (2002) Temporal decoupling of carbon and nitrogen dynamics in a mesocosm diatom bloom. Limnol Oceanogr 47(3):753–761
Evershed RP, Bull ID, Corr LT, Crossman ZM, van Dongen B, Evans CJ, Jim S, Mottram HR, Mukherjee AJ, Pancost RD (2007) Compound-specific stable isotope analysis in ecology and paleoecology. In: Lajtha K, Michener RH (eds) Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental science. Blackwell, London, pp 480–540
Falkowski PG (1991) Species variability in the fractionation of δ 13C and δ 12C by marine phytoplankton. J Plankton Res 13(Suppl):21–28
Falkowski PG, Katz ME, Knoll AH, Quigg A, Raven JA, Schofield O, Taylor FJR (2004) The evolution of modern eukaryotic phytoplankton. Science 305:354–360
Farkas T (1979) Adaptation of fatty acid compositions to temperature—a study on planktonic crustaceans. Comp Biochem Phys B 64:71–76
Fenchel T (1984) Suspended marine bacteria as a food source. In: Fasham MJR (ed) Flows of energy and materials in marine ecosystems—theory and practice. Plenum, New York, pp 301–316
Fenchel T (1988) Marine plankton food chains. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 19:19–38
Fennel W, Neumann T (2001) Coupling biology and oceanography in models. Ambio 30(4/5):232–236
Fessenden L, Cowles TJ (1994) Copepod predation on phagotrophic ciliates in Oregon coastal waters. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 107:103–111
Fichez R, Dennis P, Fontaine MF, Jickells TD (1993) Isotopic and biochemical composition of particulate organic matter in a shallow water estuary (Great Ouse, North Sea, England). Mar Chem 43:263–276
Field JG, Clarke KR, Warwick RM (1982) A practical strategy for analysing multispecies distribution patterns. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 8:37–52
Fransz HG, Colebrook JM, Gamble JC, Krause M (1991) The zooplankton of the North Sea. Neth J Sea Res 28(1/2):1–52
Fry B (2006) Stable isotope ecology. Springer, New York
Fry B, Wainwright SC (1991) Diatom sources of 13C-rich carbon in marine food webs. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 76:149–157
Gentsch E, Kreibich T, Hagen W, Niehoff B (2009) Dietary shifts in the copepod Temora longicornis during spring: evidence from stable isotope signatures, fatty acid biomarkers and feeding experiments. J Plankton Res 31(1):45–60
Graeve M, Dauby P, Scailteur Y (2001) Combined lipid, fatty acid and digestive tract content analysis: a penetrating approach to estimate feeding of Antarctic amphipods. Polar Biol 24(11):852–862
Graeve M, Albers C, Kattner G (2005) Assimilation and biosynthesis of lipids in Arctic Calanus species based on feeding experiments with a 13C labelled diatom. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 317:109–125
Greenwood N, Parker ER, Fernand L, Sivyer DB, Weston K, Painting SJ, Kröger S, Lees HE, Mills DK, Laane RWPM (2009) Detection of low bottom water oxygen concentrations in the North Sea; implications for monitoring and assessment of ecosystem health. Biogeosci Dis 6:8411–8453
Hagen W, Auel H (2001) Seasonal adaptations and the role of lipids in the oceanic zooplankton. Zoology 104:312–326
Halsband-Lenk C, Hirche H-J, Carlotti F (2002) Temperature impact on reproduction and development of congener copepod population. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 271:121–153
Harwood AJP, Dennis PF, Marca AD, Pilling GM, Millner RS (2008) The oxygen isotope composition of water masses within the North Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 78:353–359
Helaouët P, Beaugrand G (2007) Macroecology of Calanus finmarchicus and C. helgolandicus in the North Atlantic Ocean and adjacent seas. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 345:147–165
Hobson KA (1999) Tracing origins and migration of wildlife using stable isotopes: a review. Oecologia 120:314–326
Hobson KA, Welch HE (1992) Determination of trophic relationships within a high Arctic marine food web using δ 13C and δ 15N analysis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 84:9–18
Irigoien X, Flynn KJ, Harris RP (2005) Phytoplankton blooms: a ‘loophole’ in microzooplankton grazing impact. J Plankton Res 27(4):313–321
Jennings S (2005) Size-based analysis of aquatic food webs. In: Belgrano A, Scharler UM, Dunne J, Ulanovicz RE (eds) Aquatic food webs: an ecosystem approach. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 86–97
