Abstract
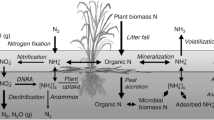
Nitrogen (N) dynamics at the sediment–water interface were examined in four regions of Florida Bay to provide mechanistic information on the fate and effects of increased N inputs to shallow, subtropical, coastal environments. Dissimilatory nitrate (NO3 −) reduction to ammonium (DNRA) was hypothesized to be a significant mechanism retaining bioreactive N in this warm, saline coastal ecosystem. Nitrogen dynamics, phosphorus (P) fluxes, and sediment oxygen demand (SOD) were measured in north-central (Rankin Key; eutrophic), north-eastern (Duck Key; high N to P seston ratios), north-western (Murray Key; low N to P ratios), and central (Rabbit Key; typical central site) Florida Bay in August 2004, January 2005, and November 2006. Site water was passed over intact sediment cores, and changes in oxygen (O2), phosphate (o-PO4 3−), ammonium (NH4 +), NO3 −, nitrite (NO2 −), and N2 concentrations were measured, without and with addition of excess 15NO3 − or 15NH4 + to inflow water. These incubations provided estimates of SOD, nutrient fluxes, N2 production, and potential DNRA rates. Denitrification rates were lowest in summer, when SOD was highest. DNRA rates and NH4 + fluxes were high in summer at the eutrophic Rankin site, when denitrification rates were low and almost no N2 came from added 15NO3 −. Highest 15NH4 + accumulation, resulting from DNRA, occurred at Rabbit Key during a picocyanobacteria bloom in November. 15NH4 + accumulation rates among the stations correlated with SOD in August and January, but not in November during the algal bloom. These mechanistic results help explain why bioreactive N supply rates are sometimes high in Florida Bay and why denitrification efficiency may decrease with increased NO3 − inputs in sub-tropical coastal environments.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
An S, Gardner WS (2002) Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) as a nitrogen “link”, versus denitrification as a “sink” in a shallow estuary (Laguna Madre/Baffin Bay, Texas). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 237:41–50. doi:10.3354/meps237041
An S, Gardner WS, Kana T (2001) Simultaneous measurement of denitrification and nitrogen fixation using isotope pairing with membrane inlet mass spectrometry analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1171–1178. doi:10.1128/AEM.67.3.1171-1178.2001
Bianchi TS, Pennock JR, Twilley RR (eds) (1999) Biogeochemistry of Gulf of Mexico Estuaries. John Wiley Inc., New York, p 428
Boyer JN, Fourqurean JW, Jones RD (1997) Spatial characterization of water quality in Florida Bay and Whitewater Bay by multivariate analysis: zones of similar influence (ZSI). Estuaries 20:743–758. doi:10.2307/1352248
Boyer JN, Fourqurean JW, Jones RD (1999) Seasonal and long-term trends in the water quality of Florida Bay (1989–1997). Estuaries 22:417–430. doi:10.2307/1353208
Brunet RC, Garcia-Gil LJ (1996) Sulfide-induced dissimilitory nitrate reduction to ammonia in anaerobic freshwater sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 21:131–138. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.1996.tb00340.x
Burgin AJ, Hamilton SK (2007) Have we overemphasized the role of denitrification in aquatic ecosystems? A review of nitrate removal pathways. Rev Ecol Soc Am 5(2):89–96. www.frontiersinecology.org
Christensen PL, Rysgaard S, Sloth NP, Dalsgaard T, Schwaerter S (2000) Sediment mineralization, nutrient fluxes, denitrification and dissimilatgory nitrate reduction to ammonium in an estuarine fjord with sea cage trout farms. Aquat Microb Ecol 21:73–84. doi:10.3354/ame021073
Cornwell JC, Kemp WM, Kana TM (1999) Denitrification in coastal ecosystems: methods, environmental controls, and ecosystem level controls, a review. Aquat Ecol 33:41–54. doi:10.1023/A:1009921414151
Cotner JB, Sada RH, Bootsma H, Johengen T, Cavaletto JF, Gardner WS (2000) Nutrient limitation of heterotrophic bacteria in Florida Bay. Estuaries 23:611–620. doi:10.2307/1352888
Dalsgaard T, Thamdrup B (2002) Factors controlling anaerobic ammonium oxidation with nitrite in marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3802–3808. doi:10.1128/AEM.68.8.3802-3808.2002
