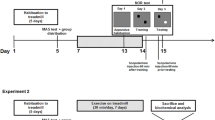
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the expression of memory-related antioxidant genes and miRNAs under simulated weightlessness and the regulation of mechano growth factor (MGF) E domain, the peptide preventing nerve damage.
Results
Igf-iea and mgf mRNA levels, expression of antioxidant genes sod1 and sod2 and levels of miR-134 and miR-125b-3p increased in rat hippocampus after 14 days tail suspension to simulate weightlessness which was inhibited with intramuscular injection of E domain peptide. Therefore, administration of MGF E domain peptide could reverse increased expressions of memory-related igf-iea, mgf, sod1, sod2, miR-134 and miR-125b-3p in rat hippocampus under simulated weightlessness.
Conclusions
MGF may regulate the redox state and miRNA-targeted NR-CREB signaling, and intramuscular injection may be the alternative administration because of its safety, convenience and ability to pass through the blood brain barrier.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksoy-Aksel A, Zampa F, Schratt G (2014) MicroRNAs and synaptic plasticity–a mutual relationship. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 369(2013):0515
Aperghis M, Johnson IP, Cannon J, Yang SY, Goldspink G (2004) Different levels of neuroprotection by two insulin-like growth factor-I splice variants. Brain Res 1009:213–218
Chang HC, Yang YR, Wang PS, Kuo CH, Wang RY (2010) Effects of insulin-like growth factor 1 on muscle atrophy and motor function in rats with brain ischemia. Chin J Physiol 53:337–348
Chang HC, Yang YR, Wang PS, Kuo CH, Wang RY (2013) The neuroprotective effects of intramuscular insulin-like growth factor-I treatment in brain ischemic rats. PLoS One 8:e64015
Chen HL, Lv K, Qu LN, Zhang YL, Bi L, Zhong P, Ji GH, Cao HQ, Li YH (2013) Tail suspension disrupts cognition function and down-regulates memory-related proteins expression in rat hippocampus. Space Med Med Eng (Beijing) 26:426–432
Clausen A, Doctrow S, Baudry M (2010) Prevention of cognitive deficits and brain oxidative stress with superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetics in aged mice. Neurobiol Aging 31:425–433
Dharap A, Bowen K, Place R, Li LC, Vemuganti R (2009) Transient focal ischemia induces extensive temporal changes in rat cerebral microRNAome. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29:675–687
Dluzniewska J, Sarnowska A, Beresewicz M, Johnson I, Srai SK, Ramesh B, Goldspink G, Górecki DC, Zabłocka B (2005) A strong neuroprotective effect of the autonomous C-terminal peptide of IGF-1 Ec (MGF) in brain ischemia. FASEB J 19:1896–1898
Edbauer D, Neilson JR, Foster KA, Wang CF, Seeburg DP, Batterton MN, Tada T, Dolan BM, Sharp PA, Sheng M (2010) RRegulation of synaptic structure and function by FMRP-associated microRNAs miR-125b and miR-132. Neuron 65:373–384
Follert P, Cremer H, Béclin C (2014) MicroRNAs in brain development and function: a matter of flexibility and stability. Front Mol Neurosci 7:5
Frigeri A, Iacobas DA, Iacobas S, Nicchia GP, Desaphy JF, Camerino DC, Svelto M, Spray DC (2008) Effect of microgravity on gene expression in mouse brain. Exp Brain Res 191:289–300
Gao J, Wang WY, Mao YW, Gräff J, Guan JS, Pan L, Mak G, Kim D, Su SC, Tsai LH (2010) A novel pathway regulates memory and plasticity via SIRT1 and miR-134. Nature 466:1105–1109
Griffin AL (2015) Role of the thalamic nucleus reuniens in mediating interactions between the hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex during spatial working memory. Front Syst Neurosci 9:29
Hardingham GE, Fukunaga Y, Bading H (2002) Extrasynaptic NMDARs oppose synaptic NMDARs by triggering CREB shut-off and cell death pathways. Nat Neurosci 5:405–414
Kandalla PK, Goldspink G, Butler-Browne G, Mouly V (2011) Mechano growth factor E peptide (MGF-E), derived from an isoform of IGF-1, activates human muscle progenitor cells and induces an increase in their fusion potential at different ages. Mech Ageing Dev 132:154–162
Lee WH, Kumar A, Rani A, Foster TC (2014) Role of antioxidant enzymes in redox regulation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor function and memory in middle-aged rats. Neurobiol Aging 35:1459–1468
Liu Q, Zhou R, Chen S, Tan C (2012) Effects of head-down bed rest on the executive functions and emotional response. PLoS One 7:e52160
Liu Q, Zhou R, Zhao X, Oei TP (2015) Effects of prolonged head-down bed rest on working memory. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 11:835–842
Lusardi TA, Farr CD, Faulkner CL, Pignataro G, Yang T, Lan J, Simon RP, Saugstad JA (2010) Ischemic preconditioning regulates expression of microRNAs and a predicted target, MeCP2, in mouse cortex. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:744–756