Jennings S, Pinnegar JK, Polunin NVC, Boon TW (2001) Weak cross-species relationships between body size and trophic level belie powerful size-based trophic structuring in fish communities. J Anim Ecol 70:934–944
Jennings S, Greenstreet SPR, Hill L, Piet GJ, Pinnegar JK, Warr KJ (2002) Long-term trends in the trophic structure of the North Sea fish community: evidence from stable-isotope analysis, size-spectra and community metrics. Mar Biol 141:1085–1097
Käkela A, Crane J, Votier S, Furness RW, Käkela R (2006) Fatty acid signatures as indicators of diet in great skuas Stercorarius skua, Shetland. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 319:297–310
Kattner G, Krause M (1989) Seasonal variation of lipids (wax esters, fatty acids and alcohols) in Calanoid copepods from the North Sea. Mar Chem 26:261–275
Kattner G, Gerken G, Eberlein K (1983) Development of lipids during a spring phytoplankton bloom in the northern North Sea. I. Particulate fatty acids. Mar Chem 14(2):149–162
Klein Breteler WCM, Schogt N, Rampen S (2005) Effect of diatom nutrient limitation on copepod development: role of essential lipids. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 291:125–133
Koch PL (2007) Isotopic study of the biology of modern and fossil vertebrates. In: Lajtha K, Michener RH (eds) Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental science. Blackwell, London, pp 99–154
Kürten B (2010) An end-to-end study of spatial differences in North Sea food webs. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, pp 93–129
Laevastu T (1963) Surface water types of the North Sea and their characteristics. Ser Atlas Mar Environ Folio 4:1–5
Lancelot C, Billen G (1985) Carbon–nitrogen relationships in nutrient metabolism of coastal marine ecosystems. In: Jannash HW, Williams PJ (eds) Advances in aquatic microbiology 3. Academic, London, pp 263–321
Landry MR (2002) Integrating classical and microbial food web concepts: evolving views from the open-ocean tropical Pacific. Hydrobiologia 480:29
Landry MR, Calbet A (2004) Microzooplankton production in the oceans. ICES J Mar Sci 61:501–507
Lawrence SG, Ahmad A, Azam F (1993) Fate of particle-bound bacteria ingested by Calanus pacificus. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 97:299–307
Laws EA, Popp BN, Bidigare RR, Kennicutt MC, Macko SA (1995) Dependence of phytoplankton carbon composition on growth rate and [CO2]aq; theoretical considerations and experimental results. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59(6):1131–1138
Lebour MV (1922) The food of plankton organisms. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 12(4):644–677
Lee RF, Nevenzel JC, Paffenhöfer GA (1971) Importance of wax esters and other lipids in the marine food chain: phytoplankton and copepods. Mar Biol 9:99–108
Lee RF, Hagen W, Kattner G (2006) Lipid storage in marine zooplankton. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 307:273–306
Legendre L, Rassoulzadegan F (1995) Plankton and nutrient dynamics in marine waters. Ophelia 41:153–172
Mackinson S, Daskalov G, Heymans JJ, Neira S, Arancibia H, Zetina-Rejòn M, Jiang H, Coll M, Arreguin-Sanchez F, Keeble K, Shannon L (2009) Which forcing factors fit? Using ecosystem models to investigate the relative influence of fishing and changes in primary productivity on the dynamics of marine ecosystems. Eco Model 220(21):2972–2987
Michener RH, Kaufman L (2007) Stable isotope ratios as tracers in marine food webs: an update. In: Lajtha K, Michener RH (eds) Stable isotopes in ecology and environmental science. Blackwell, London, pp 238–282
Middelburg JJ, Herman PMJ (2007) Organic matter processing in tidal estuaries. Mar Chem 106:127–147
Middelburg JJ, Nieuwenhuize J (1998) Carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes in suspended matter and sediments from the Schelde estuary. Mar Chem 60:217–225
Minagawa M, Wada E (1984) Stepwise enrichment of 15N along food chains: further evidence and the relation between δ 15N and animal age. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:1135–1140
Mintenbeck K, Brey T, Jacob U, Knust R, Struck U (2008) How to account for the lipid effect on carbon stable-isotope ratio (δ 13C): sample treatment effects. J Fish Biol 72:815–830