Fourqurean JW, Robblee MB (1999) Florida Bay: a history of recent ecological changes. Estuaries 22:345–357. doi:10.2307/1353203
Fourqurean JW, Jones RD, Zieman JC (1993) Processes influencing water column nutrient characteristics and phosphorus limitation of phytoplankton biomass in Florida Bay, FL, USA: inferences from spatial distributions. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 36:295–314. doi:10.1006/ecss.1993.1018
Galloway JN, Townsend AR, Erisman JW, Bekunda M, Cai Z, Freney JR, Martineli LA, Seitzinger SP, Sutton MA (2008) Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 320:889–897. doi:10.1126/science.1136674
Gardner WS, Bootsma HA, Evans C, St. John PA (1995) Improved chromatographic analysis of 15N:14N ratios in ammonium or nitrate for isotope dilution experiments. Mar Chem 48:271–282. doi:10.1016/0304-4203(94)00060-Q
Gardner WS, McCarthy MJ, An S, Sobolev D, Sell KS, Brock D (2006) Nitrogen fixation and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA) support nitrogen dynamics in Texas estuaries. Limnol Oceanogr 51:558–568 (Special issue on eutrophication)
Glibert PM, Heil CA, Hollander D, Revilla M, Hoare A, Alexander J, Murasko S (2004) Evidence for dissolved organic nitrogen and phosphorus uptake during a cyanobacterial bloom in Florida Bay. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 280:73–83. doi:10.3354/meps280073
Horner-Devine MC, Martiny AC (2008) News about nitrogen. Science 320:757–758. doi:10.1126/science.1147012
Joye SB, Hollibaugh JT (1995) Influence of sulfide inhibition on nitrification on nitrogen regeneration in sediments. Science 270:623–625. doi:10.1126/science.270.5236.623
Kana TM, Darkangelo C, Hunt MD, Oldham JB, Bennett GE, Cornwell JC (1994) Membrane inlet mass spectrometer for rapid high-precision determination of N2, O2, and Ar in environmental water samples. Anal Chem 66:4166–4170. doi:10.1021/ac00095a009
Kelly-Gerreyn BA, Trimmer M, Hydes DJ (2001) A diagenetic model discriminating denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in a temperate estuarine sediment. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 220:33–46. doi:10.3354/meps220033
Kelso BHL, Smith RV, Laughlin RJ (1999) Effects of carbon substrates on nitrite accumulation in freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:61–66
King D, Nedwell DB (1984) Changes in the bacteria nitrate-reducing community of an anaerobic saltmarsh sediment in response to seasonal selection by temperature. J Gen Microbiol 130:2935–2941
Koch MS, Erskine JM (2001) Sulfide as a phytotoxin to the tropical seagrass Thalassia testudinum: interactions with light, salinity and temperature. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 266:81–95. doi:10.1016/S0022-0981(01)00339-2
Koike I, Hattori A (1978) Denitrification and ammonium formation in anaerobic coastal sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 35:278–282
Kuypers MM, Sliekers AO, Lavik G, Schmid M, Jorgensen BB, Kuenen JG, Sinninghe Damsté JS, Strous M, Jetten MS (2003) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation by anammox bacteria in the Black Sea. Nature 422:608–611. doi:10.1038/nature01472
Lapointe BE, Barile PJ (2004) Comment on J.C. Zieman, J.W. Fourqurean, and T.A. Frankovich. 1999. Seagrass dieoff in Florida Bay: long-term trends in abundance and growth of turtle grass, Thalassia testudinum. Estuaries 22:460–470. Estuaries and Coasts 27:157–176. doi:10.1007/BF02803569
Lapointe BE, Clark MW (1992) Nutrient inputs from the watershed and coastal eutrophication in the Florida Keys. Estuaries 15:465–476. doi:10.2307/1352391
Lavrentyev PJ, Bootsma HA, Johengen TH, Cavaletto JF, Gardner WS (1998) Microbial plankton response to resource limitation: insights from the cummunity structure and seston stoichiometry in Florida Bay, USA. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 165:45–57. doi:10.3354/meps165045
Lavrentyev PJ, Gardner WS, Yang L (2000) Effects of the zebra mussel on nitrogen dynamics and the microbial community at the sediment–water interface. Aquat Microb Ecol 21:187–194. doi:10.3354/ame021187
