Abstract
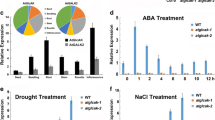
GDP-mannose 3′, 5′-epimerase (GME) catalyses the conversion of GDP-d-mannose to GDP-l-galactose, an important step in the ascorbic acid (ascorbic acid) biosynthetic pathway in higher plants. In this study, a novel cDNA fragment (MsGME) encoding a GME protein was isolated and characterised from alfalfa (Medicago sativa). An expression analysis confirmed that MsGME expression was induced by salinity, PEG and acidity stresses. MsGME overexpression in Arabidopsis enhanced tolerance of the transgenic plants to salt, drought and acid. Real-time PCR analysis revealed that the transcript levels of GDP-d-mannose pyrophosphorylase (GMP), l-galactose-phosphate 1-P phosphatase (GP) and GDP-l-galactose phosphorylase (GGP) were increased in transgenic Arabidopsis (T3 generation). Moreover, the ascorbate content was increased in transgenic Arabidopsis. Our results suggest that MsGME can effectively enhance tolerance of transgenic Arabidopsis to acid, drought and salt by increasing ascorbate accumulation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agius F, Gonzclez-Lamothe R, Caballero J, Mu oz-Blanco J, Botella M, Valpuesta V (2003) Engineering increased vitamin C levels in plants by overexpression of a d-galacturonic acid reductase. Nat Biotechnol 21:177–181
Bao A, Wang S, Wu G, Xi J, Zhang J, Wang C (2009) Overexpression of the Arabidopsis H+ -PPase enhanced resistance to salt and drought stress in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Sci 176:232–240
Barber G (1975) The synthesis of guanosine 5′-diphosphate-l-galactose by extracts of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Arch Biochem Biophys 167:718–722
Barber G (1979) Observations on the mechanism of the reversible epimerization of GDP-d-mannose to GDP-l-galactose by an enzyme from Chlorella pyrenoidosa. J Biol Chem 254:7600–7603
Chang CCC, Slesak I, Jorda L, Sotnikov A, Melzer M, Miszalski Z, Mullineaux PM, Parker JE, Karpinska B, Karpinski S (2009) Arabidopsis chloroplastic glutathione peroxidases play a role in cross talk between photooxidative stress and immune response. Plant Physiol 150:670–683
Chen Z, Gallie D (2005) Increasing tolerance to ozone by elevating foliar ascorbic acid confers greater protection against ozone than increasing avoidance. Plant Physiol 138:1673–1689
Cho U-H, Park J-O (2000) Mercury-induced oxidative stress in tomato seedlings. Plant Sci 156:1–9
Clough S, Bent A (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Conklin P, Barth C (2004) Ascorbic acid, a familiar small molecule intertwined in the response of plants to ozone, pathogens and the onset of senescence. Plant, Cell Environ 27:959–970
Conklin P, Williams E, Last R (1996) Environmental stress sensitivity of an ascorbic acid-deficient Arabidopsis mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:9970–9974
Davey MW, Gilot C, Persiau G, Ostergaard J, Han Y, Bauw GC, Van MMC (1999) Ascorbate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis cell suspension culture. Plant Physiol 121:535–543
Dutilleul C, Garmier M, Noctor G, Mathieu C, Chetrit P, Foyer CH, de Paepe R (2003) Leaf mitochondria modulate whole cell redox homeostasis, set antioxidant capacity, and determine stress resistance through altered signaling and diurnal regulation. Plant Cell 15:1212–1226
Eltayeb A, Kawano N, Badawi G, Kaminaka H, Sanekata T, Shibahara T, Inanaga S, Tanaka K (2007) Overexpression of monodehydroascorbate reductase in transgenic tobacco confers enhanced tolerance to ozone, salt and polyethylene glycol stresses. Planta 225:1255–1264
Fujimoto Ohta M, Usui A, Shinshi H, Ohme-Takagi M (2000) Arabidopsis ethylene-responsive element binding factors act as transcriptional activators or repressors of GCC box-mediated gene expression. Plant Cell 2:393–404
Gilbert L, Alhagdow M, Nunes-Nesi A, Quemener B, Guillon F, Bouchet B, Faurobert M, Gouble B, Page D, Garcia V (2009) The GDP-d-mannose 3, 5-epimerase (GME) plays a key role at the intersection of ascorbate and non-cellulosic cell wall biosynthesis in tomato. Plant J 60:499–508
Girotti AW (2001) Photosensitized oxidation of membrane lipids: reaction pathways, cytotoxic effects and cytoprotective mechanisms. J Photochem Photobiol, B 63:103–113