Nedwell DB, Dong LF, Sage A, Underwood GJC (2002) Variations of the nutrients loads to the mainland UK estuaries: correlation with catchment areas, urbanization and coastal eutrophication. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 54:951–970
Otto L, Zimmermann JTF, Furnes GK, Mork MSR, Becker G (1990) Review of the physical oceanography of the North Sea. Neth J Sea Res 26(2–4):161–238
Painting SJ, Lucas MI, Peterson WT, Brown PC, Hutchings L, Mitchell-Innes BA (1993) Dynamics of bacterioplankton, phytoplankton and mesozooplankton communities during the development of an upwelling bloom in the southern Benguela. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 100:35–53
Pancost RD, Freeman KH, Wakeham SG (1999) Controls on the carbon-isotopic compositions of compounds in Peru surface waters. Org Geochem 30:319–340
Peters J, Renz J, van Beusekom JEE, Boersma M, Hagen W (2006) Trophodynamics and seasonal cycle of the copepod Pseudocalanus acuspes in the Central Baltic Sea (Bornholm Basin) evidence from lipid composition. Mar Biol 149:1417–1429
Peterson BJ, Fry B (1987) Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 18:293–320
Petursdottir H, Gislason A, Falk-Petersen S, Hop H, Svavarsson J (2008) Trophic interactions of the pelagic ecosystem over the Reykjanes Ridge as evaluated by fatty acid and stable isotope analyses. Deep-Sea Res Pt II 55:83–93
Pomeroy LR (2001) Caught in the food web: complexity made simple? Sci Mar 65(2):31–40
Post DM (2002) Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology 83(3):703–718
Rau GH, Riebesell U, Wolf-Gladrow D (1996) A model of photosynthetic 13C fractionation by marine phytoplankton based on diffusive molecular CO2 uptake. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 133:275–285
Riebesell U (1991) Particle aggregation during a diatom bloom. II. Biological aspects. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 69:281–291
Riebesell U, Revill AT, Holdsworth DG, Volkman JK (2000) The effects of varying CO2 concentration on lipid composition and carbon isotope fractionation in Emiliania huxleyi. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64(2):4179–4192
Rolff C (2000) Seasonal variation in δ 13C and δ 15N of size fractionated plankton at a coastal station in the northern Baltic proper. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 203:47–65
Rothschild BJ (1998) Year class strengths of zooplankton in the North Sea and their relation to cod and herring abundance. J Plankton Res 20(9):1721–1741
Schmidt K, Atkinson A, Stübing D, McClelland JW, Montoya JP, Voss M (2003) Trophic relationship among Southern Ocean copepod and krill: Some uses and limitations of a stable isotope approach. Limnol Oceanogr 48(1):277–289
Schouten S, Klein Breteler WCM, Blokker P, Schogt N, Rijpstra WIC, Grice K, Baas M, Damsté JSS (1998) Biosynthetic effects on the stable carbon isotopic composition of algal lipids: Implications for deciphering the carbon isotopic biomarker record. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 62(8):1397–1406
Smith BN, Epstein S (1971) Two categories of 13C/12C ratios for higher plants. Plant Physiol 47:380–384
Soreide JE, Hop H, Carroll ML, Falk-Petersen S, Hegseth EN (2006) Seasonal food web structures and sympagic–pelagic coupling in the European Arctic revealed by stable isotopes and a two-source food web model. Prog Oceanogr 71:59–87
Soreide JE, Falk-Petersen S, Hegseth EN, Hop H, Carroll ML, Hobson K, Blachowiak-Samolyk K (2008) Seasonal feeding strategies of Calanus in the high-Arctic Svalbard region. Deep-Sea Res Pt II 55:2225–2244
Spokes LJ, Jickells TD (2005) Is the atmosphere really an important source of reactive nitrogen to coastal waters? Cont Shelf Res 25:2022–2035
St. John M, Lund T (1996) Lipid biomarkers: linking the utilization of frontal plankton biomass to enhanced conditions of juvenile North Sea cod. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 131:75–85
Sterner RW, Schulz ZL (1998) Zooplankton nutrition: recent progress and a reality check. Aquat Ecol 32:261–279
Stoecker DK (1999) Mixotrophy among dinoflagellates. J Eukaryot Microbiol 46(4):397–401
Suratman S, Weston K, Jickells TD, Fernand L (2009) Spatial and seasonal changes of dissolved and particulate organic C in the North Sea. Hydrobiologia 628:13–25
Sweeting CJ, Jennings S, Polunin NVC (2005) Variance in isotopic signatures as a descriptor of tissue turnover and degree of omnivory. Funct Ecol 19:777–784
