Abstract
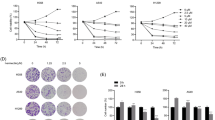
Bortezomib is a novel proteasome inhibitor that has promising antitumor activity against various cancer cells. We have assessed its antitumor activity in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) A549 and H157 cells in vitro where it inhibited cell growth and induced apoptosis, which was associated with cytochrome c release and caspase-3 activation. Bortezomib upregulated autophagic-related proteins, the Atg12–Atg5 complex and LC3-II, which indicated autophagy had occurred. The combination of bortezomib with autophagic inhibitor 3-methyladenine or chloroquine significantly enhanced suppression of cell growth and apoptosis induced by bortezomib in A549 and H157 cells. Our study indicated that inhibition of both proteasome and autophagy has great potential for NSCLC treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaravadi RK, Yu D, Lum JJ, Bui T, Christophorou MA, Evan GI et al (2007) Autophagy inhibition enhances therapy-induced apoptosis in a Myc-induced model of lymphoma. J Clin Investig 117:326–336
Apel A, Herr I, Schwarz H, Rodemann HP, Mayer A (2008) Blocked autophagy sensitizes resistant carcinoma cells to radiation therapy. Cancer Res 68:1485–1494
Blackburn C, Gigstad KM, Hales P, Garcia K, Jones M, Bruzzese FJ et al (2010) Characterization of a new series of non-covalent proteasome inhibitors with exquisite potency and selectivity for the 20S beta5-subunit. Biochem J 430:461–476
Chen S, Rehman SK, Zhang W, Wen A, Yao L, Zhang J (2010) Autophagy is a therapeutic target in anticancer drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1806:220–229
Dalby KN, Tekedereli I, Lopez-Berestein G, Ozpolat B (2010) Targeting the prodeath and prosurvival functions of autophagy as novel therapeutic strategies in cancer. Autophagy 6:322–329
Hoang T, Campbell TC, Zhang C, Kim K, Kolesar JM, Oettel KR et al (2013) Vorinostat and bortezomib as third-line therapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a Wisconsin Oncology Network Phase II study. Investig New Drugs. doi:10.1007/s10637-013-9980-5
Jia L, Gopinathan G, Sukumar JT, Gribben JG (2012) Blocking autophagy prevents bortezomib-induced NF-kappaB activation by reducing I-kappaBalpha degradation in lymphoma cells. PLoS ONE 7:e32584
McConkey DJ, Zhu K (2008) Mechanisms of proteasome inhibitor action and resistance in cancer. Drug Resist Update 11:164–179
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM, Klionsky DJ (2008) Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature 451:1069–1075
Ourari-Dhahri B, Ben Slima H, Ben Amar J, El Gharbi L, Ali M, Baccar Azzabi S et al (2012) Management of non small cell lung cancer. Tunis Med 90:847–851
Piperdi B, Walsh WV, Bradley K, Zhou Z, Bathini V, Hanrahan-Boshes M et al (2012) Phase-I/II study of bortezomib in combination with carboplatin and bevacizumab as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 7:1032–1040
Selimovic D, Porzig BB, El-Khattouti A, Badura HE, Ahmad M, Ghanjati F et al (2013) Bortezomib/proteasome inhibitor triggers both apoptosis and autophagy-dependent pathways in melanoma cells. Cell Signal 25:308–318
Shi YH, Ding ZB, Zhou J, Hui B, Shi GM, Ke AW et al (2011) Targeting autophagy enhances sorafenib lethality for hepatocellular carcinoma via ER stress-related apoptosis. Autophagy 7:1159–1172
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 62:10–29
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, G., Li, H., Ji, Z. et al. Inhibition of autophagy by autophagic inhibitors enhances apoptosis induced by bortezomib in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Biotechnol Lett 36, 1171–1178 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1470-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1470-0