Abstract
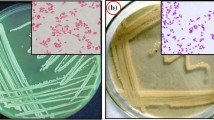
Two biphenyl-degrading bacterial strains, SS1 and SS2, were isolated from polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB)-contaminated soil. They were identified as Rhodococcus ruber and Rhodococcus pyridinivorans based on the 16S rRNA gene sequence, as well as morphological, physiological and biochemical characteristics. SS1 and SS2 exhibited tolerance to 2000 and 3000 mg/L of biphenyl. And they could degrade 83.2 and 71.5% of 1300 mg/L biphenyl within 84 h, respectively. In the case of low-chlorinated PCB congeners, benzoate and 3-chlorobenzoate, the degradation activities of SS1 and SS2 were also significant. In addition, these two strains exhibited chemotactic response toward TCA-cycle intermediates, benzoate, biphenyl and 2-chlorobenzoate. This study indicated that, like the flagellated bacteria, non-flagellated Rhodococcus spp. might actively seek substrates through the process of chemotaxis once the substrates are depleted in their surroundings. Together, these data provide supporting evidence that SS1 and SS2 might be good candidates for restoring biphenyl/PCB-polluted environments.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham WR, Nogales B, Golyshin PN, Pieper DH, Timmis KN (2002) Polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading microbial communities in soils and sediments. Curr Opin Microbiol 5:246–253
Adebusoye SA, Picardal FW, Ilori MO, Amund OO (2008a) Influence of chlorobenzoic acids on the growth and degradation potentials of PCB-degrading microorganisms. World J Microb Biotechnol 24:1203–1208
Adebusoye SA, Ilori MO, Picardal FW, Amund OO (2008b) Cometabolic degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) by axenic cultures of Ralstonia sp. strain SA-5 and Pseudomonas sp. strain SA-6 obtained from Nigerian contaminated soils. World J Microb Biotechnol 24:61–68
Aken BV, Correa PA, Schnoor JL (2010) Phytoremediation of polychlorinated biphenyls: new trends and promises. Environ Sci Technol 44:2767–2776
Aoki Y (2001) Polychlorinated biphenyls, polychloronated dibenzo-p-dioxins, and polychlorinated dibenzofurans as endocrine disrupters: what we have learned from Yusho disease. Environ Res 86:2–11
Atago Y, Shimodaira J, Araki N, Bin Othman N, Zakaria Z, Fukuda M, Futami J, Hara H (2016) Identification of novel extracellular protein for PCB/biphenyl metabolism in Rhodococcus jostii RHA1. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 80:1012–1019
Bartels F, Backhaus S, Moore E, Timmis KN, Hofer B (1999) Occurrence and expression of glutathiane-S-transferase-encoding bphK genes in Burkholderia sp. strain LB400 and other biphenyl-utilizing bacteria. Microbiol-SGM 145:2821–2834
Bedard DL, Haberl ML (1990) Influence of chlorine substitution pattern on the degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls by eight bacterial strains. Microb Ecol 20:87–102
Bopp LH (1986) Degradation of highly chlorinated PCBs by Pseudomonas strain LB400. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 47:247–254
Camara B, Herrera C, Gonzalez M, Couve E, Hofer B, Seeger M (2004) From PCBs to highly toxic metabolites by the biphenyl pathway. Environ Microbiol 6:842–850
Chung SY, Maeda M, Song E, Horikoshij K, Kudo T (1994) A gram-positive polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading bacterium, Rhodococcus erythropolis strain TA421, isolated from a termite ecosystem. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58:2111–2113
Eklund T (1985) Inhibition of microbial growth at different pH levels by benzoic and propionic acids and esters of p-hydroxybenzoic acid. Int J Food Microbiol 2:159–167
Faroon O, Jones D, Rosa CD (2000) Effects of polychlorinated biphenyls on the nervous system. Toxicol Ind Health 16:305–333
Furukawa K, Tomizuka N, Kamibayashi A (1979) Effect of chlorine substitution on the bacterial metabolism of various polychlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol 38:301–310
Gordillo F, Chavez FP, Jerez CA (2007) Motility and chemotaxis of Pseudomonas sp. B4 towards polychlorobiphenyls and chlorobenzoates. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 60:322–328