Heath R, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Hebda P, Barber G (1982) GDP-d-mannose: GDP-l-galactose epimerase from Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Meth Enzymol 83:522–525
Hebda P, Behrman E, Barber G (1979) The guanosine 5′- diphosphate d-mannose: guanosine 5′-diphosphate l-galactose epimerase of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Chemical synthesis of guanosine 50-diphosphate l-galactose and further studies of the enzyme and the reaction it catalyzes. Arch Biochem Biophys 194:496–502
Ioannidi E, Kalamaki M, Engineer C, Pateraki I, Alexandrou D, Mellidou I, Giovannonni J, Kanellis A (2009) Expression profiling of ascorbic acid-related genes during tomato fruit development and ripening and in response to stress conditions. J Exp Bot 60:663–678
Jain A, Nessler C (2000) Metabolic engineering of an alternative pathway for ascorbic acid biosynthesis in plants. Mol Breed 6:73–78
Laing W, Wright M, Cooney J, Bulley S (2007) The missing step of the l-galactose pathway of ascorbate biosynthesis in plants, an l-galactose guanyltransferase, increases leaf ascorbate content. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:9534–9539
Linster CL, Clarke SG (2008) l-Ascorbate biosynthesis in higher plants: the role of VTC2. Trends Plant Sci 13:567–573
Linster C, Gomez T, Christensen K, Adler L, Young B, Brenner C, Clarke S (2007) Arabidopsis VTC2 encodes a GDP-l-galactose phosphorylase, the last unknown enzyme in the Smirnoff-Wheeler pathway to ascorbic acid in plants. J Biol Chem 282:18879–18885
Lorence A, Chevone B, Mendes P, Nessler C (2004) myo-Inositol oxygenase offers a possible entry point into plant ascorbate biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 134:1200–1205
Moller IM, Sweetlove LJ (2010) ROS signalling-specificity is required. Trends Plant Sci 15:370–374
Nishikirni M, Fukuyama R, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Yagi K (1994) Cloning and chromosomal mapping of the human non-functional gene for l-gulono-g-lactone oxidase, the enzyme for l-ascorbic acid biosynthesis missing in man. J Biol Chem 269:13685–13688
Rizzolo A, Forni E, Polesello A (1984) HPLC assay of ascorbic acid in fresh and processed fruit and vegetables. Food Chem 14:189–199
Running JA, Burlingame RP, Berry A (2003) The pathway of l-ascorbic acid biosynthesis in the colourless microalga Prototheca moriformis. J Exp Bot 54:1841–1849
Upadhyaya C, Young K, Akula N, Kim H, Heung J, Oh O, Aswath C, Chun S, Kim D, Park S (2009) Over-expression of strawberry d-galacturonic acid reductase in potato leads to accumulation of vitamin C with enhanced abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Sci 177:659–667
Watanabe K, Suzuki K, Kitamura S (2006) Characterization of a GDP-d-mannose 3′, 5′-epimerase from rice. Phytochemistry 67:338–346
Wheeler G, Jones M, Smirnoff N (1998) The biosynthetic pathway of vitamin C in higher plants. Nature 393:365–369
Wolucka B, Van Montagu M (2003) GDP-mannose 3′, 5′-epimerase forms GDP-l-gulose, a putative intermediate for the de novo biosynthesis of vitamin C in plants. J Biol Chem 278:47483–47490
Wolucka A, Van Montagu M (2007) The VTC2 cycle and the de novo biosynthesis pathways for vitamin C in plants: an opinion. Phytochemistry 68:2602–2613
Wolucka B, Persiau G, Van Doorsselaere J, Davey M, Demol H, Vandekerckhove J, Van Montagu M, Zabeau M, Boerjan W (2001) Partial purification and identification of GDP-mannose 3′, 5′-epimerase of Arabidopsis thaliana, a key enzyme of the plant vitamin C pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:14843–14848
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2014CB138704) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31072072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, L., Wang, Y., Liu, W. et al. Overexpression of an alfalfa GDP-mannose 3, 5-epimerase gene enhances acid, drought and salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis by increasing ascorbate accumulation. Biotechnol Lett 36, 2331–2341 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1598-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1598-y