Maier RM, Pepper IL, Gerba CP (2000) Environmental microbiology. Academic Press, San Diego
McCarthy MJ, Gardner WS, Lavrentyev PL, Jochem FJ, Williams CJ (2009) Water column nitrogen cycling and microbial plankton in Florida Bay. Contrib Mar Sci (in press)
McCarthy MJ, Lavrentyev PL, Yang L, Zhang L, Chen Y, Qin B, Gardner WS (2007) Nitrogen dynamics relative to microbial food web structure in a subtropical, shallow, well-mixed, eutrophic lake (Taihu Lake, China). Hydrobiologia 581:195–207. doi:10.1007/s10750-006-0496-2 (special issue on Lake Taihu)
Megonigal JP, Hines ME, Visscher PT (2004) Anaerobic metabolism: Linkages to trace gasses and aerobic processes. In: Schlesinger WH (ed) Biogeochemistry. Elsevier-Pergamon, Oxford, pp 317–424
Morse JW, Morin J (2005) Ammonium interaction with coastal marine sediments: influence of redox conditions on K*. Mar Chem 95:107–112. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2004.08.008
Mulholland PJ et al (2008) Stream denitrification across biomes and its response to anthropogenic nitrate loading. Nature 452:202–205. doi:10.1038/nature06686
Nielsen LP (1992) Denitrification in sediment determined from nitrogen isotope pairing. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 86:35–362. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb04828.x
Phlips EJ, Badylak S (1996) Spatial variability in phytoplankton standing crop and composition in a shallow inner-shelf lagoon, Florida Bay, Florida. Bull Mar Sci 58:203–216
Phlips EJ, Lynch TC, Badylak S (1995) Chlorophyll a, tripton, color, and light availability in a shallow tropical innershelf lagoon, Florida Bay, USA. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 127:223–234. doi:10.3354/meps127223
Phlips EJ, Badylak S, Lynch TC (1999) Blooms of the picoplanktonic cyanobacterium Synechococcus in Florida Bay, a subtropical inner-shelf lagoon. Limnol Oceanogr 44:1166–1175
Robblee MB, Barber TR, Carlson PR, Durako MJ, Fourqurean JW, Muehlstein LK, Porter D, Yarbro LA, Zieman RT, Zieman JC (1991) Mass mortality of the tropical seagrass Thalassia testudinum in Florida Bay. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 71:297–299. doi:10.3354/meps071297
Rysgaard S, Risgaard-Petersen N, Sloth NP (1996) Nitrification, denitrification, and nitrate ammonification in sediments of two coastal lagoons in southern France. Hydrobiologia 329:133–141. doi:10.1007/BF00034553
Seitzinger SP (1988) Denitrification in freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems: ecological and geochemical significance. Limnol Oceanogr 33:702–724
Seitzinger SP (2008) Nitrogen cycle out of reach. Nature 425:162–163. doi:10.1038/452162a
Sørensen J (1978) Capacity for denitrification and reduction of nitrate to ammonia in a coastal marine sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol 35:301–305
Tiedje JM (1988) Ecology of denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium. In: Zehnder AJB (ed) Biology of anaerobic microorganisms. New York, John Wiley, pp 179–243
Zieman JC, Fourqurean JW, Frankovich TA (1999) Seagrass die-off in Florida Bay: Long-term trends in abundance and growth of turtle grass, Thalassia testudinum. Estuaries 22:460–470. doi:10.2307/1353211
Acknowledgments
We thank Lisa Tipsword, the boat captains, and other Keys Marine Laboratory personnel for laboratory and vessel support, Jim Cotner, Frank Jochem, Peter Lavrentyev, Zhang Lu, Ted Stets, and Clayton Williams for discussions and field assistance, Associate Editor Jan Mulder and two unidentified reviewers for constructive suggestions, and Jiqing Liu for reading the final manuscript. This research was sponsored by the NOAA Coastal Ocean Program National Center for Coastal Ocean Science, Grant # NA04NOS4780017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gardner, W.S., McCarthy, M.J. Nitrogen dynamics at the sediment–water interface in shallow, sub-tropical Florida Bay: why denitrification efficiency may decrease with increased eutrophication. Biogeochemistry 95, 185–198 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-009-9329-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-009-9329-5