Harwood CS (1989) A methyl-accepting protein is involved in benzoate taxis in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol 171:4603–4608
Harwood CS, Parales RE, Dispensa M (1990) Chemotaxis of Pseudomonas putida toward chlorinated benzoates. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1501–1503
Heuer H, Krsek M, Baker P, Smalla K, Wellington E (1997) Analysis of actinomycete communities by specific amplification of genes encoding 16S rRNA and gel-electrophoretic separation in denaturing gradients. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3233–3241
Hong Q, Dong XJ, He LJ, Jiang X, Li SP (2009) Isolation of a biphenyl-degrading bacterium, Achromobacter sp. BP3, and cloning of the bph gene cluster. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 63:365–370
Hu JX, Qian MR, Zhang Q, Cui JL, Yu CN, Su XM, Shen CF, Hashmi MZ, Shi JY (2015) Sphingobium fuliginis HC3: a novel and robust isolated biphenyl- and polychlorinated biphenyls-degrading bacterium without dead-end intermediates accumulation. PLoS ONE 10:e122740. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0122740
Jarrell KF, McBride MJ (2008) The surprisingly diverse ways that prokaryotes move. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:466–476
Kang JW (2014) Removing environmental organic pollutants with bioremediation and phytoremediation. Biotechnol Lett 36:1129–1139
Kohler HP, Kohler-Staub D, Focht DD (1988) Co-metabolism of polychlorinated biphenyls: enhanced transformation of Aroclor 1254 by growing bacterial cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1940–1945
Krell T, Lacal J, Reyes-Darias JA, Jimenez-Sanchez C, Sungthong R, Ortega-Calvo JJ (2013) Bioavailability of pollutants and chemotaxis. Curr Opin Microbiol 24:451–456
Labbe D, Garnon J, Lau P (1997) Characterization of the genes encoding a receptor-like histidine kinase and a cognate response regulator from a biphenyl/polychlorobiphenyl-degrading bacterium, Rhodococcus sp. strain M5. J Bacteriol 179:2772–2776
Law A, Aitken MD (2003) Bacterial chemotaxis to naphthalene desorbing from a nonaqueous liquid. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5968–5973
Leigh MB, Prouzova P, Mackova M, Macek T, Nagle DP, Fletcher JS (2006) Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB)-degrading bacteria associated with trees in a PCB-contaminated site. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2331–2342
Li A, Qu YY, Zhou JT, Gou M (2009) Isolation and characteristics of a novel biphenyl-degrading bacterial strain, Dyella ginsengisoli LA-4. J Environ Sci (China) 21:211–217
Marx RB, Aitken MD (1999) Quantification of chemotaxis to naphthalene by Pseudomonas putida G7. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2847–2852
Marx RB, Aitken MD (2000) Bacterial chemotaxis enhances naphthalene degradation in a heterogeneous aqueous system. Environ Sci Technol 34:3379–3383
McKay DB, Prucha M, Reineke W, Timmis KN, Pieper DH (2003) Substrate specificity and expression of three 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl 1,2-dioxygenases from Rhodococcus globerulus strain P6. J Bacteriol 185:2944–2951
Moody JD, Doerge DR, Freeman JP (2002) Degradation of biphenyl by Mycobacterium sp. strain PYR-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:364–369
Ohtsubo Y, Kudo T, Tsuda M, Nagata Y (2004) Strategies for bioremediation of polychlorinated biphenyls. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:250–258
Pandey G, Jain RK (2002) Bacterial chemotaxis toward environmental pollutants: role in bioremediation. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5789–5795
Pandey G, Chauhan A, Samanta SK, Jain RK (2002) Chemotaxis of a Ralstonia sp. SJ98 toward co-metabolizable nitroaromatic compounds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 299:404–409
Parales RE, Harwood CS (2002) Bacterial chemotaxis to pollutants and plant-derived aromatic molecules. Curr Opin Microbiol 5:266–273
Parales RE, Luu RA, Hughes JG, Ditty JL (2015) Bacterial chemotaxis to xenobiotic chemicals and naturally-occurring analogs. Curr Opin Biotechnol 33:318–326
Parnell JJ, Park J, Denef V, Tsoi T, Hashsham S, Quensen J, Tiedje JM (2006) Coping with polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) toxicity: physiological and genome-wide responses of Burkholderia xenovorans LB400 to PCB-mediated stress. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:6607–6614
