Abstract
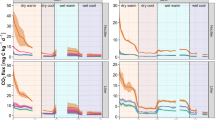
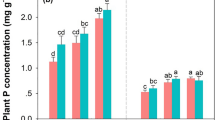
A field study was conducted in a nutrient-impacted marsh in Water Conservation Area 2A (WCA-2A) of the Everglades in southern Florida, USA, to evaluate early stages of plant litter (detritus) decomposition along a well-documented trophic gradient, and to determine the relative importance of environmental factors and substrate composition in governing decomposition rate. Vertically stratified decomposition chambers containing native plant litter (cattail and sawgrass leaves) were placed in the soil and water column along a 10-km transect coinciding with a gradient of soil phosphorus (P) enrichment. Decomposition rate varied significantly along the vertical water–soil profile, with rates typically higher in the water column and litter layer than below the soil surface, presumably in response to vertical gradients of such environmental factors as O2 and nutrient availability. An overall decrease in decomposition rate occurred along the soil P gradient (from high- to low-impact). First-order rate constant (k) values for decomposition ranged from 1.0 to 9.2 × 10−3 day−1 (mean = 2.8 ×10−3 day−1) for cattails, and from 6.7 × 10−4 to 3.0 × 10−3 day−1 (mean = 1.7 × 10−3 day−1) for sawgrass. Substantial N and P immobilization occurred within the litter layer, being most pronounced at nutrient-impacted sites. Nutrient content of the decomposing plant tissue was more strongly correlated to decomposition rate than was the nutrient content of the surrounding soil and water. Our experimental results suggest that, although decomposition rate was significantly affected by initial substrate composition, the external supply or availability of nutrients probably played a greater role in controlling decomposition rate. It was also evident that nutrient availability for litter decomposition was not accurately reflected by ambient nutrient concentration, e.g., water and soil porewater nutrient concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- WCA:
-
Water Conservation Area
References
J.D. Aber J.M. Melillo C.A. McClaugherty (1990) ArticleTitlePredicting longterm patterns of mass loss, nitrogen dynamics, and soil organic matter formation from initial fine litter chemistry in temperate forest ecosystems Can. J. Bot. 68 2201–2208
J.A. Amador R.D. Jones (1993) ArticleTitleNutrient limitations on microbial respiration in peat soils with different total phosphorus content Soil Biol. Biochem. 25 793–801 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(93)90125-U
J.A. Amador R.D. Jones (1995) ArticleTitleCarbon mineralization in the pristine and phosphorusenriched peat soils of the Florida Everglades Soil Sci. 159 129–141
J.M. Anderson (1976) ArticleTitleAn ignition method for determination of total phosphorus in lake sediments Water Res. 10 329–331 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(76)90175-5
J.M. Bremner C.S. Mulvaney (1982) Nitrogentotal A.L. Page (Eds) Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2 American Society of Agronomy – Soil Science Society of America Madison, WI 595–624
S.D. Bridgham K. Updegraff J. Pastor (2001) ArticleTitleA comparison of nutrient availability indices along an ombrotrophic–minerotrophic gradient in Minnesota wetlands Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 65 259–269
R.S. Clymo (1983) Peat A.J.P. Gore (Eds) Mires: Swamp, Bog, Fen and Moor Elsevier Amsterdam 159–224
S.R. Cooper J. Huvane P. Vaithiyanathan C.J. Richardson (1999) ArticleTitleCalibration of diatoms along a nutrient gradient in Florida Everglades Water Conservation Area 2AUSA J. Paleolimnol. 22 413–437 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008049224045
E.M. Dȁ9Angelo K.R. Reddy (1999) ArticleTitleRegulators of heterotrophic microbial potentials in wetland soils Soil Biol. Biochem. 31 815–830 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0038-0717(98)00181-3
S.M. Davis (1991) ArticleTitleGrowthdecomposition, and nutrient retention of Cladium jamaicense Crantz and Typha domingensis Pers. in the Florida Everglades Aquat. Bot. 40 203–224 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3770(91)90059-E
W.F. DeBusk K.R. Reddy (2003) ArticleTitleNutrient and hydrology effects on soil respiration in a northern Everglades marsh J. Environ. Qual. 32 702–710 Occurrence Handle12708696
W.F. DeBusk S. Newman K.R. Reddy (2001) ArticleTitleSpatio-temporal patterns of soil phosphorus enrichment in Everglades WCA-2A J. Environ. Qual. 30 1438–1446 Occurrence Handle11476523
W.F. DeBusk K.R. Reddy (1998) ArticleTitleTurnover of detrital organic carbon in a nutrient-impacted Everglades marsh Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 62 1460–1468
W.F. DeBusk K.R. Reddy M.S. Koch Y. Wang (1994) ArticleTitleSpatial distribution of soil nutrients in a northern Everglades marsh: Water Conservation Area 2A Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 58 543–552
H.L. Drake N.G. Aumen C. Kuhner C. Wagner A. Grießhammer M. Schmittroth (1996) ArticleTitleAnaerobic microflora of Everglades sediments: effects of nutrients on population profiles and activities Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62 486–493
P.J. Gleason A.D. Cohen H.K. Brooks P. Stone R. Goodrick W.G. Smith W. Spackman SuffixJr. (1974) The environmental significance of Holocene sediments from the Everglades and saline tidal plain P.J. Gleason (Eds) Environments of South Florida: Present and Past Miami Geological Society MiamiFlorida 287–341
G.L. Godshalk R.G. Wetzel (1978) ArticleTitleDecomposition of aquatic angiosperms. II. Particulate components Aquat. Bot. 5 301–327 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3770(78)90074-8
