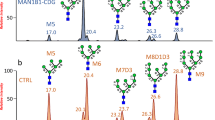
Abstract
Objectives
To develop a sensitive and quantitative method for monitoring the abnormal glycosylation of clinical and biopharmaceutical products.
Results
MALDI-MS-based quantitative targeted glycomics (MALDI-QTaG) was proposed for sensitive and quantitative analysis of total N-glycans. The derivatization reactions (i.e., amidation of sialic acid and incorporation of a positive charge moiety into the reducing end) dramatically increased the linearity (R2 > 0.99) and sensitivity (limit of detection is 0.5 pmol/glycoprotein) relative to underivatized glycans. In addition, the analytical strategy was chromatographic purification-free and non-laborious process accessible to the high-throughput analyses. We used MALDI-QTaG to analyze the N-glycans of α-fetoprotein (AFP) purified from normal cord blood and HCC cell line (Huh7 cells). The total percentages of core-fucosylated AFP N-glycans from Huh7 cells and normal cord blood were 98 and 18 %, respectively.
Conclusions
This MALDI-MS-based glycomics technology has wide applications in many clinical and bioengineering fields requiring sensitive, quantitative and fast N-glycosylation validation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoyagi Y, Suzuki Y, Isemura M, Nomoto M, Sekine C, Igarashi K, Ichida F (1988) The fucosylation index of alpha-fetoprotein and its usefulness in the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 61:769–774
Bereman MS, Williams TI, Muddiman DC (2009) Development of a nanoLC LTQ orbitrap mass spectrometric method for profiling glycans derived from plasma from healthy, benign tumor control, and epithelial ovarian cancer patients. Anal Chem 81:1130–1136
Durand G, Seta N (2000) Protein glycosylation and diseases: blood and urinary oligosaccharides as markers for diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. Clin Chem 46:795–805
Gil GC, Kim YG, Kim BG (2008) A relative and absolute quantification of neutral N-linked oligosaccharides using modification with carboxymethyl trimethylammonium hydrazide and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 379:45–59
Gil GC, Iliff B, Cerny R, Velander WH, Van Cott KE (2010) High throughput quantification of N-glycans using one-pot sialic acid modification and matrix assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 82:6613–6620
Jang KS, Kim YG, Gil GC, Park SH, Kim BG (2009) Mass spectrometric quantification of neutral and sialylated N-glycans from a recombinant therapeutic glycoprotein produced in the two Chinese hamster ovary cell lines. Anal Biochem 386:228–236
Kang P, Mechref Y, Klouckova I, Novotny MV (2005) Solid-phase permethylation of glycans for mass spectrometric analysis. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 19:3421–3428
Kobata A (1992) Structures and functions of the sugar chains of glycoproteins. Eur J Biochem 209:483–501
Miyoshi E, Moriwaki K, Terao N, Tan CC, Terao M, Nakagawa T, Matsumoto H, Shinzaki S, Kamada Y (2012) Fucosylation is a promising target for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Biomolecules 2:34–45
Selman MH, Hoffmann M, Zauner G, McDonnell LA, Balog CI, Rapp E, Deelder AM, Wuhrer M (2012) MALDI-TOF-MS analysis of sialylated glycans and glycopeptides using 4-chloro-alpha-cyanocinnamic acid matrix. Proteomics 12:1337–1348
Stockmann H, Adamczyk B, Hayes J, Rudd PM (2013) Automated, high-throughput IgG-antibody glycoprofiling platform. Anal Chem 85:8841–8849
Wang C, Wu Z, Yuan J, Wang B, Zhang P, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Huang L (2014) Simplified quantitative glycomics using the stable isotope label Girard’s reagent p by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res 13:372–384
Wheeler SF, Domann P, Harvey DJ (2009) Derivatization of sialic acids for stabilization in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry and concomitant differentiation of alpha(2→3)- and alpha(2→6)-isomers. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 23:303–312
Wiegandt A, Meyer B (2014) Unambiguous characterization of N-glycans of monoclonal antibody cetuximab by integration of LC-MS/MS and (1)H NMR spectroscopy. Anal Chem 86:4807–4814
Wu S, Grimm R, German JB, Lebrilla CB (2011) Annotation and structural analysis of sialylated human milk oligosaccharides. J Proteome Res 10:856–868
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (NRF-2013R1A1A1004998) and Polar Academic Program (PAP, PD13010) from KOPRI.
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—Comparison between relative intensities of the N-glycans derived from AFP of human cord serum and Auh7 cell labeled with Ah and GP obtained by MALDI-MS
Supplementary Figure 1—Determination of limit of detection (LOD) for N-glycans from bovine fetuin using MALDI-QTaG method (0.5 pmol on the MALDI spot)
Supplementary Figure 2—Comparison of relative quantities of N-glycans derived from human IgG using MALDI-MS and UPLC
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, KJ., Kim, YW., Hwang, CH. et al. A MALDI-MS-based quantitative targeted glycomics (MALDI-QTaG) for total N-glycan analysis. Biotechnol Lett 37, 2019–2025 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1881-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1881-6