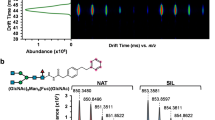
Abstract
N-glycan analyses may serve uncovering disease-associated biomarkers, as well as for profiling distinctive changes supporting diagnosis of genetic disorders of glycan biosynthesis named congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG). Strategies based on liquid chromatography (LC) preferentially coupled to electrospray ionization (ESI) - mass spectrometry (MS) have emerged as powerful analytical methods for N-glycan identification and characterization. To enhance detection sensitivity, glycans are commonly labelled with a functional tag prior to LC-MS analysis. Since most derivatization techniques are notoriously time-consuming, some commercial analytical kits have been developed to speed up N-deglycosylation and N-glycan labelling of glycoproteins of pharmaceutical and biological interest such as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). We exploited the analytical capabilities of RapiFluor-MS (RFMS) to perform, by a slightly modified protocol, a detailed N-glycan characterization of total serum and single serum glycoproteins from specific patients with CDG (MAN1B1-CDG, ALG12-CDG, MOGS-CDG, TMEM199-CDG). This strategy, accomplished by Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC)-UPLC-ESI-MS separation of the RFMS derivatized N-glycans, allowed us to uncover structural details of patients serum released N-glycans, thus extending the current knowledge on glycan profiles in these individual glycosylation diseases. The applied methodology enabled to differentiate in some cases either structural isomers and isomers differing in the linkage type. All the here reported applications demonstrated that RFMS method, coupled to HILIC-UPLC-ESI-MS, represents a sensitive high throughput approach for serum N-glycome analysis and a valuable option for glycan detection and separation particularly for isomeric species.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-Dor, S., Esterman, N., Rubin, E., Sharon, N.: Biases and complex patterns in the residues flanking protein N-glycosylation sites. Glycobiology. 14, 95–101 (2004)
Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., Freeze, H.H., Stanley, P., Bertozzi, C.R., Hart, G.W., Etzler, M.E.: Essentials of Glycobiology, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor (NY) (2009)
Fuster, M.M., Esko, J.D.: The sweet and sour of cancer: glycans as novel therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Cancer 5, 526–542 (2005)
Adamczyk, B., Tharmalingam, T., Rudd, P.M.: Glycans as cancer biomarkers. BBA-Gen. Subjects. 1820, 1347–1353 (2012)
Barone, R., Sturiale, L., Palmigiano, A., Zappia, M., Garozzo, D.: Glycomics of pediatric and adulthood diseases of the central nervous system. J. Proteomics. 75, 5123–5139 (2012)
Kizuka, Y., Kitazume, S., Fujinawa, R., Saito, T., Iwata, N., Saido, T.C., Nakano, M., Yamaguchi, Y., Hashimoto, Y., Staufenbiel, M., Hatsuta, S., Manya, H., Endo, T.: Taniguchi, N.: An aberrant sugar modification of BACE1 blocks its lysosomal targeting in Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 7, 175–189 (2015)
Palmigiano, A., Barone, R., Sturiale, L., Sanfilippo, C., Bua, R.O., Romeo, D.A., Messina, A., Capuana, M.L., Maci, T., Le Pira, F., Zappia, M., Garozzo, D.: CSF N-glycoproteomics for early diagnosis in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Proteomics. 131, 29–37 (2016)
Kizuka, Y., Kitazume, S., Taniguchi, N.: N-glycan and Alzheimer’s disease. BBA-Gen Subjects. 1861, 2447–2454 (2017)
Karlsson, I., Ndreu, L., Quaranta, A., Thorsén, G.: Glycosylation patterns of selected proteins in individual serum and cerebrospinal fluid samples. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 145, 431–439 (2017)