Tamelander T, Renaud PE, Hop H, Carroll ML, Ambrose WG Jr, Hobson KA (2006a) Trophic relationships and pelagic-benthic coupling during summer in the Barent Sea marginal ice zone, revealed by stable carbon and nitrogen isotope measurement. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 310:33–46
Tamelander T, Soreide JE, Hop H, Carroll ML (2006b) Fractionation of stable isotopes in the Arctic marine copepod Calanus glacialis: Effects on the isotopic composition of marine particulate organic matter. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 333(2):231–240
Tamelander T, Reigstad M, Hop H, Carroll ML, Wassmann P (2008) Pelagic and sympagic contribution of organic matter to zooplankton and vertical export in the Barents Sea marginal ice zone. Deep-Sea Res Pt II 55:2330–2339
Tamelander T, Kivimäe C, Bellerby RGJ, Kristiansen S (2009) Base-line variations in stable isotope values in an Arctic marine ecosystem: effects of carbon and nitrogen uptake by phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 630:63–73
Van den Meersche K, Middelburg JJ, Soetaert K, van Rijswijk P, Boschker HTS, Heip CHR (2004) Carbon-nitrogen coupling and algal-bacterial interactions during an experimental bloom: Modelling a 13C tracer experiment. Limnol Oceanogr 49(3):862–878
van Raaphorst W, Phillipart CJM, Smit JPC, Dijkstra FJ, Malschaert JFP (1998) Distribution of suspended particulate matter in the North Sea as inferred from NOAA/AVHRR reflectance images and in situ observations. J Sea Res 39:197–215
Vargas CA, González HE (2004) Plankton community structure and carbon cycling in a coastal upwelling system. I. Bacteria, microprotozoans and phytoplankton in the diet of copepods and appendicularians. Aquat Microb Ecol 34:151–164
Vargas CA, Martinez RA, Cuevas LA, Pavez M, Cartes C, González HE, Escribano R, Daneri G (2007) The relative importance of microbial and classical food webs in a highly productive upwelling area. Limnol Oceanogr 52(4):1495–1510
Virtue P, Mayzaud P, Albessard E, Nichols P (2000) Use of fatty acids as dietary indicators in northern krill, Meganyctiphanes norvegica, from northeastern Atlantic, Kattegat, and Mediterranean waters. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 57(3):104–114
Viso A-C, Marty J-C (1993) Fatty acids from 28 marine microalgae. Phytochemistry 34(6):1521–1533
Werner EE, Gilliam JF (1984) The ontogenetic niche and species interactions in size-structured populations. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 15:393–425
Weston K, Jickells TD, Fernand L, Parker ER (2004) Nitrogen cycling in the southern North Sea: consequences for total nitrogen transport. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 59:559–573
Williams R, Conway DVP, Hunt HG (1994) The role of copepods in the planktonic ecosystem of mixed and stratified waters of the European shelf seas. Hydrobiologia 292(293):521–530
Yang J (1982) A tentative analysis of the trophic levels of North Sea Fish. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 7:247–252
Yoon HS, Hackett JD, Bhattacharya D (2002) A single origin of the peridinin- and fucoxanthin-containing plastids in dinoflagellates through tertiary endosymbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(18):11724–11729
Zhao J, Ramin M, Cheng V, Arhonditsis GB (2008) Plankton community patterns across a trophic gradient: the role of zooplankton functional groups. Ecol Model 213:417–436
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the EURopean network of excellence for OCean Ecosystems ANalysiS (EUR-OCEANS) funded by the European Commission [project WP6-SYSNS-1098]. The field work was partially funded by the Centre for Environment, Fisheries and Aquaculture Science (CEFAS) and the Centre for Estuarine and Marine Ecology, Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW). We thank C. Vignot for preparatory assistance and M. Houtekamer, P. van Rijswijk, P. van Breugel and A. Knuijt for analytical support. We thank two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kürten, B., Painting, S.J., Struck, U. et al. Tracking seasonal changes in North Sea zooplankton trophic dynamics using stable isotopes. Biogeochemistry 113, 167–187 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-011-9630-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-011-9630-y