Massaad CA, Washington TM, Pautler RG, Klann E (2009) Overexpression of SOD-2 reduces hippocampal superoxide and prevents memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:13576–13581
Matheny RW Jr, Nindl BC, Adamo ML (2010) Minireview: mechano-growth factor: a putative product of IGF-I gene expression involved in tissue repair and regeneration. Endocrinology 151:865–875
Peña JR, Pinney JR, Ayala P, Desai TA, Goldspink PH (2015) Localized delivery of mechano-growth factor E-domain peptide via polymeric microstructures improves cardiac function following myocardial infarction. Biomaterials 46:26–34
Philippou A, Maridaki M, Pneumaticos S, Koutsilieris M (2014) The complexity of the IGF1 gene splicing, posttranslational modification and bioactivity. Mol Med 20:202–214
Quesada A, Micevych P, Handforth A (2009) C-terminal mechano growth factor protects dopamine neurons: a novel peptide that induces heme oxygenase-1. Exp Neurol 220:255–266
Quesada A, Ogi J, Schultz J, Handforth A (2011) C-terminal mechano-growth factor induces heme oxygenase-1-mediated neuroprotection of SH-SY5Y cells via the protein kinase Cϵ/Nrf2 pathway. J Neurosci Res 89:394–405
Rajasethupathy P, Fiumara F, Sheridan R, Betel D, Puthanveettil SV, Russo JJ, Sander C, Tuschl T, Kandel E (2009) Characterization of small RNAs in Aplysia reveals a role for miR-124 in constraining synaptic plasticity through CREB. Neuron 63:803–817
Ruiz S, Pergola PE, Zager RA, Vaziri ND (2013) Targeting the transcription factor Nrf2 to ameliorate oxidative stress and inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 83:1029–1041
Santucci D, Kawano F, Ohira T, Terada M, Nakai N, Francia N, Alleva E, Aloe L, Ochiai T, Cancedda R, Goto K, Ohira Y (2012) Evaluation of gene, protein and neurotrophin expression in the brain of mice exposed to space environment for 91 days. PLoS One 7:e40112
Sarkar P, Sarkar S, Ramesh V, Hayes BE, Thomas RL, Wilson BL, Kim H, Barnes S, Kulkarni A, Pellis N, Ramesh GT (2006) Proteomic analysis of mice hippocampus in simulated microgravity environment. J Proteome Res 5:548–553
Siegel G, Obernosterer G, Fiore R, Oehmen M, Bicker S, Christensen M, Khudayberdiev S, Leuschner PF, Busch CJ, Kane C, Hübel K, Dekker F, Hedberg C, Rengarajan B, Drepper C, Waldmann H, Kauppinen S, Greenberg ME, Draguhn A, Rehmsmeier M, Martinez J, Schratt GM (2009) A functional screen implicates microRNA-138-dependent regulation of the depalmitoylation enzyme APT1 in dendritic spine morphogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 11:705–716
Sim SE, Bakes J, Kaang BK (2014) Neuronal activity-dependent regulation of microRNAs. Mol Cells 37:511–517
Tsuru-Aoyagi K, Potts MB, Trivedi A, Pfankuch T, Raber J, Wendland M, Claus CP, Koh SE, Ferriero D, Noble-Haeusslein LJ (2009) Glutathione peroxidase activity modulates recovery in the injured immature brain. Ann Neurol 65:540–549
Vassilakos G, Philippou A, Tsakiroglou P, Koutsilieris M (2014) Biological activity of the e domain of the IGF-1Ec as addressed by synthetic peptides. Hormones (Athens) 13:182–196
Wu DW, Shen XY, Dong Q, Wang SP, Cheng ZH, Zhang SJ (2000) Effects of tail suspension on learning and memory function of mice. Space Med Med Eng (Beijing) 13:244–248
Yamahara K, Yamamoto N, Nakagawa T, Ito J (2015) Insulin-like growth factor 1: a novel treatment for the protection or regeneration of cochlear hair cells. Hear Res 330:2–9
Zhang X, Zhang L, Cheng X, Guo Y, Sun X, Chen G, Li H, Li P, Lu X, Tian M, Qin J, Zhou H, Jin G (2014) IGF-1 promotes Brn-4 expression and neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells via the PI3K/Akt pathway. PLoS One 9:e113801
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National instrumentation program of China (2013YQ190467, 2012YQ040140091), Shenzhen science & technology institute (JCYJ20150629164441050), Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Space Medicine Fundamentals and Application, China Astronaut Research and Training Center (SMFA15B01, SMFA13B02) and the Medicinal Science and Technology Research Project (BWS11J052).
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—sequences of qPCR primers for rats
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Lv, K., Dai, Z. et al. Intramuscular injection of mechano growth factor E domain peptide regulated expression of memory-related sod, miR-134 and miR-125b-3p in rat hippocampus under simulated weightlessness. Biotechnol Lett 38, 2071–2080 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2210-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2210-4