Delves, P.J.: The role of glycosylation in autoimmune disease. Autoimmunity. 27, 239–253 (1998)
Goulabchand, R., Vincent, T., Batteux, F., Eliaou, J.F., Guilpain, P.: Impact of autoantibody glycosylation in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 13, 742–750 (2014)
Butler, M., Quelhas, D., Critchley, A.J., Carchon, H., Hebestreit, H.F., Hibbert, R.G., Vilarinho, L., Teles, E., Matthijs, G., Schollen, E., Argibay, P., Harvey, D.J., Dwek, R.A., Jaeken, J., Rudd, P.M.: Detailed glycan analysis of serum glycoproteins of patients with congenital disorders of glycosylation indicates the specific defective glycan processing step and provides an insight into pathogenesis. Glycobiology. 13, 601–622 (2003)
Freeze, H.H.: Genetic defects in the human glycome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 7, 537–551 (2006)
Sparks, S.E.: Inherited disorders of glycosylation. Mol. Genet. Metab. 87, 1–7 (2006)
Sturiale, L., Barone, R., Garozzo, D.: The impact of mass spectrometry in the diagnosis of congenital disorders of glycosylation. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 34, 891–899 (2011)
Chang, I.J., He, M., Lam, C.T.: Congenital disorders of glycosylation. Ann. Trans. Med. 6 (2018)
Ng, B.G., Freeze, H.H.: Perspectives on glycosylation and its congenital disorders. Trends Genet. 34, 466–476 (2018)
Shubhakar, A., Reiding, K.R., Gardner, R.A., Spencer, D.I., Fernandes, D.L., Wuhrer, M.: High-throughput analysis and automation for glycomics studies. Chromatographia. 78, 321–333 (2015)
Gaunitz, S., Nagy, G., Pohl, N.L., Novotny, M.V.: Recent advances in the analysis of complex glycoproteins. Anal. Chem. 89, 389–413 (2017)
Palmigiano, A., Messina, A., Sturiale, L., Garozzo, D.: Advanced LC-MS Methods for N-Glycan Characterization. In: Cappiello, A., Palma, P. (eds.). Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry Advances in the Use of Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (LCMS): Instrumentation Developments and Applications. 79, pp. 147–172. Elsevier B.V., Amsterdam (2018)
Lauc, G., Essafi, A., Huffman, J.E., Hayward, C., Knezevic, A., Kattla, J.J., Polasek, O., Gornik, O., Vitart, V., Abrahams, J.L., Pucic, M., Novokmet, M., Redzic, I., Campbell, S., Wild, S.H., Borovecki, F., Wang, W., Kolcic, I., Zgaga, L., Gyllensten, U., Wilson, J.F., Wright, A.F., Hastie, N.D., Campbell, H., Rudd, P.M., Rudan, I.: Genomics meets glycomics-the first GWAS study of human N- Glycome identifies HNF1alpha as a master regulator of plasma protein fucosylation. PLoS Genet. 6, e1001256 (2010)
Ruhaak, L.R., Uh, H.W., Beekman, M., Hokke, C.H., Westendorp, R.G., Houwing-Duistermaat, J., Wuhrer, M., Deelder, A.M., Slagboom, P.E.: Plasma protein N-glycan profiles are associated with calendar age, familial longevity and health. J. Proteome Res. 10, 1667–1674 (2011)
Lauc, G., Huffman, J.E., Pucic, M., Zgaga, L., Adamczyk, B., Muzinic, A., Novokmet, M., Polasek, O., Gornik, O., Kristic, J., Keser, T., Vitart, V., Scheijen, B., Uh, H.W., Molokhia, M., Patrick, A.L., McKeigue, P., Kolcic, I., Lukic, I.K., Swann, O., van Leeuwen, F.N., Ruhaak, L.R., Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J., Slagboom, P.E., Beekman, M., de Craen, A.J., Deelder, A.M., Zeng, Q., Wang, W., Hastie, N.D., Gyllensten, U., Wilson, J.F., Wuhrer, M., Wright, A.F., Rudd, P.M., Hayward, C., Aulchenko, Y., Campbell, H., Rudan, I.: Loci associated with N-glycosylation of human immunoglobulin G show pleiotropy with autoimmune diseases and haematological cancers. PLoS Genet. 9, e1003225 (2013)
