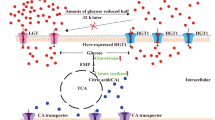
Abstract
Objectives
To enhance acid tolerance of Candida glabrata for pyruvate production by engineering AMP metabolism.
Results
The physiological function of AMP deaminase in AMP metabolism from C. glabrata was investigated by deleting or overexpresseing the corresponding gene, CgAMD1. At pH 4, CgAMD1 overexpression resulted in 59 and 51% increases in biomass and cell viability compared to those of wild type strain, respectively. In addition, the intracellular ATP level of strain Cgamd1Δ/CgAMD1 was down-regulated by 22%, which led to a 94% increase in pyruvate production. Further, various strengths of CgAMD1 expression cassettes were designed, thus resulting in a 59% increase in pyruvate production at pH 4. Strain Cgamd1Δ/CgAMD1 (H) was grown in a 30 l batch bioreactor at pH 4, and pyruvate reached 46.1 g/l.
Conclusion
CgAMD1 overexpression plays an active role in improving acid tolerance and pyruvate fermentation performance of C. glabrata at pH 4.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Canelas AB, ten Pierick A, Ras C, Seifar RM, van Dam JC, van Gulik WM, Heijnen JJ (2009) Quantitative evaluation of intracellular metabolite extraction techniques for yeast metabolomics. Anal Chem 81:7379–7389
Chen X, Song W, Gao C, Qin W, Luo Q, Liu J, Liu L (2016) Fumarate production by Torulopsis glabrata: engineering heterologous fumarase expression and improving acid tolerance. PLoS ONE 11:e0164141
Hida H, Yamada T, Yamada Y (2007) Genome shuffling of Streptomyces sp. U121 for improved production of hydroxycitric acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:1387–1393
Hua Q, Joyce AR, Fong SS, Palsson BO (2006) Metabolic analysis of adaptive evolution for in silico-designed lactate-producing strains. Biotechnol Bioeng 95:992–1002
Itoh R, Saint-Marc C, Chaignepain S, Katahira R, Schmitter JM, Daignan-Fornier B (2003) The yeast ISN1 (YOR155c) gene encodes a new type of IMP-specific 5′-nucleotidase. BMC Biochem 4:4
Liu L, Li Y, Du G, Chen J (2006a) Redirection of the NADH oxidation pathway in Torulopsis glabrata leads to an enhanced pyruvate production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:377–385
Liu L, Li Y, Li H, Chen J (2006b) Significant increase of glycolytic flux in Torulopsis glabrata by inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation. FEMS Yeast Res 6:1117–1129
Loret MO, Pedersen L, Francois J (2007) Revised procedures for yeast metabolites extraction: application to a glucose pulse to carbon-limited yeast cultures, which reveals a transient activation of the purine salvage pathway. Yeast 24:47–60
Morrison BA, Shain DH (2008) An AMP nucleosidase gene knockout in Escherichia coli elevates intracellular ATP levels and increases cold tolerance. Biol Lett 4:53–56
Parry BR, Shain DH (2011) Manipulations of AMP metabolic genes increase growth rate and cold tolerance in Escherichia coli: implications for psychrophilic evolution. Mol Biol Evol 28:2139–2145
Schmid A, Dordick JS, Hauer B, Kiener A, Wubbolts M, Witholt B (2001) Industrial biocatalysis today and tomorrow. Nature 409:258–268
Xu G, Liu L, Chen J (2012) Reconstruction of cytosolic fumaric acid biosynthetic pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Fact 11:24
Zhou J, Liu L, Shi Z, Du G, Chen J (2009) ATP in current biotechnology: regulation, applications and perspectives. Biotechnol Adv 27:94–101
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21576117, 21706095), the Key Technologies R&D Program of Jiangsu Province (BE2015307, BE2017622), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JUSRP51611A) and the National Science Foundation for Post-doctoral Scientists of China (2016M600362).
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—Strains and plasmids used.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Luo, Q., Liu, J. et al. Enhanced pyruvate production in Candida glabrata by overexpressing the CgAMD1 gene to improve acid tolerance. Biotechnol Lett 40, 143–149 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2452-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-017-2452-9