Paul D, Singh R, Jain RK (2006) Chemotaxis of Ralstonia sp. SJ98 towards p-nitrophenol in soil. Environ Microbiol 8:1797–1804
Pieper DH (2005) Aerobic degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:170–191
Pieper DH, Seeger M (2008) Bacterial metabolism of polychlorinated biphenyls. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 15:121–138
Potrawfke T, Lohnert TH, Timmis KN, Wittich RM (1998) Mineralization of low-chlorinated biphenyls by Burkholderia sp. strain LB400 and by a two membered consortium upon directed interspecies transfer of chlorocatechol pathway genes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50:440–446
Sakai M, Ezaki S, Suzuki N, Kurane R (2005) Isolation and characterization of a novel polychlorinated biphenyl-degrading bacterium, Paenibacillus sp. KBC101. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68:111–116
Stratford J, Wright MA, Reineke W, Mokross H, Havel J, Knowles CJ, Robinson GK (1996) Influence of chlorobenzoates on the utilization of chlorobiphenyls and chlorobenzoates mixtures by chlorobiphenyl/chlorobenzoate-mineralising hybrid bacterial strains. Arch Microbiol 165:213–218
Taguchi K, Motoyama M, Kudo T (2004) Multiplicity of 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl dioxygenase genes in the Gram-positive polychlorinated biphenyl degrading bacterium Rhodococcus rhodochrous K37. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:787–795
Taguchi K, Motoyama M, Iida T, Kudo T (2007) Polychlorinated biphenyl/biphenyl degrading gene clusters in Rhodococcus sp. K37, HA99, and TA431 are different from well-known bph gene clusters of Rhodococci. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:1136–1144
Tanase A, Vassu T, Csutak O, Pelinescu D, Robertina I, Stoica I (2012) Phylogenetic analysis of oil polluted soil microbial strains. Rom Biotechnol Lett 17:7093–7103
Toussaint JP, Pham TTM, Barriault D, Sylvestre M (2012) Plant exudates promote PCB degradation by a rhodococcal rhizobacteria. Appl Microbiol Biot 95:1589–1603
Tremaroli V, Suzzi CV, Fedi S, Ceri H, Zannoni D, Turner RJ (2010) Tolerance of Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes KF707 to metals, polychlorobiphenyls and chlorobenzoates: effects on chemotaxis-, biofilm- and planktonic-grown cells. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 74:291–301
Vasilyeva GK, Strijakova ER (2007) Bioremediation of soils and sediments contaminated by polychlorinated biphenyls. Microbiology 76:639–653
Wu G, Feng Y, Boyd A (2003) Characterization of bacteria capable of degrading soil-sorbed biphenyl. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 71:768–775
Yang XQ, Erickson LE, Fan LT (1995) A study of the dissolution rate-limited bioremediation of soils contaminated by residual hydrocarbons. J Hazard Mater 41:299–313
Yang X, Sun Y, Qian S (2004) Biodegradation of seven polychlorinated biphenyls by a newly isolated aerobic bacterium (Rhodococcus sp. R04). J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 31:415–420
Yun Q, Lin Z, Xin T (2009) Cometabolism and immobilized degradation of monochlorobenzoate by Rhodococcus erythropolis. Afr J Microbiol Res 3:482–486
Zhang GQ, Yang XQ, Xie FH, Chao YP, Qian SJ (2009) Cometabolic degradation of mono-chloro benzoic acids by Rhodococcus sp. R04 grown on organic carbon sources. World J Microb Biotechnol 25:1169–1174
Zhao HP, Schmidt KR, Tiehm A (2010) Inhibition of aerobic metabolic cis-1,2-di-chloroethene biodegradation by other chloroethenes. Water Res 44:2276–2282
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2016QNA6009) and the Provincial Public Technology and Applied Research Projects by Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (2014C33020, 2017C33020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Hu, J., Xu, K. et al. Biodegradation and chemotaxis of polychlorinated biphenyls, biphenyls, and their metabolites by Rhodococcus spp.. Biodegradation 29, 1–10 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-017-9809-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-017-9809-6