Ruhaak, L.R., Koeleman, C.A., Uh, H.W., Stam, J.C., van Heemst, D., Maier, A.B., Houwing- Duistermaat, J.J., Hensbergen, P.J., Slagboom, P.E., Deelder, A.M., Wuhrer, M.: Targeted biomarker discovery by high throughput glycosylation profiling of human plasma alpha1-antitrypsin and immunoglobulin A. PLoS One 8, e73082 (2013)
Staples, G.O., Bowman, M.J., Costello, C.E., Hitchcock, A.M., Lau, J.M., Leymarie, N., Miller, C., Naimi, H., Shi, X., Zaia, J.: A chip-based amide‐HILIC LC/MS platform for glycosaminoglycan glycomics profiling. Proteomics 9, 686–695 (2009)
Staples, G.O., Naimy, H., Yin, H., Kileen, K., Kraiczek, K., Costello, C.E., Zaia, J.: Improved hydrophilic interaction chromatography LC/MS of heparinoids using a chip with postcolumn makeup flow. Anal. Chem. 82, 516–522 (2010)
Reiding, K.R., Bondt, A., Hennig, R., Gardner, R.A., O’Flaherty, R., Trbojević-Akmačić, I., Shubhakar, A., Hazes, J.M.W., Reichl, U., Fernandes, D.L., Pucic-Bakovic, M., Rapp, E., Spencer, D.I.R., Dolhain, R.J.E.M., Rudd, P.M., Lauc, G., Wuhrer, M.: High-throughput serum N-glycomics: method comparison and application to study rheumatoid arthritis and pregnancy-associated changes. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 18, 3–15 (2019)
Zhang, T., Madunić, K., Holst, S., Zhang, J., Jin, C., ten Dijke, P., Karlsson, N.G., Stavenhagen, K., Wuhrer, M.: Development of a 96-well plate sample preparation method for integrated N-and O-glycomics using porous graphitized carbon liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Mol. Omics. (2020) https://doi.org/10.1039/C9MO00180H
Klapoetke, S., Zhang, J., Becht, S., Gu, X., Ding, X.: The evaluation of a novel approach for the profiling and identification of N-linked glycan with a procainamide tag by HPLC with fluorescent and mass spectrometric detection. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 53, 315–324 (2010)
Kozak, R.P., Tortosa, C.B., Fernandes, D.L., Spencer, D.I.: Comparison of procainamide and 2-aminobenzamide labeling for profiling and identification of glycans by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection coupled to electrospray ionization–mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 486, 38–40 (2015)
Lauber, M.A., Yu, Y.Q., Brousmiche, D.W., Hua, Z., Koza, S.M., Magnelli, P., Guthrie, E., Taron, C.H., Fountain, K.J.: Rapid preparation of released N-glycans for HILIC analysis using a labeling reagent that facilitates sensitive fluorescence and ESI-MS detection. Anal. Chem. 87, 5401–5409 (2015)
Kimzey, M., Szabo, Z., Sharma, V., Gyenes, A., Tep, S., Taylor, A., Jones, A., Hyche, J., Haxo, T., Vlasenko, S.: Development of an instant glycan labeling dye for high throughput analysis by mass spectrometry. Prozyme. 25, 1295 (2015)
Zhou, S., Veillon, L., Dong, X., Huang, Y., Mechref, Y.: Direct comparison of derivatization strategies for LC-MS/MS analysis of N-glycans. Analyst. 142, 4446–4455 (2017)
Sturiale, L., Barone, R., Palmigiano, A., Ndosimao, C.N., Briones, P., Adamowicz, M., Jaeken, J., Garozzo, D.: Multiplexed glycoproteomic analysis of glycosylation disorders by sequential yolk immunoglobulins immunoseparation and MALDI-TOF MS. Proteomics. 8, 3822–3832 (2008)
Ceroni, A., Maass, K., Geyer, H., Geyer, R., Dell, A., Haslam, S.M.: GlycoWorkbench: a tool for the computer-assisted annotation of mass spectra of glycans. J. Proteome Res. 7, 1650–1659 (2008)
Rymen, D., Peanne, R., Millón, M.B., Race, V., Sturiale, L., Garozzo, D., Mills, P., Clayton, P., Asteggiano, C.G., Quelhas, D., Cansu, A., Martins, E., Nassogne, M.C., Gonçalves-Rocha, M., Topaloglu, H., Jaeken, J., Foulquier, F., Matthijs, G.: MAN1B1 deficiency: an unexpected CDG-II. PLoS Genet. 9 (2013) https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003989