O.W. Heal P.W. Flanagan D.D. French S.F. MacLean SuffixJr. (1981) Decomposition and accumulation of organic matter L.C. Bliss O.W. Heal J.J. Moore (Eds) Tundra Ecosystems: A Comparative Analysis Cambridge University Press Cambridge 587–633
D.S. Jenkinson J.H. Rayner (1977) ArticleTitleThe turnover of soil organic matter in some of the Rothamsted classical experiments Soil Sci. 123 298–305
J.R. Jensen K. Rutchey M.S. Koch S. Narumalani (1995) ArticleTitleInland wetland change detection in the Everglades Water Conservation Area 2A using a time series of normalized remotely sensed data Photogram. Eng. Remote Sens. 61 199–209
M.S. Koch K.R. Reddy (1992) ArticleTitleDistribution of soil and plant nutrients along a trophic gradient in the Florida Everglades Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 56 1492–1499
P.V. McCormick R.B.E. Shuford J.G. Backus W.C. Kennedy (1998) ArticleTitleSpatial and seasonal patterns of periphyton biomass and productivity in the northern Everglades, FloridaUSA Hydrobiologia 362 185–208 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1003146920533
P.V. McCormick R.J. Stevenson (1998) ArticleTitlePeriphyton as a tool for ecological assessment and management in the Florida Everglades J. Phycol. 34 726–733 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1529-8817.1998.340726.x
J.M. Melillo J.D. Aber A.E. Linkins A. Ricca B. Fry K.J. Nadelhoffer (1989) ArticleTitleCarbon and nitrogen dynamics along the decay continuum: plant litter to soil organic matter Plant Soil 115 189–198 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02202587
J.M. Melillo J.D. Aber J.F. Muratore (1982) ArticleTitleNitrogen and lignin control of hardwood leaf litter decomposition dynamics Ecology 63 621–626
J.M. Melillo R.J. Naiman J.D. Aber A.E. Linkins (1984) ArticleTitleFactors controlling mass loss and nitrogen dynamics of plant litter decaying in northern streams Bull. Mar. Sci. 35 341–356
S.L. Miao W.F. DeBusk (1999) Effects of phosphorous enrichment on structure and function of plant communities in Florida wetlands K.R. Reddy G.A. O'Connor C.L. Schelske (Eds) Phosphorus Biogeochemistry in Subtropical Ecosystems Lewis Publishers Boca Raton, Florida 275–299
S.L. Miao F.H. Sklar (1998) ArticleTitleBiomass and nutrient allocation of sawgrass and cattail along a nutrient gradient in the Florida Everglades Wetlands Ecol. Manage. 5 245–263 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008217426392
T.R. Moore M. Dalva (1993) ArticleTitleThe influence of temperature and water table position on carbon dioxide and methane emissions from laboratory columns of peatland soils J. Soil Sci. 44 651–654
M.A. Moran R. Benner R.E. Hodson (1989) ArticleTitleKinetics of microbial degradation of vascular plant material in two wetland ecosystems Oecologia 79 158–167 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00388472
S. Newman J. Schuette J.B. Grace K. Rutchey T. Fontaine K.R. Reddy M. Pietrucha (1998) ArticleTitleFactors influencing cattail abundance in the northern Everglades Aquat. Bot. 60 265–280 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3770(97)00089-2
E.A. Paul (1984) ArticleTitleDynamics of organic matter in soils Plant Soil 76 275–285 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02205586
K.R. Reddy E.M. D'Angelo (1994) Soil processes regulating water quality in wetlands W.J. Mitsch (Eds) Global Wetlands: Old World and New Elsevier Science Amsterdam 309–324
C.J. Richardson G.M. Ferrell P. Vaithiyanathan (1999) ArticleTitleNutrient effects on stand structureresorption efficiency, and secondary compounds in Everglades sawgrass Ecology 80 2182–2192
L.A. Schipper K.R. Reddy (1995) ArticleTitleIn situ determination of detrital breakdown in wetland soilfloodwater profile Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 59 565–568
InstitutionalAuthorNameSouth Florida Water Management District (SFWMD) (1996) Hydrometeorological Database (DBHYDRO) South Florida Water Management District West Palm Beach
M.J. Swift O.W. Heal J.M. Anderson (1979) Decomposition in Terrestrial Ecosystems University of California Press Berkeley
Swift D.R. and Nicholas R.B. 1987. Periphyton and water quality relationships in the Everglades Water Conservation Areas. Technical Publication 87-2. South Florida Water Management DistrictWest Palm Beach.
R.L. Tate SuffixIII (1979) ArticleTitleEffect of flooding on microbial activities in organic soils: carbon metabolism Soil Sci. 128 267–273
InstitutionalAuthorNameU. S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (1983) Methods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes Environment Monitoring and Support Laboratory CincinnatiOhio
P. Vaithiyanathan C.J. Richardson (1999) ArticleTitleMacrophyte species changes in the Everglades: examination along a eutrophication gradient J. Environ. Qual. 28 1347–1358
J.R. Webster E.F. Benfield (1986) ArticleTitleVascular plant breakdown in freshwater ecosystems Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 17 567–594 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.es.17.110186.003031
J.R. White K.R. Reddy (2000) ArticleTitleThe effects of phosphorus loading on organic nitrogen mineralization of soils and detritus along a nutrient gradient in the northern Everglades, Florida Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 64 1525–1534
A.L. Wright K.R. Reddy (2001) ArticleTitleHeterotrophic microbial activity in northern Everglades wetland soils Soil Sci. Soc. Am J. 65 1856–1864
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Debusk, W., Reddy, K. Litter Decomposition and Nutrient Dynamics in a Phosphorus Enriched Everglades Marsh. Biogeochemistry 75, 217–240 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-004-7113-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-004-7113-0