Van Scherpenzeel, M., Timal, S., Rymen, D., Hoischen, A., Wuhrer, M., Hipgrave-Ederveen, A., Grunewald, S., Peanne, R., Saada, A., Edvardson, S., Grønborg, S., Ruijter, G., Kattentidt-Mouravieva, A., Brum, J.M., Freckmann, M.L., Tomkins, S., Jalan, A., Prochazkova, D., Ondruskova, N., Hansikova, H., Willemsen, M.A., Hensbergen, P.J., Matthijs, G., Wevers, R.A., Veltman, J.A., Morava, E., Lefeber, D.J.: Diagnostic serum glycosylation profile in patients with intellectual disability as a result of MAN1B1 deficiency. Brain. 137, 1030–1038 (2014)
Saldova, R., Stöckmann, H., O’Flaherty, R., Lefeber, D.J., Jaeken, J., Rudd, P.M.: N-Glycosylation of serum IgG and total glycoproteins in MAN1B1 deficiency. J. Proteome Res. 14, 4402–4412 (2015)
Duvet, S., Mouajjah, D., Péanne, R., Matthijs, G., Raymond, K., Jaeken, J., Morava, E., Foulquier, F.: Use of endoglycosidase H as a diagnostic tool for MAN1B1-CDG patients. Electrophoresis. 39–3141 (2018)
Barbosa, E.A., Fontes, N.D.C., Santos, S.C.L., Lefeber, D.J., Bloch, C., Brum, J.M., Brand, G.D.: Relative quantification of plasma N-glycans in type II congenital disorder of glycosylation patients by mass spectrometry. Clin. Chim. Acta. 492, 102–113 (2019)
Costello, C.E., Contado-Miller, J.M., Cipollo, J.F.: A glycomics platform for the analysis of permethylated oligosaccharide alditols. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectr. 18, 1799–1812 (2007)
Royle, L., Campbell, M.P., Radcliffe, C.M., White, D.M., Harvey, D.J., Abrahams, J.L., Kim, Y., Henry, G.W., Shadick, N.A., Weinblatt, M.E., Lee, D.M., Rudd, P.M., Dwek, R.A.: HPLC-based analysis of serum N-glycans on a 96-well plate platform with dedicated database software. Anal. Biochem. 376, 1–12 (2008)
Zhao, P., Peng, X., Luo, S., Huang, Y., Tan, L., Shao, J., He, X.: Identification and characterization of novel mutations in MOGS in a Chinese patient with infantile spams. Neurogenetics. 21, 97–104 (2020)
Sadat, M.A., Moir, S., Chun, T.W., Lusso, P., Kaplan, G., Wolfe, L., Memoli, M.J., He, M., Vega, H., Kim, L.J.Y., Huang, Y., Hussein, N., Nievas, E., Mitchell, R., Garofalo, M., Louie, A., Ireland, D.C., Grunes, C., Cimbro, R., Patel, V., Holzapfel, G., Salahuddin, D., Bristol, T., Adams, D., Marciano, B.E., Hedge, M., Li, Y., Calvo, K.R., Stoddard, J., Justement, J.S., Jacques, J., Priel, D.A.L., Murray, D., Sun, P., Kuhns, D.B., Boerkoel, C.F., Chirini, J.A., Di Pasquale, G., Verthelyi, D., Rosenzweig, S.D.: Glycosylation, hypogammaglobulinemia, and resistance to viral infections. New Engl. J. Med. 370, 1615–1625 (2014)
Jansen, J.C., Timal, S., Van Scherpenzeel, M., Michelakakis, H., Vicogne, D., Ashikov, A., Moraitou, M., Hoischen, A., Huijben, K., Steenbergen, G., van den Boogert, M.A., Porta, F., Calvo, P.L., Mavrikou, M., Cenacchi, G., van den Bogaart, G., Salomon, J., Holleboom, A.G., Rodenburg, R.J., Drenth, J.P., Huynen, M.A., Wevers, R.A., Morava, E., Foulquier, F., Veltman, J.A., Lefeber, D.J.: TMEM199 deficiency is a disorder of Golgi homeostasis characterized by elevated aminotransferases, alkaline phosphatase, and cholesterol and abnormal glycosylation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 98, 322–330 (2016)
Vajro, P., Zielinska, K., Ng, B.G., Maccarana, M., Bengtson, P., Poeta, M., Mandato, C., D’Acunto, E., Freeze, H.H., Eklund, E.A.: Three unreported cases of TMEM199-CDG, a rare genetic liver disease with abnormal glycosylation. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 13, 4 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-017-0757-3
Calvo, P.L., Pagliardini, S., Baldi, M., Pucci, A., Sturiale, L., Garozzo, D., Vinciguerra, T., Barbera, C., Jaeken, J.: Long-standing mild hypertransaminasaemia caused by congenital disorder of glycosylation (CDG) type IIx. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 31, 437–440 (2008)
Deguchi, K., Keira, T., Yamada, K., Ito, H., Takegawa, Y., Nakagawa, H., Nishimura, S.I.: Two-dimensional hydrophilic interaction chromatography coupling anion-exchange and hydrophilic interaction columns for separation of 2-pyridylamino derivatives of neutral and sialylated N-glycans. J. Chromatogr. A 1189, 169–174 (2008)
Palmisano, G., Larsen, M.R., Packer, N.H., Thaysen-Andersen, M.: Structural analysis of glycoprotein sialylation–part II: LC-MS based detection. RSC Adv. 3, 22706–22726 (2013)
Chantret, I., Dupré, T., Delenda, C., Bucher, S., Dancourt, J., Barnier, A., Charollais, A., Heron, D., Bader-Meunier, B., Danos, O., Seta, N., Durand, G., Oriol, R., Codogno, P., Moore, S.E.: Congenital disorders of glycosylation type Ig is defined by a deficiency in dolichyl-Pmannose: Man-7-GlcNAc2-PP-dolichyl mannosyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 25815–25822 (2002)
Thiel, C., Schwarz, M., Hasilik, M., Grieben, U., Hanefeld, F., Lehle, L., von Figura, K., Körner, C.: Deficiency of dolichyl-PMan: Man-7-GlcNAc2-PP-dolichyl mannosyltransferase causes congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ig. Biochem. J. 367, 195–201 (2002)
Grubenmann, C.E., Frank, C.G., Kjaergaard, S., Berger, E.G., Aebi, M., Hennet, T.: ALG12 mannosyltransferase defect in congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ig. Hum. Mol. Genet. 11, 2331–2339 (2002)
Eklund, E.A., Newell, J.W., Sun, L., Seo, N.S., Alper, G., Willert, J., Freeze, H.H.: Molecular and clinical description of the first US patients with congenital disorder of glycosylation Ig. Mol. Genet. Metab. 84, 25–31 (2005)
Di Rocco, M., Hennet, T., Grubenmann, C.E., Pagliardini, S., Allegri, A.E., Frank, C.G., Aebi, M., Vignola, S., Jaeken, J.: Congenital disorder of glycosylation (CDG) Ig: report on a patient and review of the literature. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 28, 1162–1164 (2005)
Kranz, C., Basinger, A.A., Gucsavas-Calikoglu, M., Sun, L., Powell, C.M., Henderson, F.W., Aylsworth, A.S., Freeze, H.H.: Expanding spectrum of congenital disorder of glycosylation Ig (CDG-Ig): sibs with a unique skeletal dysplasia, hypogammaglobulinemia, cardiomyopathy, genital malformations, and early lethality. Am. J. Med. Genet. 143A, 1371–1378 (2007)
Murali, C., Lu, J.T., Jain, M., Liu, D.S., Lachman, R., Gibbs, R.A., Lee, B.H., Cohn, D., Campeau, P.M.: Diagnosis of ALG12-CDG by exome sequencing in a case of severe skeletal dysplasia. Mol Genet: Metab. Rep. 1, 213–219 (2014)
Sturiale, L., Bianca, S., Garozzo, D., Terracciano, A., Agolini, E., Messina, A., Palmigiano, A., Esposito, F., Barone, C., Novelli, A., Fiumara, A., Jaeken, J., Barone, R.: ALG12-CDG: novel glycophenotype insights endorse the molecular defect. Glycoconjugate J. 36, 461–472 (2019)
Acknowledgements
Partial financial support from the association Vaincre le Maladies Lysosomales (VML), Massy France (Agreement N ° 2018-5C) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 0.97 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Messina, A., Palmigiano, A., Esposito, F. et al. HILIC-UPLC-MS for high throughput and isomeric N-glycan separation and characterization in Congenital Disorders Glycosylation and human diseases. Glycoconj J 38, 201–211 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-020-09947-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-020-09947-7